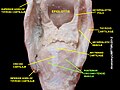
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
| Posterior cricoarytenoid | |
|---|---|
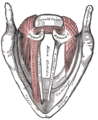
 Muscles of larynx. Side view. Right lamina of thyroid cartilage removed. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | posterior part of the cricoid |
| Insertion | posterior surface of muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
| Nerve | recurrent laryngeal nerve branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) |
| Actions | abducts and laterally rotates arytenoid cartilage, pulling vocal ligaments away from the midline and forward and so opening rima glottidis |
| Antagonist | lateral cricoarytenoid muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus cricoarytaenoideus posterior |
| TA98 | A06.2.08.004 |
| TA2 | 2196 |
| FMA | 46576 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle is a (bilaterally paired) intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It arises from the cricoid cartilage; it inserts onto the arytenoid cartilage of the same side. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Each acts to open the vocal folds by pulling the vocal fold of the same side laterally. It participates in the production of sounds.
Structure
The muscle is directed superiorly and laterally from its origin to its insertion. The muscle's fibres vary in orientation superoinferiorly: the superior-most fibres are nearly horizontally oriented, the intermediate fibres are obliquely oriented, and the inferior-most fibres are nearly vertically oriented;[1] the distinct orientations of muscle fibres may indicate that the muscle could produce different movements depending upon which portion of the muscle contracts.[2]
According to a cadaveric study, the muscle exhibits two distinct bellies - a medial belly and a lateral belly - which differ in the orientation of their muscle fibres and the site of insertion at the muscular process.[3]
Origin
The muscle originates from (the posterior aspect of) the lamina of cricoid cartilage.[1]
Insertion
The muscle's fibres converge to insert onto (the superior, posterior and (minimally the) anterolateral aspects of) the muscular process of the ipsilateral arytenoid cartilage[4] (its medial belly and lateral belly insert onto the muscular process medially and laterally, respectively).[3]
Innervation
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle receives motor innervation from (the anterior division of) the recurrent laryngeal nerve (itself a branch of the vagus nerve (CN X)).[2][5]
Different parts of the muscle (such as the medial and lateral muscle bellies) are often innervated by separate branches.[2] There may be 1-6 branches, but are usually 2-3. These may connect within the muscle.[5] This innervation modality may indicate that the different parts of the muscle can be activated at different times so that it can produce different movements.[2]
Vasculature
The muscle receives arterial supply from the laryngeal branches of the superior thyroid artery and inferior thyroid artery.[1]
Actions/movements
The muscle rotates the arytenoid cartilages laterally, thereby abducting the vocal processes and the vocal folds that are attached to them. In this, the muscle is an antagonist of the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle.[1]
The muscle additionally draws the arytenoid cartilages posterior-ward, thus (assisting in) lengthening the vocal cords (here acting as synergist of the cricothyroid muscle). The lateral-most portion of the muscle also draws the arytenoid cartilages lateral-ward, making the rima glottidis into a triangular shape.[1]
Function
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are the only muscles to open the vocal cords.[1][6] By abducting the vocal folds, the muscle opens the rima glottidis.[7]: 9 This is important in breathing and speech.[6] The muscles participate in the production of unvoiced vocal sounds.[1]
Clinical significance
Paralysis of the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles may lead to asphyxia, as they are the only laryngeal muscles to open the vocal cords (allowing breathing).[8] Denervation leads to a slow fibrosis that worsens over many months.[9]
Additional images
-
The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of larynx. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of the larynx, seen from above.
-
Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind.
-
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
-
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
-
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 727. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c d Sanders, Ira; Wu, Bei-Lian; Mu, Liancai; Biller, Hugh P. (1994). "The innervation of the human posterior cricoarytenoid muscle: Evidence for at least two neuromuscular compartments". The Laryngoscope. 104 (7): 880–884. doi:10.1288/00005537-199407000-00019. ISSN 1531-4995. PMID 8022253. S2CID 45469959.
- ^ a b Bryant, Nancy Jones; Woodson, Gayle E.; Kaufman, Kenton; Rosen, Clark; Hengesteg, Arne; Chen, Naidy; Yeung, Daniel (1996-12-01). "Human Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle Compartments: Anatomy and Mechanics". Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery. 122 (12): 1331–1336. doi:10.1001/archotol.1996.01890240039009. ISSN 0886-4470. PMID 8956745.
- ^ Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 727. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Maranillo, Eva; León, Xavier; Ibañez, Marta; Orús, César; Quer, Miguel; Sañudo, José Ramón (2003). "Variability of the Nerve Supply Patterns of the Human Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle". The Laryngoscope. 113 (4): 602–606. doi:10.1097/00005537-200304000-00004. ISSN 1531-4995. PMID 12671414. S2CID 23686151.
- ^ a b Brancatisano, T. P.; Dodd, D. S.; Engel, L. A. (1 October 1984). "Respiratory activity of posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and vocal cords in humans". Journal of Applied Physiology. 57 (4): 1143–1149. doi:10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.1143. ISSN 8750-7587. PMID 6501030.
- ^ Hydman, Jonas (2008). Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Stockholm. ISBN 978-91-7409-123-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ The Arytenoid Cartilages - a clinical overview. 2002, Dr. C Kay et al. Thorne Publishing (C)
- ^ Zealear, David L.; Hamdan, Abdul-Latif; Ratney, Cheryl L. (1994-10-01). "Effects of Denervation on Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle Physiology and Histochemistry". Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology. 103 (10): 780–788. doi:10.1177/000348949410301007. ISSN 0003-4894. PMID 7944169. S2CID 22946351.
External links
- Atlas image: rsa4p2 at the University of Michigan Health System
- lesson11 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (larynxmuscles)