Brewer–Dobson circulation
Appearance
This article is missing information about the current status of this theory and support from evidence. (September 2019) |
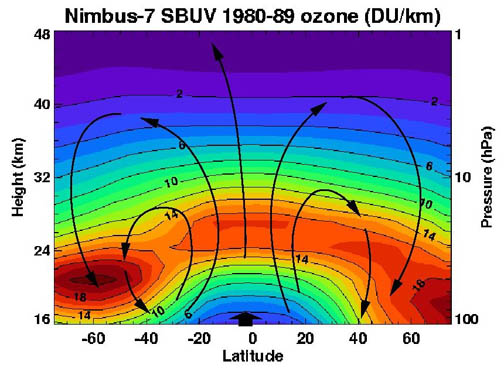
Brewer–Dobson circulation is a model of atmospheric circulation, proposed by Alan Brewer in 1949 and Gordon Dobson in 1956, which attempts to explain why tropical air has less ozone than polar air, even though the tropical stratosphere is where most atmospheric ozone is produced. It is a simple circulation model that posits the existence of a slow current in the winter hemisphere which redistributes air from the tropics to the extratropics. The Brewer–Dobson circulation is driven by atmospheric waves[1] and may be speeding up due to climate change.[2]
See also
References
- Citations
- ^ J.R. Holton (1990), "On the Global Exchange of Mass between the Stratosphere and Troposphere", Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 47 (3): 392–395, doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1990)047<0392:OTGEOM>2.0.CO;2
- ^ N.Butchart and A.A. Scaife, Removal of chlorofluorocarbons by increased mass exchange between the stratosphere and troposphere in a changing climate
- Sources
- Cordero, Eugene; Paul A. Newman; Clark Weaver; Eric Fleming. "Chapter 6: Stratospheric Dynamics and the Transport of Ozone and Other Trace Gases". Stratospheric Ozone: An Electronic Textbook. Retrieved 25 January 2012.
External links
 Media related to Brewer–Dobson circulation at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Brewer–Dobson circulation at Wikimedia Commons
