2 Marsham Street
| Home Office Building | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| General information | |
| Status | Completed |
| Address | 2 Marsham Street, SW1P 4DF |
| Town or city | London |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Construction started | 2003 |
| Opened | 2005 |
| Cost | £311 million |
| Client | Home Office, Department for Communities and Local Government |
| Technical details | |
| Floor count | 7 |
| Floor area | 800,000 sq ft (74,000 m2) |
| Lifts/elevators | 24 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Farrells |
| Structural engineer | Pell Frischmann |
| Main contractor | Bouygues |
| Awards and prizes | RIBA Award for Architecture |
2 Marsham Street is an office building on Marsham Street in the City of Westminster, London, and has been the headquarters of the Home Office, a department of the British Government, since March 2005. Before this date the Home Office was located at 50 Queen Anne's Gate.
History
The site was previously occupied by the Departments of Environment and Transport. The headquarters offices of both departments were located in Marsham Towers - three 20-floor concrete towers (North, Centre and South) joined together by 'podium' floors to level 3. The towers won an architectural award and boasted express lifts, marble entrances and escalators to the 3rd floor - very modern government offices for the early 1970s. Construction had started in the early 1960s but was finally completed in 1971 and became the office of the new Department of Environment created in October 1970 (DOE was created out of a merger between the Ministry for Housing and Local Government and the Ministry of Transport).

The towers were considered by some to be a blot on London’s landscape and were subsequently nicknamed "the three ugly sisters" and "the toast rack".[1] Michael Heseltine, the Secretary of State for the Environment in the late 1970s and early 1980s, allegedly said that the building offered the best view of London – because one could not see the towers from his north-facing 16th floor North tower office. Chris Patten called the complex "a building that deeply depresses the spirit".[1]
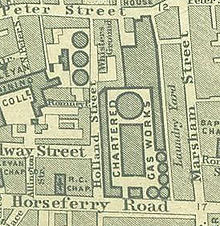
The last government staff occupied the building in the late 1990s. The building was declared unfit for future use and the towers were demolished in 2003 to make way for the new building into which the Home Office moved in 2005.[2] Prior to the ugly sisters epoch, from about 1818, the site housed the Chartered Gas Works of the Westminster Gas Light and Coke Company, as well as a laundry yard.
Soon after opening in 2005, child agencies of the Home Office like Her Majesty's Passport Office and Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs began moving to new office. Since August 2014, building has also been home to the Department for Communities and Local Government, Homes and Communities Agency and Building Regulations Advisory Committee.[3]
Design
Designed by Terry Farrell, the new building was financed through the Private Finance Initiative model with French construction firm Bouygues as contractor. It was completed within 24 months.[2] The cost of £311 million will be spread over 29 years and will be partially met by the issue of bonds. The site is made up of three buildings, designated Seacole, Peel and Fry. They are named after Mary Jane Seacole, Robert Peel and Elizabeth Fry, figures who had significant impacts in areas within the Home Office's responsibility.[4]
The buildings are connected by a bridge from the 1st to the 4th floors, forming part of a corridor that runs the whole length of the building.[2] Staff call this corridor 'The Street'. During design, the emphasis was on creating a building with a community feel. To that end, the open-plan offices are well lit, situated around three central atria and overlooking turfed 'pocket parks'. The building has also been constructed to be energy efficient and to fall well within government energy-expenditure targets. The approachable effect of the building is enhanced by art-work by Liam Gillick who used coloured glass to change the feel of the building depending on the light conditions.
The site contains 800,000 sq ft (74,000 m2) of office space. Part of the old Marsham Towers site was also turned over to blocks of residential flats, shops and restaurants behind the new Home Office building.
Critical reception
Since its completion in early 2005, 2 Marsham Street has been well received by the architectural community winning a RIBA Award for Architecture, a Leading European Architects Forum and MIPIM 2006 Awards. Giles Worsley, architecture critic of The Daily Telegraph, called the building "a triumph of urban repair".[1] The contractor's provision of the building within the time-frame required has also been praised.[5] The Home Secretary at the time of the building's completion, Charles Clarke, has stated "By moving to a newer, more efficient headquarters, the Home Office will save taxpayers around £95m. This will contribute to the Home Office's programme to save £1.97bn so that we can target more money at front line services like policing and border control."[6]
References
- ^ a b c Worsley, Giles (7 February 2005). "An artistic bargain at £311 million". The Telegraph.
- ^ a b c Powell, Kenneth (10 March 2005). "Home office comforts". Architects' Journal.
- ^ Homes and Communities Agency Annual Report 2013-2014
- ^ "UK Home Office building named after Mary Seacole". Jamaica Observer. 1 February 2005.
- ^ Sir Terry Farrell's new Home Office, London: the Government building that isn't
- ^ Planning enforcement guidelines published
