Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration
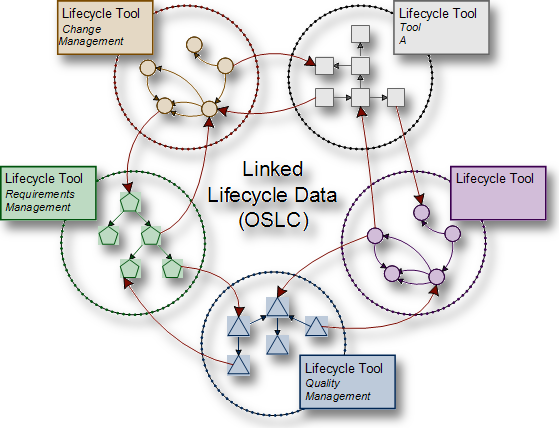
Open Service for Lifecycle Collaboration (OSLC) is an open community, originally proposed in 2008,[1] to define a set of specifications that enable integration of software development and more broadly Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) and Product lifecycle Management (PLM) products and services. The intention is to make life easier for software and product developers and tools vendors, by making it easier for tools to work together.[2]
Organization
The OSLC initiative is divided up into a dozen workgroups and each workgroup develops specifications in context of a specific part of the lifecycle.[3] For example, there are workgroups for Change Management, Quality Management, Requirements Management, Software Configuration Management and Build Automation. There is also a Core workgroup, which defines a common specification that is extended by each lifecycle workgroup.
As of June 2013, the OSLC initiative is a Member Section of the Open Standard Organization OASIS (see: http://www.oasis-oslc.org)
Open specifications
OSLC is not associated with a standards body or open source organization, but OSLC is open in the sense that anybody can participate as long as they sign a patent non-assert covenant, the specifications are under Creative Commons licensing and can be freely implemented by anybody.[4] The OSLC initiative also includes an open source project that is building an OSLC reference implementation and test suites licensed under the Apache Software License.[5]
Status
The effort was formalized in 2009 with the formation of the Change Management workgroup [6] and participation of individuals from Accenture, Eclipse Mylyn/Tasktop,[7] and IBM. Since then, new workgroups have formed around other lifecycle topics and individuals representing about 30 different organizations, including Oracle, Siemens, Northrop Grumman, Tieto, and General Motors. IBM's Cloud and Smarter Infrastructure brand is also starting to use OSLC as an integration technology.[8]
Technologies
The OSLC specifications build on the W3C Resource Description Framework (RDF), Linked Data and REST, enabling integration at data level via links between related resources. OSLC resources are defined in terms of RDF properties. Operations on resources are performed using HTTP. OSLC also specifies user interface techniques to enable preview, creation and selection of links.[9]
See also
External links
- http://open-services.net - The OSLC homepage
- Eclipse Lyo proposal - Proposed Eclipse project to develop an OSLC SDK
- OSLC Primer - explains concepts of OSLC
- OSLC Tutorial - explains how to consume and provide OSLC services with lots of example code
- https://jazz.net/open-services/ - Jazz.net page on OSLC
References
- ^ "IBM hails ALM standards participation". Networkworld.com. 2009-08-25. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ "Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration". Open-services.net. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ "WebHome < Main < TWiki". Open-services.net. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ Speicher, Steve (2011-02-23). "Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration and More: The "O" in OSLC". Stevespeicher.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "IBM supports Open CM initiative in tools - SD Times: Software Development News". SD Times. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ "OSLC Lifecycle Interoperability Makes Headway | Dr Dobb's". Drdobbs.com. 2009-08-26. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ "IBM Pulse 2011 – The Tivoli with two minds – Trip Report – Coté's People Over Process". Redmonk.com. 2011-03-07. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
- ^ "OslcCoreSpecification < Main < TWiki". Open-services.net. Retrieved 2013-07-18.
