Protein crystallization: Difference between revisions
Dixiang Yuan (talk | contribs) Add more details about the history of protein crystallization |
Dixiang Yuan (talk | contribs) Add a section called "Technologies that identify the structure of protein crystallization" |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
===Protein engineering=== |
===Protein engineering=== |
||
Techniques of [[molecular biology]], especially [[molecular cloning]], [[recombinant protein expression]], and [[site-directed mutagenesis]] can be employed to engineer and produce proteins with increased propensity to crystallize, or can even direct polymorph selection during protein crystallization <ref>{{Cite journal|last=Van Driesshe|first=Alexander E.S.|last2=Van Gerven|first2=Nani|last3=Bomans|first3=Paul H.H.|last4=Joosten|first4=Rick R.M.|last5=Friedrich|first5=Heiner|last6=Gil-Carton|first6=David|last7=Gerven|first7=Sommerdijk|last8=Sleutel|first8=Mike|date=April 2018|title=Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nature25971|journal=Nature|language=en|volume=556|issue=7699|pages=89–94|doi=10.1038/nature25971|issn=1476-4687|via=}}</ref>. Frequently, problematic [[cysteine]] residues can be replaced by alanine to avoid [[disulfide]]-mediated aggregation, and residues such as lysine, glutamate, and glutamine can be changed to alanine to reduce intrinsic protein flexibility, which can hinder crystallization. |
Techniques of [[molecular biology]], especially [[molecular cloning]], [[recombinant protein expression]], and [[site-directed mutagenesis]] can be employed to engineer and produce proteins with increased propensity to crystallize, or can even direct polymorph selection during protein crystallization <ref>{{Cite journal|last=Van Driesshe|first=Alexander E.S.|last2=Van Gerven|first2=Nani|last3=Bomans|first3=Paul H.H.|last4=Joosten|first4=Rick R.M.|last5=Friedrich|first5=Heiner|last6=Gil-Carton|first6=David|last7=Gerven|first7=Sommerdijk|last8=Sleutel|first8=Mike|date=April 2018|title=Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nature25971|journal=Nature|language=en|volume=556|issue=7699|pages=89–94|doi=10.1038/nature25971|issn=1476-4687|via=}}</ref>. Frequently, problematic [[cysteine]] residues can be replaced by alanine to avoid [[disulfide]]-mediated aggregation, and residues such as lysine, glutamate, and glutamine can be changed to alanine to reduce intrinsic protein flexibility, which can hinder crystallization. |
||
== Technologies that identify the structure of protein crystallization == |
|||
For the macromolecule structural solving, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) are the three main ways in the field. |
|||
=== [[Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy|Nuclear magnetic resonance ('''NMR''')]] === |
|||
Specifically for proteins, NMR covers the smaller sizes of the range.<ref name=":6">{{Cite web|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.18785/fa.dg0021|title=Victor Ambrus Papers|last=University of Southern Mississippi|first=Special Collections, University Libraries|date=1992-01-01|website=dx.doi.org|access-date=2019-03-18}}</ref> The largest protein that has had its structure successfully solved by NMR was malate synthase G with 723 amino acid residues at 81.4kDa in 2002.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Tugarinov|first=Vitali|last2=Muhandiram|first2=Ranjith|last3=Ayed|first3=Ayeda|last4=Kay|first4=Lewis E.|date=2002-08|title=Four-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy of a 723-Residue Protein: Chemical Shift Assignments and Secondary Structure of Malate Synthase G|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja0205636|journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society|volume=124|issue=34|pages=10025–10035|doi=10.1021/ja0205636|issn=0002-7863}}</ref> This puts a huge limitation on NMR usage in analyzing complex protein structures with molecular weight above that limit.<ref name=":6" /> |
|||
=== [[Powder diffraction|X-ray powder diffraction ('''XRD''')]] === |
|||
Due to having no limit to protein molecular weight, the use of XRD in protein structural determination is more popular compared to NMR.<ref name=":6" /> As a reference, XRD had successfully solved and provided high resolution structures (< 1.5Å) for proteins such as human phosphodiesterase 2A at a molecular weight of 161.4kDa (and with a resolution of 1.43Å), which NMR would not have been able to achieve.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Gomez|first=Laurent|last2=Xu|first2=Rui|last3=Sinko|first3=William|last4=Selfridge|first4=Brandon|last5=Vernier|first5=William|last6=Ly|first6=Kiev|last7=Truong|first7=Richard|last8=Metz|first8=Markus|last9=Marrone|first9=Tami|date=2018-08-02|title=Mathematical and Structural Characterization of Strong Nonadditive Structure–Activity Relationship Caused by Protein Conformational Changes|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00713|journal=Journal of Medicinal Chemistry|volume=61|issue=17|pages=7754–7766|doi=10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00713|issn=0022-2623}}</ref> |
|||
=== [[Cyrogenic-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)|'''Cryogenic electron microscopy''' ('''cryo-EM''')]] === |
|||
Cryo-EM is most notably known for the advantage of completely eliminating the need of crystallizing protein samples.<ref name=":7">{{Cite journal|last=Zanotti|first=Giuseppe|date=2016|title=Cryo-EM and X-Ray Crystallography: Complementary or Alternative Techniques?|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.17756/nwj.2016-025|journal=NanoWorld Journal|volume=2|issue=2|doi=10.17756/nwj.2016-025|issn=2379-1101}}</ref> The cryo-EM sample preparation process is relatively more instantaneous and easier than XRD. The protein sample for cryo-EM analysis is usually prepare by fast freezing using liquid ethane.<ref name=":8">{{Cite journal|last=Saibil|first=Helen R.|date=2000-10-01|title=Macromolecular structure determination by cryo-electron microscopy|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/s0907444900010787|journal=Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography|volume=56|issue=10|pages=1215–1222|doi=10.1107/s0907444900010787|issn=0907-4449}}</ref> After fast freezing, samples are ready for visualization under EM.<ref name=":8" /> This completely avoids the time and effort needed for protein crystallization for XRD analysis. Yet, in comparison with structures being solved by XRD, structures solved by cryo- EM are significantly lower in resolution.<ref name=":7" /> |
|||
==Alternatives== |
==Alternatives== |
||
Revision as of 13:32, 19 March 2019
This article focuses too much on specific examples. (December 2013) |

Protein crystallization is the process of formation of a protein crystal. In the process, proteins will dissolve in an aqueous environment, and sample solution to reach the supersaturated state.[1] Different methods are used to reach that state. Such as, Vapor diffusion, Microbatch, Microdialysis, Free-interface diffusion, etc. In additional, some parameters including pH, temperature, ionic strength in the crystallization solution and other factors could influence the yield of crystallization as well.[1]These crystals can then be used in structural biology to study the molecular structure of the protein, or for various industrial or biotechnological purposes.
Based on the crystals, the determination of protein structure can be achieved traditionally by utilizing X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). Alternatively, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) could also be used for protein structure determination. The structural of proteins is significant to the structural analysis in biochemistry and translational medicine. Meanwhile, the protein structure is essential for the development of targeted therapy in modern drug advancement.[2][3]
Development of protein crystallization
This article is missing information about the history of protein crystallization techniques. (December 2013) |
Crystallization of protein molecules has been known for over 150 years.[4]
In 1840, Friedrich Ludwig Hünefeld accidentally discovered the formation of crystalline material in samples of the earthworm blood held under two glass slides and occasionally observed small plate‐like crystals in desiccated swine or human blood samples. These crystals ware named as ‘haemoglobin’, by Felix Hoppe‐Seyler in 1864. The seminal findings of Hünefeld have inspired lots of scientist in the future.[5]
Thus, in 1851, Funke described the process of producing human haemoglobin crystals by diluting red blood cells with solvents such as pure water, alcohol or ether, followed by slow evaporation of the solvent from the protein solution 23. In 1871, William T. Preyer, Professor at University of Jena, published a book entitled Die Blutkrystalle (The Crystals of Blood), reviewing the features of haemoglobin crystals from around 50 species of mammals, birds, reptiles and fishes.[5]
In 1909 when the physiologist Edward T. Reichert, together with the mineralogist Amos P. Brown, published an treatise on the preparation, physiology and geometrical characterization of haemoglobin crystals from several hundreds animals, including extinct species such as the Tasmanian wolf.[5] Increasing protein crystals were found.
In 1934, John Desmond Bernal and his student Dorothy Hodgkin discovered that protein crystals surrounded by their mother liquor gave better diffraction patterns than dried crystals. Using pepsin, they were the first to discern the diffraction pattern of a wet, globular protein. Prior to Bernal and Hodgkin, protein crystallography had only been performed in dry conditions with inconsistent and unreliable results. This is the first X‐ray diffraction pattern of a protein crystal.[6]
In 1958, the structure of myoglobin (a red protein containing heme), determined by X-ray crystallography, was first reported by John Kendrew.[7] Kendr ew shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Max Perutz for this discovery.
Now, based on the protein crystals, the structures of them play a significant role in biochemistry and translational medicine.
Principles of protein crystallization

The solubility of protein molecules is subject to many factors, especially the interaction with other compounds in solution. Most proteins are soluble at physiological conditions, but as the concentration of solutes rises, the protein becomes less soluble, driving it to crystallize or precipitate. This phenomenon is known as "salting out". Counterintuitively, at very low solute concentrations, proteins also become less soluble, because some solutes are necessary for the protein to remain in solution. This converse phenomenon is known as "salting in". Most protein crystallization techniques form crystals by salting out the protein into crystals, although some experimental setups can produce crystals using the salting in effect.
The goal of crystallization is to produce a well-ordered crystal that is lacking in contaminants while still large enough to provide a diffraction pattern when exposed to X-rays. This diffraction pattern can then be analyzed to discern the protein’s tertiary structure. Protein crystallization is inherently difficult because of the fragile nature of protein crystals. Proteins have irregularly shaped surfaces, which results in the formation of large channels within any protein crystal. Therefore, the noncovalent bonds that hold together the lattice must often be formed through several layers of solvent molecules.[9]
In addition to overcoming the inherent fragility of protein crystals, a number of environmental factors must also be overcome. Due to the molecular variations between individual proteins, conditions unique to each protein must be obtained for a successful crystallization. Therefore, attempting to crystallize a protein without a proven protocol can be very challenging and time consuming.
Crystallization conditions
Many factors influence the likelihood of crystallization of a protein sample. Some of these factors include protein purity, pH, concentration of protein, temperature, precipitants and additives. The more homogeneous the protein solution is, the more likely that it will crystallize. Typically, protein samples above 97% purity are considered suitable for crystallization[citation needed], although high purity is neither necessary nor sufficient for crystallization. Solution pH can be very important and in extreme cases can result in different packing orientations. Buffers, such as Tris-HCl, are often necessary for the maintenance of a particular pH.[10] Precipitants, such as ammonium sulfate or polyethylene glycol, are usually used to promote the formation of protein crystals.[9]
Methods of protein crystallization
Vapor diffusion
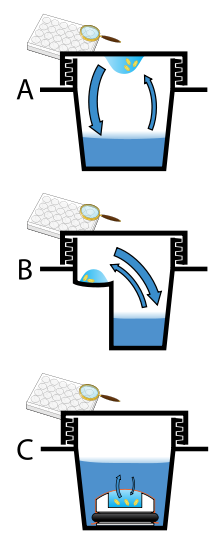
Vapor diffusion is the most commonly employed method of protein crystallization. In this method, a droplet containing purified protein, buffer, and precipitant are allowed to equilibrate with a larger reservoir containing similar buffers and precipitants in higher concentrations. Initially, the droplet of protein solution contains comparatively low precipitant and protein concentrations, but as the drop and reservoir equilibrate, the precipitant and protein concentrations increase in the drop. If the appropriate crystallization solutions are used for a given protein, crystal growth will occur in the drop.[9][11] This method is used because it allows for gentle and gradual changes in concentration of protein and precipitant concentration, which aid in the growth of large and well-ordered crystals.
Vapor diffusion can be performed in either hanging-drop or sitting-drop format. Hanging-drop apparatus involve a drop of protein solution placed on an inverted cover slip, which is then suspended above the reservoir. Sitting-drop crystallization apparatus place the drop on a pedestal that is separated from the reservoir. Both of these methods require sealing of the environment so that equilibration between the drop and reservoir can occur.[9][12]
Microbatch
A microbatch usually involves immersing a very small volume of protein droplets in oil (as little as 1 µl). The reason that oil is required is because such low volume of protein solution is used and therefore evaporation must be inhibited to carry out the experiment aqueously. Although there are various oils that can be used, the two most common sealing agent are paraffin oils (described by Chayen et al.) and silicon oils (described by D’Arcy). There are also other methods for Microbatching that don't use a liquid sealing agent and instead require a scientist to quickly place a film or some tape on a welled plate after placing the drop in the well.
Besides the very limited amounts of sample needed, this method also has as a further advantage that the samples are protected from airborne contamination, as they are never exposed to the air during the experiment.
Microdialysis
This article is missing information about microdialysis methods for protein crystallization. (December 2013) |
Microdialysis takes advantage of a semi-permeable membrane, across which small molecules and ions can pass, while proteins and large polymers cannot cross. By establishing a gradient of solute concentration across the membrane and allowing the system to progress toward equilibrium, the system can slowly move toward supersaturation, at which point protein crystals may form.
Microdialysis can produce crystals by salting out, employing high concentrations of salt or other small membrane-permeable compounds that decrease the solubility of the protein. Very occasionally, some proteins can be crystallized by dialysis salting in, by dialyzing against pure water, removing solutes, driving self-association and crystallization.
Free-interface diffusion
This technique brings together protein and precipitation solutions without premixing them, but instead, injecting them through either sides of a channel, allowing equilibrium through diffusion. The two solutions come into contact in a reagent chamber, both at their maximum concentrations, initiating spontaneous nucleation. As the system comes into equilibrium, the level of supersaturation decreases, favouring crystal growth.[13]
Specialized protein crystallization techniques
Some proteins present unique challenges for crystallization. Membrane proteins frequently require the addition of a detergent for isolation and crystallization, and tend to form "very small, weakly (x-ray) diffracting, radiation-sensitive crystals".[14] Proteins that form fibres need to be stabilized in a monomeric form. Small proteins can have poor solubility in water and require specialized crystallization techniques.[15]
Technologies that assist with protein crystallization
High throughput crystallization screening [16]
High through-put methods exist to help streamline the large number of experiments required to explore the various conditions that are necessary for successful crystal growth. There are numerous commercials kits available for order which apply preassembled ingredients in systems guaranteed to produce successful crystallization. Using such a kit, a scientist avoids the hassle of purifying a protein and determining the appropriate crystallization conditions.
Liquid-handling robots can be used to set up and automate large number of crystallization experiments simultaneously. What would otherwise be slow and potentially error-prone process carried out by a human can be accomplished efficiently and accurately with an automated system. Robotic crystallization systems use the same components described above, but carry out each step of the procedure quickly and with a large number of replicates. Each experiment utilizes tiny amounts of solution, and the advantage of the smaller size is two-fold: the smaller sample sizes not only cut-down on expenditure of purified protein, but smaller amounts of solution lead to quicker crystallizations. Each experiment is monitored by a camera which detects crystal growth.[11]
Protein engineering
Techniques of molecular biology, especially molecular cloning, recombinant protein expression, and site-directed mutagenesis can be employed to engineer and produce proteins with increased propensity to crystallize, or can even direct polymorph selection during protein crystallization [17]. Frequently, problematic cysteine residues can be replaced by alanine to avoid disulfide-mediated aggregation, and residues such as lysine, glutamate, and glutamine can be changed to alanine to reduce intrinsic protein flexibility, which can hinder crystallization.
Technologies that identify the structure of protein crystallization
For the macromolecule structural solving, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) are the three main ways in the field.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Specifically for proteins, NMR covers the smaller sizes of the range.[18] The largest protein that has had its structure successfully solved by NMR was malate synthase G with 723 amino acid residues at 81.4kDa in 2002.[19] This puts a huge limitation on NMR usage in analyzing complex protein structures with molecular weight above that limit.[18]
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD)
Due to having no limit to protein molecular weight, the use of XRD in protein structural determination is more popular compared to NMR.[18] As a reference, XRD had successfully solved and provided high resolution structures (< 1.5Å) for proteins such as human phosphodiesterase 2A at a molecular weight of 161.4kDa (and with a resolution of 1.43Å), which NMR would not have been able to achieve.[20]
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM)
Cryo-EM is most notably known for the advantage of completely eliminating the need of crystallizing protein samples.[21] The cryo-EM sample preparation process is relatively more instantaneous and easier than XRD. The protein sample for cryo-EM analysis is usually prepare by fast freezing using liquid ethane.[22] After fast freezing, samples are ready for visualization under EM.[22] This completely avoids the time and effort needed for protein crystallization for XRD analysis. Yet, in comparison with structures being solved by XRD, structures solved by cryo- EM are significantly lower in resolution.[21]
Alternatives
This section may contain information not important or relevant to the article's subject. (November 2017) |
Some proteins do not fold properly outside their native environment, e.g. proteins which are part of the cell membrane like ion channels and G-protein coupled receptors, their structure is altered by interacting proteins or switch between different states. All those conditions prevent crystal growth or give crystal structures which do not represent the natural structure of the protein. In order to determine the 3D structure of proteins which are hard to crystallize researchers may use nuclear magnetic resonance, also known as protein NMR, which is best suited to small proteins, or transmission electron microscopy, which is best suited to large proteins or protein complexes.
Applications of protein crystallization
Protein crystallization is required for structural analysis by X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, and some techniques of electron microscopy. These techniques can be used to determine the molecular structure of the protein. For a better part of the 20th century, progress in determining protein structure was slow due to the difficulty inherent in crystallizing proteins. When the Protein Data Bank was founded in 1971, it contained only seven structures.[23] Since then, the pace at which protein structures are being discovered has grown exponentially, with the PDB surpassing 20,000 structures in 2003, and containing over 100,000 as of 2014.
Crystallization of proteins can also be useful in the formulation of proteins for pharmaceutical purposes.[24]
See also
References
- ^ a b McPherson, Alexander; Gavira, Jose A. (2013-12-24). "Introduction to protein crystallization". Acta Crystallographica Section F Structural Biology Communications. 70 (1): 2–20. doi:10.1107/s2053230x13033141. ISSN 2053-230X.
- ^ Blundell, Tom L. (2017-06-29). "Protein crystallography and drug discovery: recollections of knowledge exchange between academia and industry". IUCrJ. 4 (4): 308–321. doi:10.1107/s2052252517009241. ISSN 2052-2525.
- ^ Tripathy, Debu; Bardia, Aditya; Sellers, William R. (2017-03-28). "Ribociclib (LEE011): Mechanism of Action and Clinical Impact of This Selective Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor in Various Solid Tumors". Clinical Cancer Research. 23 (13): 3251–3262. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-3157. ISSN 1078-0432.
- ^ McPherson, Alexander (1991-03). "A brief history of protein crystal growth". Journal of Crystal Growth. 110 (1–2): 1–10. doi:10.1016/0022-0248(91)90859-4. ISSN 0022-0248.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c Giegé, Richard (2013-12). "A historical perspective on protein crystallization from 1840 to the present day". The FEBS journal. 280 (24): 6456–6497. doi:10.1111/febs.12580. ISSN 1742-4658. PMID 24165393.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Tulinsky, A. (1996), "Chapter 35. The Protein Structure Project, 1950–1959: First Concerted Effort of a Protein Structure Determination in the U.S.", Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry, Elsevier, pp. 357–366, ISBN 9780120405312, retrieved 2019-03-12
- ^ KENDREW, J. C.; BODO, G.; DINTZIS, H. M.; PARRISH, R. G.; WYCKOFF, H.; PHILLIPS, D. C. (1958-03). "A Three-Dimensional Model of the Myoglobin Molecule Obtained by X-Ray Analysis". Nature. 181 (4610): 662–666. doi:10.1038/181662a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Blundell, Tom L. (2017-06-29). "Protein crystallography and drug discovery: recollections of knowledge exchange between academia and industry". IUCrJ. 4 (4): 308–321. doi:10.1107/s2052252517009241. ISSN 2052-2525.
- ^ a b c d Rhodes, G. (2006) Crystallography Made Crystal Clear, Third Edition: A Guide for Users of Macromolecular Models, 3rd Ed., Academic Press
- ^ Branden C, Tooze J (1999). Introduction to Protein Structure. New York: Garland. pp. 374–376. ISBN 9780815303442.
- ^ a b "The Crystal Robot". December 2000. Retrieved 2003-02-18.
- ^ McRee, D (1993). Practical Protein Crystallography. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-0-12-486052-0.
- ^ Rupp, Bernhard (20 October 2009). Biomolecular Crystallography: Principles, Practice, and Application to Structural Biology. Garland Science. p. 800. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ^ Liszewski, Kathy (1 October 2015). "Dissecting the Structure of Membrane Proteins". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News. 35 (17): 14.(subscription required)
- ^ Teeter MM, Hendrickson WA (1979). "Highly ordered crystals of the plant seed protein crambin". J Mol Biol. 127 (2): 219–23. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(79)90242-0. PMID 430565.
- ^ Lin, Yibin (20 April 2018). "What's happened over the last five years with high-throughput protein crystallization screening?". Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery: 1–5. doi:10.1080/17460441.2018.1465924. PMID 29676184.
- ^ Van Driesshe, Alexander E.S.; Van Gerven, Nani; Bomans, Paul H.H.; Joosten, Rick R.M.; Friedrich, Heiner; Gil-Carton, David; Gerven, Sommerdijk; Sleutel, Mike (April 2018). "Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection". Nature. 556 (7699): 89–94. doi:10.1038/nature25971. ISSN 1476-4687.
- ^ a b c University of Southern Mississippi, Special Collections, University Libraries (1992-01-01). "Victor Ambrus Papers". dx.doi.org. Retrieved 2019-03-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tugarinov, Vitali; Muhandiram, Ranjith; Ayed, Ayeda; Kay, Lewis E. (2002-08). "Four-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy of a 723-Residue Protein: Chemical Shift Assignments and Secondary Structure of Malate Synthase G". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 124 (34): 10025–10035. doi:10.1021/ja0205636. ISSN 0002-7863.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); no-break space character in|title=at position 60 (help) - ^ Gomez, Laurent; Xu, Rui; Sinko, William; Selfridge, Brandon; Vernier, William; Ly, Kiev; Truong, Richard; Metz, Markus; Marrone, Tami (2018-08-02). "Mathematical and Structural Characterization of Strong Nonadditive Structure–Activity Relationship Caused by Protein Conformational Changes". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 61 (17): 7754–7766. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00713. ISSN 0022-2623.
- ^ a b Zanotti, Giuseppe (2016). "Cryo-EM and X-Ray Crystallography: Complementary or Alternative Techniques?". NanoWorld Journal. 2 (2). doi:10.17756/nwj.2016-025. ISSN 2379-1101.
- ^ a b Saibil, Helen R. (2000-10-01). "Macromolecular structure determination by cryo-electron microscopy". Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 56 (10): 1215–1222. doi:10.1107/s0907444900010787. ISSN 0907-4449.
- ^ Berman H, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat T, Weissig H, Shindyalov I, Bourne P (2000). "The Protein Data Bank". Nucleic Acids Research. 28 (1): 235–242. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.235. PMC 102472. PMID 10592235.
- ^ Jen, A., and Merkle, H. P. (2001) Diamonds in the Rough: Protein Crystals from a Formulation Perspective Pharm Res 18, 1483–1488
External links
- "Protein Crystallization and Dumb Luck". An essay on the haphazard side of protein crystallization by Bob Cudney: http://www.rigaku.com/downloads/journal/Vol16.2.1999/cudney.pdf
- Owens, Ray. "Protein Crystals". Backstage Science. Brady Haran.
- This page was reproduced (with modifications) with expressed consent from Dr. A. Malcolm Campbell. As of 2010, the original page can be found at http://www.bio.davidson.edu/Courses/Molbio/MolStudents/spring2003/Kogoy/protein.html
