Uniform continuity: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
We have the following chain of inclusions for functions over a [[Compact space|compact]] subset of the real line |
We have the following chain of inclusions for functions over a [[Compact space|compact]] subset of the real line |
||
: '''[[Continuously differentiable]]''' ⊆'''[[Lipschitz continuous]]''' ⊆ '''α-[[Hölder continuous]]''' ⊆ '''uniformly continuous''' ⊆ '''[[Continuous function|continuous]]''' |
: '''[[Differentiable function#Differentiability classes|Continuously differentiable]]''' ⊆ '''[[Lipschitz continuity|Lipschitz continuous]]''' ⊆ '''α-[[Hölder condition|Hölder continuous]]''' ⊆ '''uniformly continuous''' ⊆ '''[[Continuous function|continuous]]''' |
||
== Definition for functions on metric spaces == |
== Definition for functions on metric spaces == |
||
Revision as of 14:02, 13 September 2016
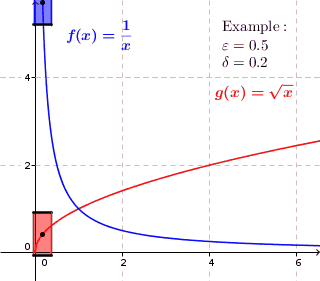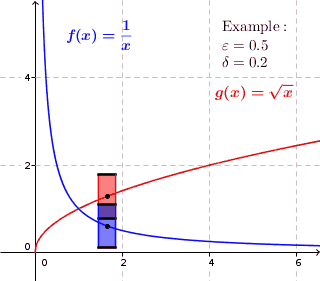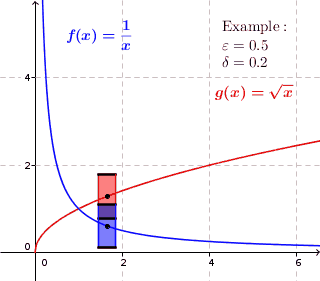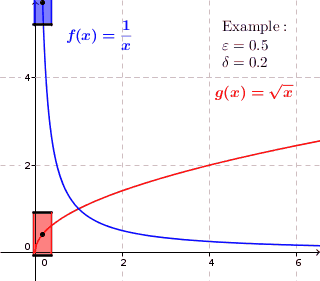
In mathematics, a function f is uniformly continuous if, roughly speaking, it is possible to guarantee that f(x) and f(y) be as close to each other as we please by requiring only that x and y are sufficiently close to each other; unlike ordinary continuity, the maximum distance between f(x) and f(y) cannot depend on x and y themselves. For instance, any isometry (distance-preserving map) between metric spaces is uniformly continuous.
Every uniformly continuous function between metric spaces is continuous. Uniform continuity, unlike continuity, relies on the ability to compare the sizes of neighbourhoods of distinct points of a given space. In an arbitrary topological space, comparing the sizes of neighborhoods may not be possible. Instead, uniform continuity can be defined on a metric space where such comparisons are possible, or more generally on a uniform space.
We have the following chain of inclusions for functions over a compact subset of the real line
- Continuously differentiable ⊆ Lipschitz continuous ⊆ α-Hölder continuous ⊆ uniformly continuous ⊆ continuous
Definition for functions on metric spaces
Given metric spaces (X, d1) and (Y, d2), a function f : X → Y is called uniformly continuous if for every real number ε > 0 there exists δ > 0 such that for every x, y ∈ X with d1(x, y) < δ, we have that d2(f(x), f(y)) < ε.
If X and Y are subsets of the real numbers, d1 and d2 can be the standard Euclidean norm, || · ||, yielding the definition: for all ε > 0 there exists a δ > 0 such that for all x, y ∈ X, |x − y| < δ implies |f(x) − f(y)| < ε.
The difference between being uniformly continuous, and being simply continuous at every point, is that in uniform continuity the value of δ depends only on ε and not on the point in the domain.
Local continuity versus global uniform continuity
Continuity itself is a local (more precisely, pointwise) property of a function—that is, a function f is continuous, or not, at a particular point. When we speak of a function being continuous on an interval, we mean only that it is continuous at each point of the interval. In contrast, uniform continuity is a global property of f, in the sense that the standard definition refers to pairs of points rather than individual points. On the other hand, it is possible to give a definition that is local in terms of the natural extension f* (the characteristics of which at nonstandard points are determined by the global properties of f), although it is not possible to give a local definition of uniform continuity for an arbitrary hyperreal-valued function, see below.
The mathematical statements that a function is continuous on an interval I and the definition that a function is uniformly continuous on the same interval are structurally very similar. Continuity of a function for every point x of an interval can thus be expressed by a formula starting with the quantification
whereas for uniform continuity, the order of the second and third quantifiers is reversed:
(the domains of the variables have been deliberately left out so as to emphasize quantifier order). Thus for continuity at each point, one takes an arbitrary point x, and then there must exist a distance δ,
while for uniform continuity a single δ must work uniformly for all points x (and y):
Examples
- Every Lipschitz continuous map between two metric spaces is uniformly continuous. In particular, every function which is differentiable and has bounded derivative is uniformly continuous. More generally, every Hölder continuous function is uniformly continuous.
- Despite being nowhere differentiable, the Weierstrass function is everywhere uniformly continuous
- Every member of a uniformly equicontinuous set of functions is uniformly continuous.
- The tangent function is continuous on the interval (−π/2, π/2) but is not uniformly continuous on that interval.
- The exponential function x ex is continuous everywhere on the real line but is not uniformly continuous on the line.
Properties
Every uniformly continuous function is continuous, but the converse does not hold. Consider for instance the function . Given an arbitrarily small positive real number , uniform continuity requires the existence of a positive number such that for all with , we have . But
and for all sufficiently large x this quantity is greater than .
Any absolutely continuous function is uniformly continuous. On the other hand, the Cantor function is uniformly continuous but not absolutely continuous.
The image of a totally bounded subset under a uniformly continuous function is totally bounded. However, the image of a bounded subset of an arbitrary metric space under a uniformly continuous function need not be bounded: as a counterexample, consider the identity function from the integers endowed with the discrete metric to the integers endowed with the usual Euclidean metric.
The Heine–Cantor theorem asserts that every continuous function on a compact set is uniformly continuous. In particular, if a function is continuous on a closed bounded interval of the real line, it is uniformly continuous on that interval. The Darboux integrability of continuous functions follows almost immediately from this theorem.
If a real-valued function is continuous on and exists (and is finite), then is uniformly continuous. In particular, every element of , the space of continuous functions on that vanish at infinity, is uniformly continuous. This is a generalization of the Heine-Cantor theorem mentioned above, since .
History
The first published definition of uniform continuity was by Heine in 1870, and in 1872 he published a proof that a continuous function on an open interval need not be uniformly continuous. The proofs are almost verbatim given by Dirichlet in his lectures on definite integrals in 1854. The definition of uniform continuity appears earlier in the work of Bolzano where he also proved that continuous functions on an open interval do not need to be uniformly continuous. In addition he also states that a continuous function on a closed interval is uniformly continuous, but he does not give a complete proof.[1]
Other characterisations
Non-standard analysis
In non-standard analysis, a real-valued function f of a real variable is microcontinuous at a point a precisely if the difference f*(a + δ) − f*(a) is infinitesimal whenever δ is infinitesimal. Thus f is continuous on a set A in R precisely if f* is microcontinuous at every real point a ∈ A. Uniform continuity can be expressed as the condition that (the natural extension of) f is microcontinuous not only at real points in A, but at all points in its non-standard counterpart (natural extension) *A in *R. Note that there exist hyperreal-valued functions which meet this criterion but are not uniformly continuous, as well as uniformly continuous hyperreal-valued functions which do not meet this criterion, however, such functions cannot be expressed in the form f* for any real-valued function f. (see non-standard calculus for more details and examples).
Cauchy continuity
For a function between metric spaces, uniform continuity implies Cauchy continuity (Fitzpatrick 2006). More specifically, let A be a subset of Rn. If a function f : A → Rm is uniformly continuous then for every pair of sequences xn and yn such that
we have
Relations with the extension problem
Let X be a metric space, S a subset of X, and a continuous function. When can f be extended to a continuous function on all of X?
If S is closed in X, the answer is given by the Tietze extension theorem: always. So it is necessary and sufficient to extend f to the closure of S in X: that is, we may assume without loss of generality that S is dense in X, and this has the further pleasant consequence that if the extension exists, it is unique.
Let us suppose moreover that X is complete, so that X is the completion of S. Then a continuous function extends to all of X if and only if f is Cauchy-continuous, i. e., the image under f of a Cauchy sequence remains Cauchy. (In general, Cauchy continuity is necessary and sufficient for extension of f to the completion of X, so is a priori stronger than extendability to X.)
It is easy to see that every uniformly continuous function is Cauchy-continuous and thus extends to X. The converse does not hold, since the function is, as seen above, not uniformly continuous, but it is continuous and thus -- since R is complete -- Cauchy continuous. In general, for functions defined on unbounded spaces like R, uniform continuity is a rather strong condition. It is desirable to have a weaker condition from which to deduce extendability.
For example, suppose a > 1 is a real number. At the precalculus level, the function can be given a precise definition only for rational values of x (assuming the existence of qth roots of positive real numbers, an application of the Intermediate Value Theorem). One would like to extend f to a function defined on all of R. The identity
shows that f is not uniformly continuous on all of Q; however for any bounded interval I the restriction of f to is uniformly continuous, hence Cauchy-continuous, hence f extends to a continuous function on I. But since this holds for every I, there is then a unique extension of f to a continuous function on all of R.
More generally, a continuous function whose restriction to every bounded subset of S is uniformly continuous is extendable to X, and the converse holds if X is locally compact.
A typical application of the extendability of a uniform continuous function is the proof of the inverse Fourier transformation formula. We first prove that the formula is true for test functions, there are densely many of them. We then extend the inverse map to the whole space using the fact that linear map is continuous; thus, uniformly continuous.
Generalization to topological vector spaces
In the special case of two topological vector spaces and , the notion of uniform continuity of a map becomes: for any neighborhood of zero in , there exists a neighborhood of zero in such that implies
For linear transformations , uniform continuity is equivalent to continuity. This fact is frequently used implicitly in functional analysis to extend a linear map off a dense subspace of a Banach space.
Generalization to uniform spaces
Just as the most natural and general setting for continuity is topological spaces, the most natural and general setting for the study of uniform continuity are the uniform spaces. A function f : X → Y between uniform space is called uniformly continuous if for every entourage V in Y there exists an entourage U in X such that for every (x1, x2) in U we have (f(x1), f(x2)) in V.
In this setting, it is also true that uniformly continuous maps transform Cauchy sequences into Cauchy sequences.
Each compact Hausdorff space possesses exactly one uniform structure compatible with the topology. A consequence is a generalisation of the Heine-Cantor theorem: each continuous function from a compact Hausdorff space to a uniform space is uniformly continuous.
References
Further reading
- Bourbaki, Nicolas. General Topology: Chapters 1–4. ISBN 0-387-19374-X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) Chapter II is a comprehensive reference of uniform spaces. - Dieudonné, Jean (1960). Foundations of Modern Analysis. Academic Press.
- Fitzpatrick, Patrick (2006). Advanced Calculus. Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0-534-92612-6.
- Kelley, John L. (1955). General topology. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-90125-6.
- Kudryavtsev, L.D. (2001) [1994], "Uniform continuity", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press
- Rudin, Walter (1976). Principles of Mathematical Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-054235-8.
- Rusnock, P.; Kerr-Lawson, A. (2005), "Bolzano and uniform continuity", Historia Mathematica, 32 (3): 303–311, doi:10.1016/j.hm.2004.11.003




































