Indigoidine
Appearance
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (May 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
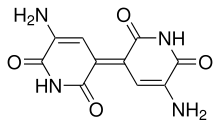
| Systematic IUPAC name
(5E)-3-amino-5-(5-amino-2,6-dioxopyridin-3-ylidene)pyridine-2,6-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 248,19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | blue powder[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Indigoidine is a blue compound produced by several bacterial species suitable for use as a dye.
References
[edit]- ^ R. A. Abramovitch: The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Pyridine and its Derivatives. John Wiley & Sons, New York 1974, ISBN 0-471-37915-8
External links
[edit]- PubChem: [1]
- ACS article: [2] "High-Level Production of the Natural Blue Pigment Indigoidine from Metabolically Engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum for Sustainable Fabric Dyes"
