2023–24 South Pacific cyclone season
| 2023–24 South Pacific cyclone season | |
|---|---|
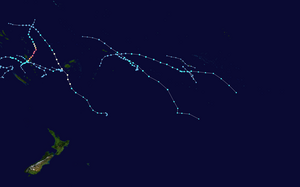 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | October 19, 2023 |
| Last system dissipated | Season ongoing |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Lola |
| • Maximum winds | 215 km/h (130 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 930 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total disturbances | 2 |
| Total depressions | 2 |
| Tropical cyclones | 2 |
| Severe tropical cyclones | 1 |
| Total fatalities | 2 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
The 2023–24 South Pacific cyclone season is an ongoing weather event in the South Pacific Ocean, to the east of 160°E. The season officially started on November 1, 2023, and will end on April 30, 2024, however a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, as shown by Cyclone Lola which formed in October. During the season, tropical cyclones will be officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, Australian Bureau of Meteorology and New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) will also monitor the basin and issue unofficial warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The BoM, FMS and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate windspeeds with a period of approximately ten minutes, while the JTWC estimates sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).
Seasonal forecasts
| Source/Record | Region | Tropical Cyclone |
Severe Tropical Cyclones |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Records | ||||
| Average (1969-70 - 2022–23): | 160°E - 120°W | 7 | 3 | [1] |
| Record high: | 160°E - 120°W | 1997–98: 16 | 1982–83: 9 | [2] |
| Record low: | 160°E - 120°W | 1990–91: 2 | 2008–09: 0 | [2] |
| Predictions | ||||
| CWCL July | 135°E - 120°W | 8–11 | — | [3] |
| CWCL August | 135°E - 120°W | 8–11 | — | [3] |
| CWCL September | 135°E - 120°W | 8-14 | — | [3] |
| CWCL October | 135°E - 120°W | 9-14 | — | [4] |
| NIWA October | 135°E - 120°W | 9–14 | 4–8 | [5] |
| FMS Whole | 160°E - 120°W | 8-14 | 6-9 | [1] |
| FMS Western | 160°E - 180° | 4-6 | 2-4 | [1] |
| FMS Eastern | 180° - 120°W | 6-9 | 3-4 | [1] |
Ahead of the season officially starting on November 1, the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS), Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BoM), National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) and the University of Newcastle's Australian Centre for Water, Climate and Land (ACWCL), each issued a tropical cyclone outlook that discussed the upcoming season. These outlooks took into account a variety of factors such as a developing El Nino event and what had happened in previous seasons such as 1972-73, 1982-83, 1987-88, 1991-92, 1997-98, 2002-03, 2004-05, 2009-10 and 2015-16.[1][5]
The first two of these outlooks were issued in July and August by the ACWCL who suggested that it would be a near-normal season, with eight and eleven tropical cyclones occurring between 135°E and 120°W during the season.[3] The ACWCL tweaked its forecast during September and suggested that up to fourteen tropical cyclones would occur between 135°E and 120°W during the season.[3] They subsequently joined NIWA, the FMS, BoM, MetService and various other Pacific meteorological services and contributed towards the Southwest Pacific tropical cyclone outlook.[5] This outlook suggested that between nine and fourteen tropical cyclones would occur between 135°E and 120°W.[5] Four to eight of these tropical cyclones were expected to intensify and become either a Category three, four or five severe tropical cyclone on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale.[5]
In addition to contributing towards the Southwest Pacific tropical cyclone outlook, the FMS and the BoM issued their own seasonal forecasts for the South Pacific region.[1][6] The BoM issued two seasonal forecasts for the Southern Pacific Ocean, for their self-defined eastern and western regions of the South Pacific Ocean.[6] They predicted that the Western region between 142.5°E and 165°E, had a 32% chance of seeing activity above its average of 4 tropical cyclones.[6] The BoM also predicted that the Eastern Region between 165°E and 120°W, had a 60% chance of seeing activity above its average of 6 tropical cyclones.[6] Within their outlook the FMS predicted that between eight and fourteen tropical cyclones would occur within the basin compared to an average of around 7.[1] At least five of these tropical cyclones were expected to intensify further and become either a Category three, four or five severe tropical cyclone on the Australian scale.[1] The FMS also predicted that the majority of systems would occur to the east of the International Dateline, with 4-6 tropical cyclones expected to occur between 160°E - 180° while 6-9 were expected to occur between 180° - 120°W.[1] On October 21, the ACWCL issued their final outlook for the season and predicted that it would be an above average season with 9-14 tropical cyclones occurring between 135°E and 120°W.[4]
Seasonal summary

The season began with the formation of Cyclone Lola on October 19, thirteen days before the official start of the season. Three days later it intensified to a Category 5 severe tropical cyclone on the Australian scale, making it the first such start to a South Pacific cyclone season since Cyclone Xavier in 2006.
Systems
Severe Tropical Cyclone Lola
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 19 – October 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (10-min); 930 hPa (mbar) |
On October 19, the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS) reported that Tropical Disturbance 01F had developed out of an area of low pressure, about 1295 km (805 mi) to the northeast of Honiara in the Solomon Islands.[7][8] At this time the system located in an area favourable for further development, with warm sea-surface temperatures of 30–31 °C (86–88 °F) and low to moderate vertical windshear.[7][9] Over the next couple of days, the system gradually moved southwestward before the FMS classified it as a tropical depression.[10] The cyclone drifted southward until an upper-level ridge forced the storm to the south.[11] During the next day, it intensified into a Category 1 tropical cyclone, with the FMS naming it as Lola.[12] Lola rapidly intensified into a Category 4 intensity was reached by 12:00 UTC that day, with Lola exhibiting maximum ten-minute sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph).[13] With convective rain bands wrapping into the circulation, the JTWC assessed Lola as having one-minute sustained winds of 215 km/h (130 mph).[14] At the same time, the FMS followed suit and upgraded the system to a Category 5 severe tropical cyclone.[15] Lola's eye quickly disappeared, signaling a phase of rapid weakening.[16] Lola made landfall in Sowan, at around 03:00 UTC on October 25.[17] During October 26, Lola degenerated into a tropical depression, before it was last noted the next day and the JTWC issued their final advisory on the storm.[18][19]
Tropical Cyclone Lola was the third severe tropical cyclone to impact Vanuatu during 2023, after Cyclones Judy and Kevin impacted the island nation during March 2023.[20] Vanuatu Prime Minister Charlot Salwai took a Royal Australian Air Force to inspect the early damage. At least 10,000 households have been affected by the storm. Additionally, the New Zealand, Australian, and French defense forces will provide further aid and assess damages.[21] In Solomon Islands, the Solomon Islands National Disaster Management Office (NDMO) reported that Cyclone Lola had severe impacts on Tikopia.[22]
Tropical Cyclone Mal
| |||
| Current storm information | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| As of | 12:00 UTC, November 13 | ||
| Location | 12°24′S 173°00′E / 12.4°S 173.0°E | ||
| Movement | SE at 23 kn (43 km/h; 26 mph) | ||
| 10-minute sustained (FMS) | |||
| Sustained winds | 95 km/h (60 mph) | ||
| Pressure | 988 hPa (mbar); 29.18 inHg | ||
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC) | |||
| Sustained winds | 110 km/h (70 mph) | ||
| Gusts | 130 km/h (80 mph) | ||
| Pressure | 986 hPa (mbar); 29.12 inHg | ||
On November 11, the FMS reported that Tropical Disturbance 02F had formed near the Solomon Islands and moved towards Fiji.[23] By November 12, the system intensified into a Tropical Depression.[24] It intensified into a Category 1 tropical cyclone later on, with the FMS naming it as Mal.[25] On November 14, it intensified into a Category 2 tropical cyclone.[26]
On November 12, a gale alert was issued for the Yasawa and Mamunca groups as well as the western and northern regions of Viti Levu.[27] The FMS anticipated the system to become a Tropical Cyclone by November 13.[28] Nevertheless, the National Disaster Management Office of Fiji issued a tropical cyclone alert and citizens were urged to exercise caution.[29]
Current storm information
As of 12:00 UTC November 13, Tropical Cyclone Mal is located near 12°24′S 173°00′E / 12.4°S 173.0°E. Maximum 10-minute sustained winds are at 35 knots (65 km/h; 40 mph), while maximum 1-minute sustained winds are at 55 knots (100 km/h; 65 mph). The minimum central barometric pressure is 993 hPa (29.32 inHg), and the system is moving southeast at 23 knots (43 km/h; 26 mph).
For the latest official information, see:
- FMS's Tropical Disturbance Advisory for Tropical Cyclone Mal
- JTWC's Tropical Cyclone Warning on Tropical Cyclone 02P (Mal)
Storm names
Within the Southern Pacific, a tropical depression is judged to have reached tropical cyclone intensity should it reach winds of 65 km/h (40 mph) and it is evident that gales are occurring at least halfway around the center. With tropical depressions intensifying into a tropical cyclone between the Equator and 25°S and between 160°E - 120°W named by the FMS. However should a tropical depression intensify to the south of 25°S between 160°E and 120°W it will be named in conjunction with the FMS by MetService. Should a tropical cyclone move out of the basin and into the Australian region it will retain its original name. The name Mal was used for the first time this season, which replaced Meena in 2005 season.The names that will be used for the 2023–24 season are listed below:[30]
|
|
Season effects
This table lists all the storms that developed in the South Pacific to the east of longitude 160°E during the 2023–24 season. It includes their intensity on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale, duration, name, landfalls, deaths, and damages. All data is taken from RSMC Nadi and/or TCWC Wellington, and all of the damage figures are in 2023 or 2024 USD.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| Lola | October 19 – 27 | Category 5 severe tropical cyclone | 215 km/h (130 mph) | 930 hPa (27.46 inHg) | Solomon Islands, Vanuatu | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Mal | November 10 – present | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 95 km/h (60 mph) | 988 hPa (29.18 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 2 systems | October 19, 2023 – Season ongoing | 215 km/h (130 mph) | 930 hPa (30 inHg) | Unknown | Unknown | |||
See also
- Weather of 2023 and 2024
- List of Southern Hemisphere cyclone seasons
- Tropical cyclones in 2023 and 2024
- Atlantic hurricane seasons: 2023, 2024
- Pacific hurricane seasons: 2023, 2024
- Pacific typhoon seasons: 2023, 2024
- North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2023, 2024
- 2023–24 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
- 2023–24 Australian region cyclone season
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre Nadi – Tropical Cyclone Centre (RSMC Nadi – TCC) Tropical Cyclone Seasonal Outlook 2023–24 Detailed Outlook" (PDF). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 12, 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 12, 2023. Retrieved October 12, 2023.
- ^ a b Tropical Cyclone Guidance for Season 2010/11 for the Fiji and the Southwest Pacific (PDF) (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 26, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 27, 2012. Retrieved October 17, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e Magee, Andrew (September 23, 2023). September 2023 Long-Range Outlook for the 2023/24 Southwest Pacific Tropical Cyclone Season (PDF) (Report). Australian Centre for Water, Climate and Land. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 12, 2023. Retrieved October 12, 2023.
- ^ a b Magee, Andrew (October 22, 2023). October 2023 Long-Range Outlook for the 2023/24 Southwest Pacific Tropical Cyclone Season (PDF) (Report). Australian Centre for Water, Climate and Land. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved October 23, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e 2023-24 Southwest Pacific Tropical Cyclone Outlook (PDF) (Report). New Zealand's National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research. October 12, 2023. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 12, 2023. Retrieved October 12, 2023.
- ^ a b c d South Pacific tropical cyclone season forecast for 2023 to 2024 (Report). Australian Bureau of Meteorology. October 12, 2023. Archived from the original on October 12, 2023. Retrieved October 12, 2023.
- ^ a b Tropical Disturbance Summary October 19, 2023 0838 UTC (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 19, 2023. Archived from the original on October 19, 2023. Retrieved October 19, 2023.
- ^ "Off season tropical disturbance monitored in the region" (PDF) (Press release). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 20, 2023. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 23, 2023. Retrieved October 23, 2023.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans October 20, 2023 00:30z (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 21, 2023. Archived from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved October 21, 2023.
- ^ Tropical Depression 01F Advisory Number A5 (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 21, 2023. Archived from the original on October 21, 2023. Retrieved October 21, 2023.
- ^ Tropical Depression 01F Advisory Number A6 (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 22, 2023. Archived from the original on October 22, 2023. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Lola Storm Warning Number 06 (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 22, 2023. Archived from the original on October 22, 2023. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ Severe Tropical Cyclone Lola Hurricane Warning Number 11 (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 23, 2023. Archived from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved October 23, 2023.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Cyclone 01P (Lola) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 23 October 2023. Archived from the original on 23 October 2023. Retrieved 23 October 2023.
- ^ Severe Tropical Cyclone Lola Hurricane Warning Number 12 (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 23, 2023. Archived from the original on October 23, 2023. Retrieved October 23, 2023.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Cyclone 01P (Lola) Warning No. 11 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 24 October 2023. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 24 October 2023.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Cyclone 01P (Lola) Warning No. 14 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 25 October 2023. Archived from the original on 25 October 2023. Retrieved 25 October 2023.
- ^ Tropical Disturbance Summary October 26, 2023 0105 UTC (Report). Fiji Meteorological Service. October 26, 2023. Archived from the original on October 26, 2023. Retrieved October 26, 2023.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone 01P (Lola) Warning No. 18 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 26 October 2023. Archived from the original on 26 October 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "Cyclone Lola leaves trail of destruction in Northern Vanuatu, warning for cyclone season | IFRC". www.ifrc.org. Archived from the original on 2023-10-27. Retrieved 2023-10-28.
- ^ "Vanuatu Prime Minister Charlot Salwai surveys Cyclone Lola damage from the air". RNZ. 2023-10-26. Archived from the original on 2023-10-26. Retrieved 2023-10-28.
- ^ "Cyclone Lola batters remote Tikopia in Solomon Islands - disaster office confirms". RNZ. 2023-10-27. Archived from the original on 2023-10-27. Retrieved 2023-10-28.
- ^ "A Tropical Disturbance analysed near the Solomon Islands which is expected to drift towards Fiji by early next week" (PDF) (Press release). Fiji Meteorological Service. November 11, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- ^ "Tropical disturbance TDO2F approaches Fiji". Fiji Broadcasting Corporation. 12 November 2023. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ "TC Mal heads our way". Fiji Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Mal strengthens to category 2 system". RNZ. 14 November 2023. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ Fijivillage. "Weather Office stresses that the whole of Fiji should be on alert for a possible Tropical Cyclone". www.fijivillage.com. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ Fijivillage. "TD02F to become a Tropical Cyclone in next 6 to 18 hours, Fiji to feel further effects from tomorrow into Wednesday". www.fijivillage.com. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ "Fijians urged to exercise caution". Fiji Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- ^ RA V Tropical Cyclone Committee (2023). Tropical Cyclone Operational Plan for the South-East Indian Ocean and the Southern Pacific Ocean 2023 (PDF) (Report). World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved October 23, 2023.





