Church of Christ (Temple Lot)
| Church of Christ (Temple Lot) | |
|---|---|
 Headquarters building (built in 1990) at Temple Lot | |
| Classification | Latter Day Saint movement |
| Orientation | Latter Day Saints |
| Polity | Quorum of the Twelve |
| Moderator | None; all members of the Quorum of the Twelve are seen as equal |
| Region | World |
| Founder | Granville Hedrick, John E. Page and others |
| Origin | April 6, 1830 (officially given); Winter, 1852 (establishment as separate organization)[1] |
| Separated from | Claims to be the sole legitimate continuation of the Church of Christ (Latter Day Saints) |
| Separations | Church of Christ (Fettingite), Church of Christ with the Elijah Message, others |
| Congregations | 32[2] |
| Members | 2,400[2] |
The Church of Christ (Temple Lot) is a denomination of the Latter Day Saint movement headquartered in Independence, Missouri on what is known as the Temple Lot. Members of the church have been known colloquially as "Hedrickites", after Granville Hedrick, who was ordained as the church's first leader in July 1863. Unlike The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and Community of Christ, the Temple Lot church rejects the office of prophet or president, being led by its Quorum of Twelve Apostles instead. It equally rejects the doctrines of Baptism for the Dead and Eternal Marriage promulgated by the Utah LDS church, as well as the Doctrine and Covenants and Pearl of Great Price. While once avidly engaged in dialogue with other Latter Day Saint factions, the church no longer has any official contact with any other organization. Its most notable claim to fame today rests in its sole ownership of the Temple Lot, which it has held for nearly 150 years. Current membership is about 2400, with members in 11 or 12 countries.[2]
History
Origins
The Temple Lot church shares its early history with the larger Latter Day Saint denominations, including The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and the Community of Christ (formerly the RLDS Church). After the assassination of the movement's founder, Joseph Smith, Jr. on June 27, 1844, several leaders vied for control and established rival organizations. By the 1860s, five early Mormon branches found themselves unaffiliated with any larger group. Located in Bloomington, Illinois, Crow Creek, Illinois, Half Moon Prairie, Illinois, Eagle Creek, Illinois, and Vermillion, Indiana, these branches united under the leadership of Granville Hedrick in May 1863.[3] On July 18, 1863 Hedrick was ordained as "President, Prophet, Seer and Revelator" of this organization. Participating in Hedrick's ordination was John E. Page[3] who had been a Apostle under Joseph Smith.[4] The Church of Christ and the LDS Church both affirm a founding date of April 6, 1830, in Fayette, New York, each claiming to be the sole legitimate continuance of that organization. Hedrick later distanced himself from the title of "President", as he ultimately came to believe that this was an unscriptural office.
At the time of its commencement in 1863, Hedrick's retained the name of "The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints" for his organization, reflecting his insistence that it was a continuation of Joseph Smith's church. This was soon shortened to "Church of Christ", however, as this had been the name under which Joseph Smith originally incorporated in 1830. They also wished to distinguish themselves from the church in Utah, members of whom are often referred to by Hedrickites as "Utah Mormons" or "Brighamites", because they followed Brigham Young to Utah Territory in 1847.
The Temple Lot
The church currently occupies a property in Independence, Missouri known as the Temple Lot. This grassy, 2-acre plot is considered by Latter Day Saints of nearly all persuasions to be the site designated by Smith for the temple of the New Jerusalem, a sacred city to be built preparatory to the Second Coming of Jesus Christ. The Hedrickites returned to Independence in 1867 to purchase lots for this temple in the name of the "Church of Christ" and have been headquartered there ever since. In 1891, the church was sued by the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (today called the Community of Christ) for title to the property. The RLDS Church won at trial, but this decision was later reversed on appeal. In the 1930s, the Temple Lot church excavated the site in an attempt to build a temple, but their efforts stalled because of the Great Depression and internal disputes, and the excavation was filled in 1946. The lot was re-landscaped, and is today occupied only by the church's headquarters and a few trees in its northeast corner. No further plans to erect such an edifice have been announced as of 2009.
The Fettingite split
In 1929, the Temple Lot church split between adherents and opponents of a series of "messages" allegedly given by John the Baptist to Otto Fetting, an apostle of the church. While the first eleven of these missives were accepted by the Temple Lot membership, the twelfth was rejected, leading Fetting to withdraw with a portion of the membership and found The Church of Christ (Fettingite). The Temple Lot organization retained the church name and properties, including the Temple Lot. Fetting's organization later divided after his death between adherents of William Draves, who claimed that the "Messenger" was appearing to him, and those who rejected Draves' assertions. Draves' adherents would form the Church of Christ with the Elijah Message, while those rejecting him remained in Fetting's organization, which later gave birth to other sects. None of these organizations is considered legitimate by the main Temple Lot church.
Church burnings
In July 1898, W. D. C. Pattison, a suspended member of the LDS Church from Boston, Massachusetts,[5] was arrested and briefly detained after attempting to remove a fence placed around the Temple Lot.[6] Late in the following month, he reportedly demanded that church officials sign ownership of the property over to him because he believed he was the "One Mighty and Strong".[7] He was detained by police but released a few days later. Early on September 5, 1898, he set fire to the tiny headquarters building, and then walked to the police station and turned himself in.[8] After he testified in court appearances in November 1898 Pattison was found guilty but insane and sentenced to a stay in a mental institution.[5] The building was reconstructed in 1905.
On January 1, 1990, a member of the Church of Christ (Temple Lot) who had recently joined the LDS Church set fire to the unoccupied church building on the Temple Lot,[9][10][11] claiming that his actions were part of a political protest and a prophecy that war was coming to America.[11] The fire caused significant damage to the second storey of the building, although the first floor containing church records and documents remained intact. On February 1, 1990, the remainder of the building was razed. Construction of a new headquarters building began in August 1990. The man was convicted by a jury of second-degree arson and breaking and entering on January 16, 1991.[12]
On Friday April 2, 1999, yet another LDS youth attacked the Temple Lot church, reportedly waving a "tree branch" and an "air pistol"[1] in a protest action he said was patterned after Jesus's Temple Site protest described in the New Testament. The man, from Australia, who also states in his websites that he is a descendant of the criminal and "folk hero" Ned Kelly, was then deported from the United States to Honduras at Temple Lot officials' urging, and was there accused and acquitted of rape charges. [2]
Doctrines
Church leadership
Although the Temple Lot church accepts the veracity of Joseph Smith as a prophet of God, they do not necessarily accept everything that Smith taught or claimed as revelation. One distinct difference between them and other Latter Day Saint churches lies in their rejection of the office of President of the Church. Instead of a president-prophet, the Church of Christ is led by its Quorum of Twelve Apostles, with all members of that body being considered equal in precedence and authority. Members of the Temple Lot church believe that Smith was wrong to assume the office of church president, an office they deem to not have been provided for in either the Bible or the Book of Mormon, their two scriptural standards. Although Granville Hedrick was ordained to be president of his church in 1863, he later repudiated this ordination, even referring to Smith as a "fallen prophet".[13]
Like the LDS church (but unlike the Community of Christ), the Temple Lot church limits its priesthood offices to men only.
Scriptures
The Church of Christ (Temple Lot) rejects the Doctrine and Covenants and the Pearl of Great Price, as well as Joseph Smith's Inspired Version of the Bible, preferring to use only the King James Bible and the Book of Mormon as doctrinal standards. The Book of Commandments is accepted as being superior to the Doctrine and Covenants as a compendium of Joseph Smith's early revelations (due to changes effected in many Doctrine and Covenants sections that had earlier been printed in the Book of Commandments), but is not accorded the same status as the Bible or Book of Mormon.[14] The Church of Christ publishes its own edition of the Book of Mormon, identical in chaptering and versification to versions printed by the Community of Christ. The Word of the Lord, used by the Fettingite and Elijah Message organizations (who broke off from the Temple Lot church), is rejected; however, the Temple Lot church maintains an openeness to the idea that revelation might conceivably come to any member of the church at any time, whether male or female, holder of the priesthood or not.
Other distinctives
Baptism for the Dead, eternal marriage, polygamy and the eternal progression doctrine are all rejected. The offices of High Priest and Patriarch are rejected, as well, as being "doctrinal innovations" not sanctioned in the Bible, Book of Mormon or Book of Commandments.
Temples
Temple Lot church members still believe that a temple will be reared on the Temple Lot, but it will not be like any of the LDS or Community of Christ temples currently in use. Rather, it has been generally described by the Temple Lot organization as a place for Jesus to show himself and "endow his servants whom he chooses with power to preach the gospel in all the world to every kindred, tongue, and people, that the promise of God to Israel may be fulfilled".[15] They do not accept the legitimacy of the Community of Christ's Independence Temple located across the street from the Temple Lot, nor of any temples constructed by the LDS church.
David Whitmer
Doctrines of the Church of Christ (Temple Lot) are heavily influenced by the writings of David Whitmer, a leading figure of early Mormonism who was expelled from Joseph Smith's church in 1838. In 1887, Whitmer published a pamphlet deeply critical of Sidney Rigdon and Smith. This pamphlet, entitled An Address to all Believers in Christ, is widely read and promoted among membership of the Church of Christ (Temple Lot) today, and is on sale in the lobby of its headquarters building. In it, Whitmer repeatedly claims that Smith had "fallen"—or began to "fall"—from his Divine calling almost as soon as the church was established in 1830, or perhaps even before then. Whitmer's reasoning includes his charge that Smith was to have "pretended to no other gift" except the translation of the Book of Mormon, and was never to be more than a "first elder" among "fellow elders" in the fledgling church.[16]
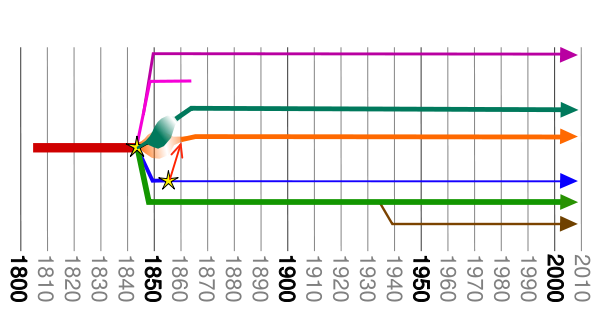
Provenance of the Temple Lot church
References
- ^ GRANVILLE HEDRICK AND THE CROW CREEK BRANCH - centerplace.org - Retrieved January 20, 2008
- ^ a b c adherents.com - Retrieved January 20, 2008
- ^ a b "History of the Church of Christ", churchofchrist-tl.org, accessed 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Grampa Bill's G.A. Pages: John E. Page", gapages.com, accessed 2008-11-21.
- ^ a b "Fanatic Burns a Mormon Church", New York Times. 1898-12-01, p. 5.
- ^ The Kansas City Star, 1998-09-05, p. A-3.
- ^ Court testimony by defendant W. D. C. Pattison in November and December 1898
- ^ The Kansas City Star, 1998-09-05,, p. A-3.
- ^ Blakeman, Karen and Beverly Potter (1990-01-02). "Ex-church member dances as vintage sanctuary burns". Kansas City Times. p. A-1, A-7.
- ^ "Missouri Man Charged in Arson and Burglary of Historic Building", Deseret News, 1990-01-04, p. B5.
- ^ a b James Walker, "Former Member Burns 'Temple Lot' Church After Joining Mormons", Watchman Expositor, vol. 7, no. 2 (1990).
- ^ "Missouri Man Convicted in Temple Lot Fire", Deseret News, 1991-01-19, p. A7.
- ^ History of the Church of Christ. From the official church website. Retrieved on 2009-08-05.
- ^ A Synopsis of the Church of Christ Beliefs and Practices as Compared to Other Latter Day Saint Churches, by Apostle William Sheldon. Refers to the Bible and Book of Mormon as "the only safe standards".
- ^ Articles of Faith and Practice of the Church of Christ, Article 23. From the official church website. Retrieved on 2009-08-05.
- ^ An Address to All Believers in Christ, by David Whitmer. Retrieved on 2009-08-05.
External links
- Church of Christ. Official church website.
- A Synopsis of the Church of Christ Beliefs and Practices as Compared to Other Latter Day Saint Churches. Comparison of beliefs between the Temple Lot, Community of Christ and LDS churches, written by an apostle in the Temple Lot organization.

