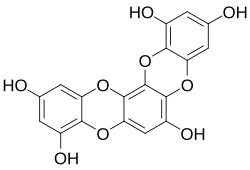
Eckstolonol
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,4]Benzodioxino[2,3-a]oxanthrene-1,3,6,9,11-pentol | |
| Other names
Dioxinodehydroeckol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H10O9 | |
| Molar mass | 370.27 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Eckstolonol is a phlorotannin found in the edible brown algae arame (Eisenia bicyclis) and turuarame (Ecklonia stolonifera).[1]
References
[edit]- ^ Kang, H. S.; Chung, H. Y.; Jung, J. H.; Son, B. W.; Choi, J. S. (2003). "A new phlorotannin from the brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 51 (8): 1012–1014. doi:10.1248/cpb.51.1012. PMID 12913249.
