Cerebellar veins
| Cerebellar veins | |
|---|---|
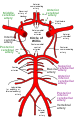
 Corresponding arterial circulation of the cerebellum (AICA and PICA). | |
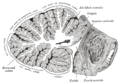
 Veins and plexa of the cerebellum seen. | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | cerebellum |
| Drains to | dural venous sinuses |
| Artery | anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA), posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Venae cerebelli |
| TA98 | A12.3.06.056 |
| TA2 | 4935 |
| FMA | 70879 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The cerebellar veins are veins which drain the cerebellum. They consist of the superior cerebellar veins and the inferior cerebellar veins (dorsal cerebellar veins). The superior cerebellar veins drain to the straight sinus and the internal cerebral veins. The inferior cerebellar veins drain to the transverse sinus, the superior petrosal sinus, and the occipital sinus.
Structure
The superior cerebellar veins pass partly forward and medialward, across the superior cerebellar vermis. They end in the straight sinus,[1] and the internal cerebral veins, partly lateralward to the transverse and superior petrosal sinuses.
The inferior cerebellar veins are larger. They end in the transverse sinus,[2] the superior petrosal sinus, and the occipital sinus.
Clinical significance
The cerebellar veins may be affected by infarction or thrombosis.[3] They may be the draining site of abnormal fistulas.[4]
Additional images
-
Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain.
-
Sagittal section of the cerebellum, near the junction of the vermis with the hemisphere. (Veins not visible, but regions can be seen).
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Drake, Richard L. (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Wayne Vogl, Adam W. M. Mitchell, Henry Gray. Philadelphia: Elsevier / Churchill Livingstone. p. 795. ISBN 0-443-06612-4. OCLC 55139039.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Scremin, Oscar U. (2015). "31 - Cerebral Vascular System". The Rat Nervous System (4th ed.). Academic Press. pp. 985–1011. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-374245-2.00031-0. ISBN 978-0-12-374245-2.
- ^ Bousser, Marie-Germaine; Barnett, Henry J. M. (2004). "12 - Cerebral Venous Thrombosis". Stroke - Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management (4th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 301–325. doi:10.1016/B0-44-306600-0/50016-X. ISBN 978-0-443-06600-9.
- ^ Cole, Tyler S.; Lawton, Michael T. (2021). "8 - Surgical management of cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas". Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas. Academic Press. pp. 105–124. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-819525-3.00010-1. ISBN 978-0-12-819525-3.