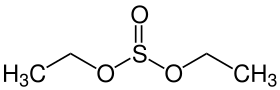
Diethyl sulfite
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethyl sulfite | |
| Other names
Diethyl sulphite
Sulfurous acid, diethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.832 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O3S | |
| Molar mass | 138.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 1.88 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 158 to 160 °C (316 to 320 °F; 431 to 433 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diethyl sulfite (C4H10O3S) is an ester of sulfurous acid. Among other properties, diethyl sulfite inhibits the growth of mold spores during grain storage.[1]
Diethyl sulfite is used as an additive in some polymers to prevent oxidation.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Pasiut, Lad A.; DeMarinis, F. (1966). "Inhibition of growth of spores of Penicillium and Aspergillus isolated from the white molds of silages". Ohio Journal of Science. 66 (1): 64–68.
- ^ Guenther, A.; Koenig, T.; Habicher, W. D.; Schwetlick, K. (1997). "Antioxidant action of organic sulfites. I. Esters of sulfurous acid as secondary antioxidants". Polymer Degradation and Stability. 55 (2): 209–216. doi:10.1016/S0141-3910(96)00150-4.
External links
[edit]
