2004 FH
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | LINEAR |
| Discovery date | March 15, 2004 |
| Designations | |
| none | |
| Aten asteroid, Earth-crosser asteroid Venus-crosser asteroid | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Aphelion | 1.0545 AU (157.75 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 0.58154 AU (86.997 Gm) |
| 0.81802 AU (122.374 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.28908 |
| 0.74 yr (270.2 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 32.237 km/s |
| 223.69° | |
| 1.3322°/day | |
| Inclination | 0.021011° |
| 291.332° | |
| 36.254° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00002265 AU (0.0088 LD) (3390 km) |
| Jupiter MOID | 4.21664 AU (630.800 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | ~30 metres (98 ft)[2] |
| Mass | 2.8×107 kg |
| 0.0504 h (3.02 min)[1] | |
| Temperature | ~308 K |
| 25.7 | |

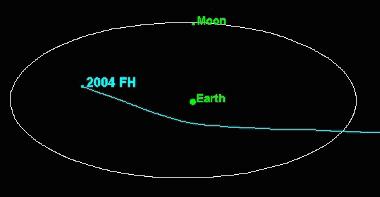
2004 FH is a near-Earth asteroid that was discovered on March 15, 2004, by the NASA-funded LINEAR asteroid survey. The object is roughly 30 metres in diameter and passed just 43,000 km (27,000 mi) above the Earth's surface on March 18, 2004, at 22:08 UTC; making it the 11th closest approach to Earth recorded as of 21 November 2008[update] (see the diagram below). For comparison, geostationary satellites orbit Earth at 35,790 km.
2004 FH is an Aten family asteroid. Despite its relatively small size (about 30 metres), it is still the fourth largest asteroid detected coming closer to the Earth than the Moon.
Had this object hit Earth, it would probably have detonated high in the atmosphere. It might have produced a blast measured in hundreds of kilotons of TNT, but may not have produced any effect on the ground. It could also have been an Earth-grazing fireball if it had been much closer but not close enough to impact.
On March 17, 2044 the asteroid will pass no closer than 0.0116 AU (1,740,000 km; 1,080,000 mi) from the Earth.[1] 2004 FH also has the distinction of having the lowest inclination of any known near-Earth asteroids.
Two weeks later another asteroid approached even closer, 2004 FU162, which was smaller, and a few years later 2009 DD45, which was closer in size passed by at similar distance.
See also
References
- ^ a b c "JPL Close-Approach Data: (2004 FH)" (last observation: 2004-03-19; arc: 3 days; uncertainty: 3). Retrieved 23 March 2016.
- ^ Steven R. Chesley; Paul W. Chodas (March 17, 2004). "Recently Discovered Near-Earth Asteroid Makes Record-breaking Approach to Earth". NASA's Near Earth Object Program Office.
