Tetrabenzylzirconium
Appearance

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H28Zr | |
| Molar mass | 455.756 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | orange solid |
| Density | 1.34-1.39 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 133–134 °C (271–273 °F; 406–407 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tetrabenzylzirconium is an organozirconium compound with the formula Zr(CH2C6H5)4. The molecule features diamagnetic Zr(IV) bonded to four benzyl ligands. It is an orange air- and photo-sensitive solid, which is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. The compound is a precursor to catalysts for the polymerization of olefins.[2] [3]
Structure, synthesis, reactions
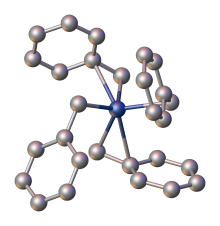
X-ray crystallography demonstrates that the benzyl ligands are highly flexible: one polymorph features four η2-ligands, whereas another has two η1- and two η2-benzyl ligands.[1]
The compound is prepared by combining benzylmagnesium chloride and zirconium tetrachloride in diethyl ether.[4]
Tetrabenzylzirconium readily undergoes protonolysis, e.g. with hydrogen chloride:
- Zr(CH2C6H5)4 + HCl → Zr(CH2C6H5)3Cl + CH3C6H5
See also
- Tetrabenzyltitanium (RN = 17520-19-3)[5]
References
- ^ a b c Rong, Yi; Al-Harbi, Ahmed; Parkin, Gerard (2012). "Highly Variable Zr–CH2–Ph Bond Angles in Tetrabenzylzirconium: Analysis of Benzyl Ligand Coordination Modes". Organometallics. 31 (23): 8208–8217. doi:10.1021/om300820b.
- ^ Tshuva, Edit Y.; Goldberg, Israel; Kol, Moshe (2000). "Isospecific Living Polymerization of 1-Hexene by a Readily Available Nonmetallocene C2-Symmetrical Zirconium Catalyst". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 122 (43): 10706–10707. doi:10.1021/ja001219g.
- ^ Zucchini, U.; Albizzati, E.; Giannini, U. (1971). "Synthesis and Properties of Some Titanium and Zirconium Benzyl Derivatives". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 26: 357–372. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)82618-2.
- ^ Mashima, Kazushi; Tsurugi, Hatato (2013). "Tetrabenzylzirconium". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01555. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ^ Davies, Gwyneth R.; Jarvis, J. A. J.; Kilbourn, B. T. (1971). "The Crystal and Molecular Structures (At –40 °C) of the Tetrabenzyls of Titanium, Hafnium, and Tin". J. Chem. Soc. D (23): 1511–1512. doi:10.1039/C29710001511.
