Dimethyldiethoxysilane
Appearance
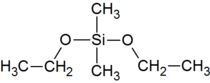
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethoxydi(methyl)silane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DMDEOS |
| 1736110 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.025 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2380 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H16O2Si | |
| Molar mass | 148.277 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.865 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −87 °C (−125 °F; 186 K) |
| Boiling point | 114 °C (237 °F; 387 K) |
| Solubility | soluble in carbon tetrachloride[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethyldiethoxysilane, sometimes abbreviated DMDEOS or DMDES, is an organosilicon compound. DMDEOS is a precursor in the production of the silicone polymer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS).
DMDEOS is an intermediate silane useful for blocking hydroxyl and amino groups in organic synthesis reactions. This silylating step allows subsequent reactions to be carried out which would be adversely affected by the presence of active hydrogen in the hydroxyl or amine groups. Following the reaction step, hydroxyl or amine groups blocked with DMDEOS may be recovered by a hydrolysis procedure. DMDEOS is also used for preparing hydrophobic and release materials as well as enhancing flow of powders.[2] [3]
References
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 3–180, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ^ Merhari, Lhadi (2009), Hybrid Nanocomposites for Nanotechnology, Springer, pp. 184–185, ISBN 978-0-387-72398-3, retrieved 2009-07-19
- ^ "GP-49 Dimethyldiethoxysilane | Genesee Polymers Corporation".
