H-bridge
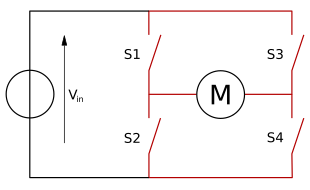
An H bridge is an electronic circuit that enables a voltage to be applied across a load in either direction. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards and backwards. H bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components.[1]
General
The term H bridge is derived from the typical graphical representation of such a circuit. An H bridge is built with four switches (solid-state or mechanical). When the switches S1 and S4 (according to the first figure) are closed (and S2 and S3 are open) a positive voltage will be applied across the motor. By opening S1 and S4 switches and closing S2 and S3 switches, this voltage is reversed, allowing reverse operation of the motor.
Using the nomenclature above, the switches S1 and S2 should never be closed at the same time, as this would cause a short circuit on the input voltage source. The same applies to the switches S3 and S4. This condition is known as shoot-through.
Operation

The H-bridge arrangement is generally used to reverse the polarity of the motor, but can also be used to 'brake' the motor, where the motor comes to a sudden stop, as the motor's terminals are shorted, or to let the motor 'free run' to a stop, as the motor is effectively disconnected from the circuit. The following table summarises operation, with S1-S4 corresponding to the diagram above.
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Motor moves right |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Motor moves left |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Motor free runs |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Motor brakes |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Motor brakes |
Construction

A solid-state H bridge is typically constructed using opposite polarity devices, such as PNP BJTs or P-channel MOSFETs connected to the high voltage bus and NPN BJTs or N-channel MOSFETs connected to the low voltage bus.
The most efficient MOSFET designs use N-channel MOSFETs on both the high side and low side because they typically have a third of the ON resistance of P-channel MOSFETs. This requires a more complex design since the gates of the high side MOSFETs must be driven positive with respect to the DC supply rail. However, many integrated circuit MOSFET drivers include a charge pump within the device to achieve this.
Alternatively, a switch-mode DC–DC converter can be used to provide isolated ('floating') supplies to the gate drive circuitry. A multiple-output flyback converter is well-suited to this application.
Another method for driving MOSFET-bridges is the use of a specialised transformer known as a GDT (Gate Drive Transformer), which gives the isolated outputs for driving the upper FETs gates. The transformer core is usually a ferrite toroid, with 1:1 or 4:9 winding ratio. However, this method can only be used with high frequency signals. The design of the transformer is also very important, as the leakage inductance should be minimized, or cross conduction may occur. The outputs of the transformer also need to be usually clamped by Zener diodes, because high voltage spikes could destroy the MOSFET gates.
A common variation of this circuit uses just the two transistors on one side of the load, similar to a class AB amplifier. Such a configuration is called a "half bridge". The half bridge is used in some switched-mode power supplies that use synchronous rectifiers and in switching amplifiers. The half-H bridge type is commonly abbreviated to "Half-H" to distinguish it from full ("Full-H") H bridges. Another common variation, adding a third 'leg' to the bridge, creates a three-phase inverter. The three-phase inverter is the core of any AC motor drive.
A further variation is the half-controlled bridge, where one of the high- and low-side switching devices (on opposite sides of the bridge) are replaced with diodes. This eliminates the shoot-through failure mode, and is commonly used to drive variable/switched reluctance machines and actuators where bi-directional current flow is not required.
A "double pole double throw" relay can generally achieve the same electrical functionality as an H bridge (considering the usual function of the device). An H bridge would be preferable to the relay where a smaller physical size, high speed switching, or low driving voltage is needed, or where the wearing out of mechanical parts is undesirable.
There are many commercially available inexpensive single and dual H-bridge packages, and L293x series are the most common ones. Few packages have built-in flyback diodes for back EMF protection.
Operation as an inverter
A common use of the H bridge is an inverter. The arrangement is sometimes known as a single- or three-phase bridge inverter.
The H bridge with a DC supply will generate a square wave voltage waveform across the load. For a purely inductive load, the current waveform would be a triangle wave, with its peak depending on the inductance, switching frequency, and input voltage.
See also
- Motor controller
- Switching amplifier
- Push–pull converter
- Bridge circuit
- Commutator (electric)
- Active rectification
References
- ^ Al Williams (2002). Microcontroller projects using the Basic Stamp (2nd ed.). Focal Press. p. 344. ISBN 9781578201013.
External links
- H-Bridge Theory and Practice
- Brief H-Bridge Theory of Operation
- H-bridge tutorial discussing various driving modes and using back-EMF
- PWM DC Motor Controller Using MOSFETs and IR2110 H-Bridge Driver
- H-Bridges on the BEAM Robotics Wiki
Projects
- Tutorial: Build a 5A H-Bridge motor controller
- Building an H-bridge-controlled motor with photocells to track light
- H-bridge motor control with 4017 (in Turkish)
- Using the HIP4081A for H-bridge control
- Using the L293D H bridge for DC motor control control
- A simple circuit designed around L293D motor driver IC
