Vozrozhdeniya Island: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Doghouse09 (talk | contribs) m →Geography: grammatical changes |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
An ideal location for such complex would be a relatively large island {{Convert|5|-|10|km|abbr=on|0}} from a coast. Initial sites discussed for this complex included [[Lake Baikal]], but choices were narrowed down to the [[Solovetsky Islands]] in the White Sea, [[Gorodomlya Island]] located on [[Lake Seliger]] and Vozrozhdeniya Island.<ref name=":0" /> The [[Russian Civil War]] and several unsuccessful attempts to build the complex from 1936 to 1941 led to a belief that such a complex must be built far from the Soviet Union's borders with other nations.<ref name=":0" /> Vozrozhdeniya Island's location in the middle of the Aral Sea, well within Soviet borders, satisfied this consideration. |
An ideal location for such complex would be a relatively large island {{Convert|5|-|10|km|abbr=on|0}} from a coast. Initial sites discussed for this complex included [[Lake Baikal]], but choices were narrowed down to the [[Solovetsky Islands]] in the White Sea, [[Gorodomlya Island]] located on [[Lake Seliger]] and Vozrozhdeniya Island.<ref name=":0" /> The [[Russian Civil War]] and several unsuccessful attempts to build the complex from 1936 to 1941 led to a belief that such a complex must be built far from the Soviet Union's borders with other nations.<ref name=":0" /> Vozrozhdeniya Island's location in the middle of the Aral Sea, well within Soviet borders, satisfied this consideration. |
||
In the summer of 1936, Ivan Mikhailovich Velikanov led the Red Army's first expedition to conduct |
In the summer of 1936, Ivan Mikhailovich Velikanov led the Red Army's first expedition to conduct biological weapons tests on Vozrozhdeniya Island. Around 100 personnel from Velikanov's Biotechnical Institute participated in the experiments. In July 1937, while planning for a second expedition to the island, Velikanov was arrested by the Soviet security organs and subsequently shot. Later that same summer, Leonid Moiseevich Khatanever, the new director of the Biotechnical Institute and an expert on ''Francisella tularensis'' (the causative agent of tularaemia), led a second expedition to Vozrozhdeniya. Two special ships and two aircraft were assigned to Khatanever for use in tests focused on the dissemination of tularaemia bacteria.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Rimmington|first=Anthony|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zfhyDwAAQBAJ&q=rimmington+stalin|title=Stalin's Secret Weapon: The Origins of Soviet Biological Warfare|date=2018-11-15|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-092885-8|language=en}}</ref> In 1948, a top-secret Soviet [[bioweapon]]s laboratory was established on the island, which tested a variety of agents, including [[anthrax]], [[smallpox]], [[Plague (disease)|plague]], [[brucellosis]], and [[tularemia]].<ref>{{cite book|author=Tom Mangold|author-link=Tom Mangold|author2=Jeff Goldberg |title=Plague Wars: The Terrifying Reality of Biological Warfare|publisher=Macmillan|year=2001|pages=46–47|isbn=9780312263799|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9_9Q7cZh91YC&pg=PA46}}</ref> In 1954, the site was expanded and named Aralsk-7, one of the main laboratories and testing sites for the [[Soviet Union]]'s Microbiological Warfare Group, tasked with inventing and testing the effects of multiple fatal diseases.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
In 1971, an accidental [[Aral smallpox incident|release of]] [[Smallpox|variola virus]] (the causative agent of smallpox) from the island infected ten people, of whom three died.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2002-06-04|title=OP#09: The 1971 Smallpox Epidemic in Aralsk, Kazakhstan, and the Soviet Biological Warfare Program|url=https://nonproliferation.org/the-1971-smallpox-epidemic-in-aralsk-kazakhstan-and-the-soviet-biological-warfare-program-commentaries/|access-date=2021-05-18|website=James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies|language=en-US}}</ref> In the 1990s, word of the island's danger was spread by Soviet defectors, including [[Ken Alibek]], the former head of the Soviet Union's bioweapons program.<ref>{{cite book|last=Hoffman|first=David|title=The Dead Hand: The Untold Story of the Cold War Arms Race and Its Dangerous Legacy|publisher=Random House|year=2009|pages=460|isbn=9780385524377|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JQGHqScEFtoC&pg=PA460}}</ref> According to released documents, [[anthrax]] [[spore]]s and [[bubonic plague]] [[bacillus|bacilli]] were made into weapons and stored at the complex. The main town on the island, where scientists and employees of the complex lived, was called [[Kantubek]], which lies in ruins today, but once held approximately 1,500 inhabitants. The official Soviet name of this city was the same as the weapons complex itself: Aralsk-7.<ref name=":0" /> It contained simple infrastructure that consisted of a social club, a stadium, a couple of schools and shops.<ref name=":0" /> A unique airfield, "Barkhan", was |
In 1971, an accidental [[Aral smallpox incident|release of]] [[Smallpox|variola virus]] (the causative agent of smallpox) from the island infected ten people, of whom three died.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2002-06-04|title=OP#09: The 1971 Smallpox Epidemic in Aralsk, Kazakhstan, and the Soviet Biological Warfare Program|url=https://nonproliferation.org/the-1971-smallpox-epidemic-in-aralsk-kazakhstan-and-the-soviet-biological-warfare-program-commentaries/|access-date=2021-05-18|website=James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies|language=en-US}}</ref> In the 1990s, word of the island's danger was spread by Soviet defectors, including [[Ken Alibek]], the former head of the Soviet Union's bioweapons program.<ref>{{cite book|last=Hoffman|first=David|title=The Dead Hand: The Untold Story of the Cold War Arms Race and Its Dangerous Legacy|publisher=Random House|year=2009|pages=460|isbn=9780385524377|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JQGHqScEFtoC&pg=PA460}}</ref> According to released documents, [[anthrax]] [[spore]]s and [[bubonic plague]] [[bacillus|bacilli]] were made into weapons and stored at the complex. The main town on the island, where scientists and employees of the complex lived, was called [[Kantubek]], which lies in ruins today, but once held approximately 1,500 inhabitants. The official Soviet name of this city was the same as the weapons complex itself: Aralsk-7.<ref name=":0" /> It contained simple infrastructure that consisted of a social club, a stadium, a couple of schools and shops.<ref name=":0" /> A unique airfield, "Barkhan", was located close to Kantubek. It was the only airfield in the Soviet Union with four runways in an intersecting [[Starburst (symbol)|starburst]] pattern. The weather on the island changed frequently; thus, planes landed on one of the four runways depending on weather and wind direction at the time.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
Faced with the imminent dissolution of the USSR, the Soviet military authorities held a meeting in November 1991 at the USSR Ministry of Defence's Virology Centre in Zagorsk to discuss the fate of Aralsk-7. Here the decision was taken to terminate experimental work on the island and by late April 1992 all military units had been evacuated from the base.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Rimmington|first=Anthony|title="Conversion of BW Facilities in Kazakstan" in Geissler, E. (Ed.), Conversion of Former BTW Facilities|publisher=Kluwer Academic Publishers|year=1998|isbn=0-7923-5249-1|location=Dordrecht, The Netherlands|pages=167–186}}</ref> All people who lived on Vozrozhdeniya Island were evacuated within several weeks; civil and military infrastructure |
Faced with the imminent dissolution of the USSR, the Soviet military authorities held a meeting in November 1991 at the USSR Ministry of Defence's Virology Centre in Zagorsk to discuss the fate of Aralsk-7. Here the decision was taken to terminate experimental work on the island, and by late April 1992, all military units had been evacuated from the base.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Rimmington|first=Anthony|title="Conversion of BW Facilities in Kazakstan" in Geissler, E. (Ed.), Conversion of Former BTW Facilities|publisher=Kluwer Academic Publishers|year=1998|isbn=0-7923-5249-1|location=Dordrecht, The Netherlands|pages=167–186}}</ref> All people who lived on Vozrozhdeniya Island were evacuated within several weeks; civil and military infrastructure was abandoned, and Kantubek became a [[ghost town]].<ref name=":0" /> Many of the containers holding biological agents were not properly stored or destroyed, and over the last decade, many of these containers have developed leaks. |
||
In 2002, through a project organized and funded by the United States with the assistance of Uzbekistan, ten [[anthrax]] burial sites were decontaminated.<ref>{{cite news| url=https://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/fortune_archive/2002/09/16/328574/index.htm | work=CNN | first=Bill | last=Powell | title=Are We Safe Yet? For all the warnings, there hasn't been another attack. But the hard work of enhancing homeland security has only just begun. Here's what we need to do | date=16 September 2002}}</ref> |
In 2002, through a project organized and funded by the United States with the assistance of Uzbekistan, ten [[anthrax]] burial sites were decontaminated.<ref>{{cite news| url=https://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/fortune_archive/2002/09/16/328574/index.htm | work=CNN | first=Bill | last=Powell | title=Are We Safe Yet? For all the warnings, there hasn't been another attack. But the hard work of enhancing homeland security has only just begun. Here's what we need to do | date=16 September 2002}}</ref> |
||
==In popular culture== |
==In popular culture== |
||
The former island and its laboratory have |
The former island and its laboratory have appeared in novels and video games. In ''[[Command & Conquer: Generals]]'', the island was under U.S. occupation but was captured by the fictional Global Liberation Army. The area and its former biological weapons base and laboratories were also featured in a mission in ''[[Call of Duty: Black Ops]]'' called "Rebirth", where Alex Mason goes lone wolf against Friedrich Steiner while Jason Hudson leads a team to extract Steiner out of the area. ''[[Call of Duty: Warzone]]'' mixes the island's chemical weapon history with a recreation of the [[Alcatraz]] prison for its Rebirth Resurgence mode. The novel ''The Home Team: Weapons Grade'' also mentions the site; the book's villains dig up two metric tons of "Anthrax 836" from an impromptu dump site 11 km from the island for use in a terror plot.<ref name="Chalker/Dockery">{{cite book | title=The Home Team: Weapons Grade | publisher=Avon Books |author1=Chalker, Dennis |author2=Dockery, Kevin |name-list-style=amp | year=2006 | location=New York City | pages=373 | isbn=9780061746901}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 05:01, 25 June 2023
 Satellite image of former Vozrozhdeniya Island, November 1994 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Central Asia |
| Coordinates | 45°09′N 59°19′E / 45.150°N 59.317°E |
| Administration | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1,500 (1980s) |
Rebirth Island (Russian: Остров Возрождения, IPA: [vəzrɐˈʐdʲenʲɪjə] , lit. 'Rebirth Island'; Kazakh: Возрождение аралы, Vozrojdenie araly; Uzbek: Возрождение ороли, Vozrojdeniye oroli) was an island in the Aral Sea. The former island's territory is split between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. In 1954, the Soviet Union constructed a biological weapons test site called Aralsk-7 there and on the neighbouring Komsomolskiy Island, which also no longer exists.[1]
Geography
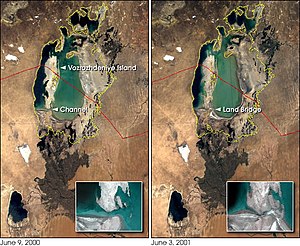
Vozrozhdeniya was once a small island; it was only 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) in the nineteenth century.[2] However, in the 1960s, the island began to grow in size as the Aral Sea began drying up as the Soviet Union dammed its feeder rivers for agricultural projects.[3] The shrinkage of the Aral continued and accelerated over time, and the receding waters briefly made Vozrozhdeniya the second-largest fresh water island in the world, at 2,300 km2 (890 sq mi),[4] in the final days of its existence in mid-2001, becoming a peninsula when the South Aral Sea dried up enough that the island joined the mainland.[5] Upon the disappearance of the Southeast Aral Sea in 2008, Vozrozhdeniya was simply a part of the surrounding land, and by 2014 it was simply a part of the land within the extensive Aralkum Desert.

History
In 1848-1849, a Russian marine expedition of the Aral Sea was organized with the schooner Konstantin, commanded by naval officer and investigator A.I. Butakov. One of the members who served as the expedition's artist was Taras Shevchenko. A group of islands was discovered that were named the Tzar Islands, consisting of Nicholas I Island, Konstantin Island and Naslednik Island. In the Soviet period Nicholas I Island was renamed Vozrozhdeniya.[6][7]
In the 1920s, leaders of the Red Army were searching for an appropriate place to build a science and military complex for inventing, producing, and testing biological weapons.[8]
An ideal location for such complex would be a relatively large island 5–10 km (3–6 mi) from a coast. Initial sites discussed for this complex included Lake Baikal, but choices were narrowed down to the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea, Gorodomlya Island located on Lake Seliger and Vozrozhdeniya Island.[2] The Russian Civil War and several unsuccessful attempts to build the complex from 1936 to 1941 led to a belief that such a complex must be built far from the Soviet Union's borders with other nations.[2] Vozrozhdeniya Island's location in the middle of the Aral Sea, well within Soviet borders, satisfied this consideration.
In the summer of 1936, Ivan Mikhailovich Velikanov led the Red Army's first expedition to conduct biological weapons tests on Vozrozhdeniya Island. Around 100 personnel from Velikanov's Biotechnical Institute participated in the experiments. In July 1937, while planning for a second expedition to the island, Velikanov was arrested by the Soviet security organs and subsequently shot. Later that same summer, Leonid Moiseevich Khatanever, the new director of the Biotechnical Institute and an expert on Francisella tularensis (the causative agent of tularaemia), led a second expedition to Vozrozhdeniya. Two special ships and two aircraft were assigned to Khatanever for use in tests focused on the dissemination of tularaemia bacteria.[9] In 1948, a top-secret Soviet bioweapons laboratory was established on the island, which tested a variety of agents, including anthrax, smallpox, plague, brucellosis, and tularemia.[10] In 1954, the site was expanded and named Aralsk-7, one of the main laboratories and testing sites for the Soviet Union's Microbiological Warfare Group, tasked with inventing and testing the effects of multiple fatal diseases.[2]
In 1971, an accidental release of variola virus (the causative agent of smallpox) from the island infected ten people, of whom three died.[11] In the 1990s, word of the island's danger was spread by Soviet defectors, including Ken Alibek, the former head of the Soviet Union's bioweapons program.[12] According to released documents, anthrax spores and bubonic plague bacilli were made into weapons and stored at the complex. The main town on the island, where scientists and employees of the complex lived, was called Kantubek, which lies in ruins today, but once held approximately 1,500 inhabitants. The official Soviet name of this city was the same as the weapons complex itself: Aralsk-7.[2] It contained simple infrastructure that consisted of a social club, a stadium, a couple of schools and shops.[2] A unique airfield, "Barkhan", was located close to Kantubek. It was the only airfield in the Soviet Union with four runways in an intersecting starburst pattern. The weather on the island changed frequently; thus, planes landed on one of the four runways depending on weather and wind direction at the time.[2]
Faced with the imminent dissolution of the USSR, the Soviet military authorities held a meeting in November 1991 at the USSR Ministry of Defence's Virology Centre in Zagorsk to discuss the fate of Aralsk-7. Here the decision was taken to terminate experimental work on the island, and by late April 1992, all military units had been evacuated from the base.[13] All people who lived on Vozrozhdeniya Island were evacuated within several weeks; civil and military infrastructure was abandoned, and Kantubek became a ghost town.[2] Many of the containers holding biological agents were not properly stored or destroyed, and over the last decade, many of these containers have developed leaks.
In 2002, through a project organized and funded by the United States with the assistance of Uzbekistan, ten anthrax burial sites were decontaminated.[14]
In popular culture
The former island and its laboratory have appeared in novels and video games. In Command & Conquer: Generals, the island was under U.S. occupation but was captured by the fictional Global Liberation Army. The area and its former biological weapons base and laboratories were also featured in a mission in Call of Duty: Black Ops called "Rebirth", where Alex Mason goes lone wolf against Friedrich Steiner while Jason Hudson leads a team to extract Steiner out of the area. Call of Duty: Warzone mixes the island's chemical weapon history with a recreation of the Alcatraz prison for its Rebirth Resurgence mode. The novel The Home Team: Weapons Grade also mentions the site; the book's villains dig up two metric tons of "Anthrax 836" from an impromptu dump site 11 km from the island for use in a terror plot.[15]
See also
- 1971 Aral smallpox incident
- Biopreparat
- Ken Alibek
- Kantubek
- Gruinard Island in Scotland, a British anthrax test site.
References
- ^ Dembek, Zygmunt F., Julie A. Pavlin, and Mark G. Kortepeter (2007), "Epidemiology of Biowarfare and Bioterrorism", Chapter 3 of: Dembek, Zygmunt F. (2007), Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare, (Series: Textbooks of Military Medicine), Washington, DC: The Borden Institute, pp 51-52.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Аральск-7 — закрытый город-призрак, где испытывали биологическое оружие". BIGPICTURE.RU. Retrieved 2015-12-13.
- ^ Michael Wines (9 December 2002). "Grand Soviet Scheme for Sharing Water in Central Asia Is Foundering". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
- ^ "Islands of the World: Largest Lake Islands". World Atlas. Retrieved 2019-06-03.
- ^ NASA Visible Earth - “Rebirth” Island Joins the Mainland Archived 2010-05-28 at the Wayback Machine, Aral Sea Archived 2010-07-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Aral Sea Encyclopedia
- ^ Oren, Aharon; Plotnikov, Igor S.; Sokolov, Sergey; Aladin, Nikolai V. (2010). "The Aral Sea and the Dead Sea: Disparate lakes with similar histories: Aral Sea - Dead Sea comparisons". Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management. 15 (3): 223–236. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1770.2010.00436.x.
- ^ "Аральск-7 — закрытый город-призрак, где испытывали биологическое оружие". Big Picture. 2014-02-20.
- ^ Rimmington, Anthony (2018-11-15). Stalin's Secret Weapon: The Origins of Soviet Biological Warfare. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-092885-8.
- ^ Tom Mangold; Jeff Goldberg (2001). Plague Wars: The Terrifying Reality of Biological Warfare. Macmillan. pp. 46–47. ISBN 9780312263799.
- ^ "OP#09: The 1971 Smallpox Epidemic in Aralsk, Kazakhstan, and the Soviet Biological Warfare Program". James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies. 2002-06-04. Retrieved 2021-05-18.
- ^ Hoffman, David (2009). The Dead Hand: The Untold Story of the Cold War Arms Race and Its Dangerous Legacy. Random House. p. 460. ISBN 9780385524377.
- ^ Rimmington, Anthony (1998). "Conversion of BW Facilities in Kazakstan" in Geissler, E. (Ed.), Conversion of Former BTW Facilities. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers. pp. 167–186. ISBN 0-7923-5249-1.
- ^ Powell, Bill (16 September 2002). "Are We Safe Yet? For all the warnings, there hasn't been another attack. But the hard work of enhancing homeland security has only just begun. Here's what we need to do". CNN.
- ^ Chalker, Dennis & Dockery, Kevin (2006). The Home Team: Weapons Grade. New York City: Avon Books. p. 373. ISBN 9780061746901.
External links
- Abandoned Anthrax: Vozrozhdeniye Island. Sometimes Interesting. 29 Nov 2014
- Youtube: Going To Extremes: Voz-Island (Part 1)
- Youtube: Going To Extremes: Voz-Island (Part 2)
- Welcome to Anthrax Island - Guardian Unlimited
- Rebirth Island joins the mainland (2000 and 2001 satellite images)
- NASA satellite image comparison between 1989 and 2003
- Biological Decontamination of Vozrozhdeniye Island: The U.S.-Uzbek Agreement
- Former Soviet Biological Weapons Facilities in Kazakhstan: Past, Present, and Future
- 1960's Satellite images of Soviet laboratory
- Top Inhospitable Places in the World
