Dictyophorine
Appearance
 Dictyophorine A
| |
 Dictyophorine B
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 232.323 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
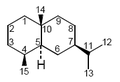
Dictyophorines are a pair of sesquiterpenes isolated from the fungus Phallus indusiatus (Dictyophora indusiata).[1][2] These compounds are based on the eudesmane skeleton, a common structure found in plant-derived flavors and fragrances, and they are the first eudesmane derivatives isolated from fungi. Dictyophorines A and B promote the synthesis of nerve growth factor in astroglial cells.[3]
-
The eudesmane skeleton upon which dictyophorines are based
-
Phallus indusiatus, in Cooktown, Queensland, Australia, which produces dictyophorines
References
[edit]- ^ Che, Zongling; Vidari, Giovanni; Finzi, Paola Vita (1997). "Two new compounds from mushroom Dictyophora indusiata Fisch". Fujian Fenxi Ceshi. 6 (4): 740–746.
- ^ CN 102633613, Liu, Dongfeng; Guo, Qin, "Extracting dictyophorine B", published 2012-08-15
- ^ Kawagishi, Hirokazu (July 1997). "Dictyophorines A and B, two stimulators of NGF-synthesis from the mushroom Dictyophora indusiata". Phytochemistry. 45 (6). Elsevier: 1203–1205. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(97)00144-1. PMID 9272967.