GTP cyclohydrolase
Appearance
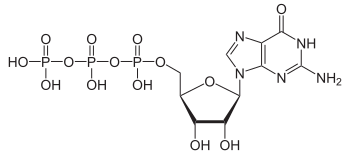
GTP cyclohydrolases are enzymes that catalyze imidazole ring opening of guanosine triphosphate (GTP).[1] This reaction is the committed step in the biosynthesis of multiple coenzymes (such as riboflavin and folate), tRNA bases, and the phytotoxin toxoflavin.[1] Several GTP cyclohydrolases exist, which sometimes synthesize different products for different pruposes:
- GTP cyclohydrolase I, part of the tetrahydrobiopterin, tetrahydrofolate, queuosine and other biosynthetic pathways[1]
- GTP cyclohydrolase Ia,
- GTP cyclohydrolase Ib, part of the tetrahydrobiopterin, tetrahydrofolate, queueosine and other biosynthetic pathways[1]
- GTP cyclohydrolase II, part of the riboflavin and toxoflavin biosynthetic pathways[1]
- GTP cyclohydrolase IIa[2] (or GTP cyclohydrolase III[3]), part of the riboflavin and deazaflavin cofactor biosynthetic pathways[1]
- GTP cyclohydrolase IV
- GTP cyclohydrolase MptA, GTP cyclohydrolase Ib paralog[1]
These enzymes require divalent cations for catalysis.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h Gräwert, Tobias; Fischer, Markus; Bacher, Adelbert (Mar 4, 2013). "Structures and reaction mechanisms of GTP cyclohydrolases". IUBMB Life. 65 (4): 310–322. doi:10.1002/iub.1153. PMID 23457054. S2CID 5470658.
- ^ Graham, David E.; Xu, Huimin; White, Robert H. (2002-12-01). "A Member of a New Class of GTP Cyclohydrolases Produces Formylaminopyrimidine Nucleotide Monophosphates". Biochemistry. 41 (50): 15074–15084. doi:10.1021/bi0268798. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 12475257.
- ^ "ENZYME - 3.5.4.29 GTP cyclohydrolase IIa". enzyme.expasy.org. Retrieved 2023-01-23.
