Tinglof Peninsula
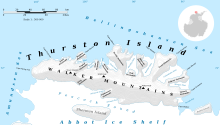

Tinglof Peninsula (72°2′S 100°6′W / 72.033°S 100.100°W) is an ice-covered peninsula, 10 nautical miles (18 km) long, between Henry and Wagoner Inlets on the north side of Thurston Island. Delineated from aerial photographs taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in December 1946. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Iver (Ivor) Tinglof,[1] tractor mechanic of the Second Byrd Antarctic Expedition in 1933–35, who built at Little America the first heavy cargo sleds for use in the Antarctic.[2]
Smith Cliff is a rock cliff midway along the ice-covered northern shore of the peninsula. It was photographed by the Eastern Group of Operation Highjump and later named by US-ACAN after Aviation Radioman William F. Smith an aircrewman from the operation.[3]
Maps
- Thurston Island – Jones Mountains. 1:500000 Antarctica Sketch Map. US Geological Survey, 1967.
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.
References
- ^ "Cover to Byrd's Wife from Crew Member", The Ohio State University Libraries. Retrieved 2020-03-31.
- ^ "Tinglof Peninsula". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2018-08-30.
- ^ "Smith Cliff". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2018-08-30.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
