G-quadruplex
In molecular biology, G-quadruplexes (also known as G-tetrads or G4-DNA) are nucleic acid sequences that are rich in guanine and are capable of forming a four-stranded structure. Four guanine bases can associate through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding to form a square planar structure called a guanine tetrad, and two or more guanine tetrads can stack on top of each other to form a G-quadruplex. The quadruplex structure is further stabilized by the presence of a cation, especially potassium, which sits in a central channel between each pair of tetrads.[1] They can be formed of DNA, RNA, LNA, and PNA, and may be intramolecular, bimolecular, or tetramolecular. Depending on the direction of the strands or parts of a strand that form the tetrads, structures may be described as parallel or antiparallel.
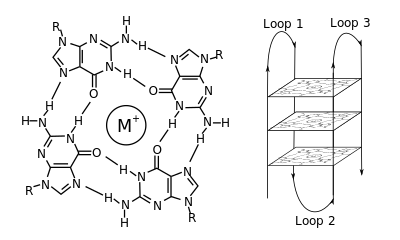

Quadruplex topology
The length of the nucleic acid sequences involved in tetrad formation determines how the quadruplex folds. Short sequences, consisting of only a single contiguous run of three or more guanine bases, require four individual strands to form a quadruplex. Such a quadruplex is described as tetramolecular, reflecting the requirement of four separate strands. Longer sequences, which contain two contiguous runs of three or more guanine bases, where the guanine regions are separated by one or more bases, only require two such sequences to provide enough guanine bases to form a quadruplex. These structures, formed from two separate G-rich strands, are termed bimolecular quadruplexes. Finally, sequences which contain four distinct runs of guanine bases can form stable quadruplex structures by themselves, and a quadruplex formed entirely from a single strand is called an intramolecular quadruplex.[2]
Depending on how the individual runs of guanine bases are arranged in a bimolecular or intramolecular quadruplex, a quadruplex can adopt one of a number of topologies with varying loop configurations.[3] If the 5' - 3’ direction of all the strands is the same, the quadruplex is termed parallel; that is, all the strands of DNA are proceeding in the same direction. For intramolecular quadruplexes, this means that any loop regions present must be of the edge, or propellor, type, which are positioned to the sides of the quadruplex. If one or more of the runs of guanine bases has a 5’-3’ direction opposite to the other runs of guanine bases, the quadruplex is said to have adopted an antiparallel topology. The loops joining runs of guanine bases in intramolecular antiparallel quadruplexes are either diagonal (joining two diagonally opposite runs of guanine bases) or edge type loops, which join two adjacent runs of guanines.
Telomeric quadruplexes
Telomeric repeats in a variety of organisms have been shown to form these structures in vitro, and they have also been shown to form in vivo in some cases.[4] The human telomeric repeat (which is the same for all vertebrates) consists of many repeats of the sequence d(GGTTAG), and the quadruplexes formed by this structure have been well studied by NMR and X-ray crystal structure determination. The formation of these quadruplexes in telomeres has been shown to decrease the activity of the enzyme telomerase, which is responsible for maintaining length of telomeres and is involved in around 85% of all cancers. This is an active target of drug discovery.
Non-telomeric quadruplexes
Recently, there has been increasing interest in quadruplexes in locations other than at the telomere. For example the proto-oncogene c-myc was shown to form a quadruplex in a nuclease hypersensitive region critical for gene activity.[5][6] Since then, many other genes have been shown to have G-quadruplexes in their promoter regions, including the chicken β-globin gene, human ubiquitin-ligase RFP2 and the proto-oncogenes c-kit, bcl-2, VEGF, H-ras and N-ras. This list is ever-increasing.
Genome-wide surveys based on a quadruplex folding rule have been performed, which have identified 376,000 Putative Quadruplex Sequences (PQS) in the human genome, although not all of these probably form in vivo.[7] A similar study has identified putative G-quadruplexes in prokaryotes.[8] There are several possible models for how quadruplexes could influence gene activity, either by upregulation or downregulation. One model is shown below, with G-quadruplex formation in or near a promoter blocking transcription of the gene, and hence de-activating it. In another model, quadruplex formed at the non-coding DNA strand helps to maintain an open conformation of the coding DNA strand and enhance an expression of the respective gene.

Quadruplex function
Nucleic acid quadruplexes have been described as "structures in search of a function",[10] as for many years there was minimal evidence pointing towards a biological role for these structures. It has been suggested that quadruplex formation plays a role in immunoglobulin heavy chain switching.[11] As cells have evolved mechanisms for resolving (i.e., unwinding) quadruplexes that form, quadruplex formation may be potentially damaging for a cell; for example, the helicases WRN and Bloom syndrome protein have a high affinity for resolving G4 DNA.[12] More recently, there are many studies that implicate quadruplexes in both positive and negative transcriptional regulation, and in allowing programmed recombination of immunologlobin heavy genes and the pilin antigenic variation system of the pathogenic Neisseria. [13] The roles of quadraduplex structure in translation control are not as well explored. The direct visualization of quadraduplex structures in human cells [14] has provided an important confirmation of their existence. The potential positive and negative roles of quadraduplexes in telomere replication and function remains controversial.
Ligands which bind quadruplexes
One way of inducing or stabilizing G-quadruplex formation, is to introduce a molecule which can bind to the G-quadruplex structure, and a number of ligands, both small molecules and proteins, have been developed which can do so. This has become an increasingly large field of research.
A number of naturally occurring proteins have been identified which selectively bind to G-quadruplexes. These include the helicases implicated in Bloom's and Werner's syndromes and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein RAP1. An artificially derived three zinc finger protein called Gq1, which is specific for G-quadruplexes has also been developed, as have specific antibodies.
Cationic porphyrins have been shown to bind intercalatively with G-quadruplexes, as well as the molecule telomestatin.
Quadruplex prediction techniques
Identifying and predicting sequences which have the capacity to form quadruplexes is an important tool in further understanding of their role. Generally, a simple pattern match is used for searching for possible quadruplex forming sequences: d(G3+N1-7G3+N1-7G3+N1-7G3+), where N is any base (including guanine).[15] This rule has been widely used in on-line algorithms.
Quadruplex Based Label Free Biosensor
G-Quadruplex can interact with a serials of small molecule, leading to the enhanced enzymatic activities and fluorescent intensity, e.g. its discovery in the crystal structure of fluorophore-binding RNA aptamer Spinach[16][17]. Based on the specific structures of G-quadruplex, a team led by jiahai has designed several biosensing platforms to analyze metal ion, virus target gene, fungi toxin and we also built a label-free signal amplification system, which has been applied by other research groups to detect the target of interest. Furthermore, they have systematically accounted for the underlying mechanism of split G-quadruplex probes by utilization of the fluorescence method developed in our lab. A review regarding the application of G-quadruplex as signal transducer was written.
Based on the specific interaction between aptamer and chiral peptide, They have designed three kinds of sensing platforms for chiral peptide detection. One is based on competitive binding of chiral peptide and dye indicator toward aptamer. Chiral peptide can displace the dye indicator away from the aptamer, leading to the decrease in the fluorescence of dye indicator. The second method is based on gold nanoparticle aggregation, which can directly tell us whether the chiral peptide is present or not. The third method is based on the electrochemical method, having the highest selectivity.
More information can be found on webpage http://nanopore.weebly.com .
Notes
- ^ Campbell, Nancy H.; Neidle, Stephen (2012). "Chapter 4. G-Quadruplexes and Metal Ions". In Astrid Sigel, Helmut Sigel and Roland K. O. Sigel (ed.). Interplay between Metal Ions and Nucleic Acids. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 10. Springer. pp. 119–1134. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2172-2_4.
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Bugaut A, Balasubramanian S (2012). "5'-UTR RNA G-quadruplexes: translation regulation and targeting". Nucleic Acids Res. 40 (11): 4727–41. doi:10.1093/nar/gks068. PMC 3367173. PMID 22351747.
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
References
- Jiangtao Ren, Jiahai Wang* , Lei Han, Erkang Wang*, Jin Wang* (2011). "Kinetically grafting G-qaudruplex onto DNA nanostructure as structure and function encoding via DNA machine". Chem. Commun. 47: 10563–10565.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Johnson JE, Smith JS, Kozak ML, Johnson FB (2008). "In vivo veritas: using yeast to probe the biological functions of G-quadruplexes". Biochimie. 90 (8): 1250–1263. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2008.02.013. PMC 2585026. PMID 18331848.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Huppert JL and Balasubramanian S (2005). "Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome". NAR. 33 (9): 2908–2916. doi:10.1093/nar/gki609. PMC 1140081. PMID 15914667.
- Todd AK, Johnston M, Neidle S (2005). "Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA". NAR. 33 (9): 2901–2907. doi:10.1093/nar/gki553. PMC 1140077. PMID 15914666.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Burge S, Parkinson GN, Hazel P, Todd AK, Neidle S (2006). "Quadruplex DNA: sequence, topology and structure". NAR. 34 (19): 5402–5415. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl655. PMC 1636468. PMID 17012276.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Siddiqui-Jain A, Grand CL, Bearss DJ, Hurley LH (2002). "Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription". PNAS. 99 (18): 11593–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.182256799. PMC 129314. PMID 12195017.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Rawal P, Kummarasetti VB, Ravindran J, Kumar N, Halder K, Sharma R, Mukerji M, Das SK, Chowdhury S (2006). "Genome-wide prediction of G4 DNA as regulatory motifs: Role in Escherichia coli global regulation". Genome Res. 16 (5): 644–55. doi:10.1101/gr.4508806. PMC 1457047. PMID 16651665.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Xu Hou, Wei Guo, Fan Xia, Fu-Qiang Nie, Hua Dong, Ye Tian, Liping Wen, Lin Wang, Liuxuan Cao, Yang Yang, Jianming Xue, Yanlin Song, Yugang Wang, Dongsheng Liu, and Lei Jiang (2009). "A biomimetic potassium responsive nanochannel: G-quadruplex DNA conformational switching in a synthetic nanopore". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (22): 7800–7805. doi:10.1021/ja901574c. PMID 19435350.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Neidle & Balasubramanian, ed. (2006). Quadruplex Nucleic Acids. ISBN 0-85404-374-8.
External links
Quadruplex websites
- COST MP0802 Quadruplex Network - the European network of G-quadruplex community: From first principles to applications
- Quadruplex.org - a website to serve the quadruplex community
- G-Quadruplex World - a website to discuss publications and other information of interest to those working in the field of G-quadruplexes
- Quadbase - downloadable data on predicted G-quadruplexes
- Greglist - a database listing potential G-quadruplex regulated genes
- Database on Quadruplex information: QuadBase from IGIB
- GRSDB- a database of G-quadruplexes near RNA processing sites.
- GRS_UTRdb- a database of G-quadruplexes in the UTRs.
- G-quadruplex Resource Site
- non-B Motif Search Tool at non-B DB- a web server to predict G-quadruplex forming motifs and other non-B DNA forming motifs from users' DNA sequences.
Tools to predict G-quadruplex motifs
- Quadparser: Downloadable program for finding putative quadruplex-forming sequences from Balasubramanian's group.
- QGRS Mapper: a web-based application for predicting G-quadruplexes in nucleotide sequences and NCBI genes from Bagga's group.
- Quadfinder: Tool for Prediction and Analysis of G Quadruplex Motifs in DNA/RNA Sequences from Maiti's group, IGIB, Delhi, India
