2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (October 2021) |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine
| |
| Other names
Pyrazine, 2,3,5-trimethyl-;2,3,5-Trimethyl pyrazine;2,3,5-Trimethyl pyrazine (natural);2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine;2,3,6-Trimethylpyrazine;5-23-05-00419 (Beilstein Handbook Reference);AI3-34442;BRN 0002423;CCRIS 2932;FEMA No. 3244;Pyrazine, trimethyl-;Trimethylpyrazine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.178 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10N2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.171 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless to slightly yellow liquid |
| Odor | roasted nut, baked potato odour |
| Density | 0.979 g mL−1 |
| Boiling point | 173.1 °C (343.6 °F; 446.2 K) |
| Alcohol, oils, water (1.521e+004 mg/L at 25 °C (est) | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5030 to 1.5050 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H226, H302 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P303+P361+P353, P330, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 54.4 °C (129.9 °F; 327.5 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
806 mg/kg rat |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine (chemical formula C7H10N2) is one of the most broadly used edible synthesis fragrances. It comes from baked food, fried barley, potatoes, and peanuts. 2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine is used for the flavor in cocoa, coffee, chocolate, potato, cereal, and fried nuts.
Physical properties[edit]
The specific gravity depends on the quality and the producer and ranges from 0.967 to 0.987.
Synthesis[edit]
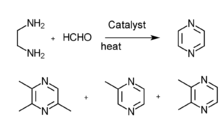
2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine can be synthesized from 2,3-butanedione and 1,2-diaminopropane. First, 1,2-diaminopropane is synthesized by amination of isopropanolamine in the presence of ammonia and a hydrogenation catalyst: Raney Ni. The effect of the amount of Raney Ni catalyst, the molar ratio of materials, reactions are as follows: the molar ratio of isopropanolamine to ammonia is 1:3.5,the reaction temperature is 160 °C, the reaction is 5 hours, the molar ratio of hydrogen to isopropanolamine is 1:5. Then the reaction consists of synthesis of 2,3,5-trimethyl-5,6-dihydropyrazine and 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine. The optimum conditions of 2,3,5-trimethyl-5,6-dihydropropyrazine synthesis are established:2,3-butanedione which is mixed with anhydrous ethyl alcohol (the mass ratio of anhydrous ethyl alcohol to 2,3-butanedione was 5:1) is dropped to the mixture of anhydrous ethyl alcohol and 1,2-diaminopropane (the mass ratio of anhydrous ethyl alcohol to 1,2-diaminopropane was 6:1) at the even pace for four hours, the molar ratio of 2,3-butanedione to 1,2-diaminopropane is 1:1.1, the condensation reaction temperature is -5 °C. The best dehydrogen oxidation conditions are as follows: air is used as oxidant, the molar ration of potassium hydroxide and 2,3,5-Trimethyl-5,6-dihydro-pyrazine is 3:1, the mass ratio of ethanol to 2,3,5-trimethyl-5,6-dihydro-pyrazine 10:1,reaction temperature 68 °C, reaction time seven hours.[1]
There are several other ways to synthesis 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine:
- Piperazine gas phase catalytic dehydrogenation
- N-(β alkane alcohol)ethanediamine gas phase catalysis
- Ethanediamine and methyl aldehyde gas phase catalysis
- Diamine and diol gas phase catalysis
Use limit in food[edit]
FEMA (mg/kg)
Soft drinks 5.0~10
Candy 5.0~10
Baked food 5.0~10
Cereal 2.0
Seasoning 2.0
Meat 2.0
Dairy 1.0
Soup 2.0
References[edit]
- ^ "2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪的合成研究" [Study on the synthesis of 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine].
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
Additional references[edit]
- [1][dead link]
- 2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪 | 14667-55-1
- 2me3me5me-pyrazine - Synthesis
- 14667-55-1, 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine, CAS No 14667-55-1 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine
- 2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪,14667-55-1,生产厂家,价格-lookchem
- 2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪的合成研究
- 2,3,5-trimethyl pyrazine, 14667-55-1
- AIST:Spectral Database for Organic Compounds,SDBS Archived 2010-06-11 at the Wayback Machine