Headstock

A headstock or peghead is part of a guitar or similar stringed instruments such as a lute, mandolin, banjo, ukulele and others of the lute lineage. The main function of a headstock is to house the tuning pegs or other mechanism that holds the strings at the "head" of the instrument; it corresponds to a pegbox in the violin family. At the "tail" of the instrument the strings are usually held by a tailpiece or bridge. Machine heads on the headstock are commonly used to tune the instrument by adjusting the tension of strings and, consequently, the pitch of sound they produce.
Construction details
[edit]
Two traditional layouts of guitar tuners are called "3+3" (3 top tuners and 3 bottom ones) and "6 in line" tuners, though many other combinations are known, especially for bass guitars and non-6-string guitars. When there are no machine heads (i.e. tuners are not needed or located in some other place, for example, on guitar body), the guitar headstock may be missing completely, as in Steinberger guitar or some Chapman stick models.

The headstock may be carved separately and glued to the neck using some sort of joint (such as a scarf joint). There are two major trends in headstock construction, based on how the string will go after passing the nut. The advantages and disadvantages of both trends are very debatable and subjective, so these two variants are used:
- Straight headstocks form a single plane with a flat surface of the neck (and fingerboard). This makes the neck and headstock easier to manufacture; they can be constructed from a single piece of wood. Fender usually uses non-angled, straight headstocks. Because of the low angle of the string over the nut, string trees may be used to avoid the string coming out of the nut while playing.[1]
- Angled headstocks form some kind of acute angle with a surface of the neck. The value of "magic angle" (called headstock pitch) that gives the best tone and stability is also very debatable, but it is usually in a range from 3° to 25°. For example, various manufacturers and particular guitar models use:
- Guitars
- 4°: Guild
- 11°: Martin[2]
- 12°: Bigsby,[3] Yamaha SGV[4]
- 13°: Peavey,[5] Warmoth[6][7]
- 14°: Gibson Firebird V[8] and VII,[9] Gibson X-plorer,[10] some vintage Gibson guitars,[11] Washburn,[12] most budget Epiphone replicas of Gibson models[13]
- 17°: Gibson ES-335,[14] Gibson Les Paul,[15] Gibson SG,[16] Epiphone Casino[17]
- Bass guitars
- Guitars
Luthiers of both styles frequently cite better sound, longer sustain and strings staying in tune longer as advantages of each style. Fragile construction is cited as a disadvantage of each style too: single-piece necks are more likely to break on occasional hits and are harder to repair, while glued-in necks can break with time.
Apart from its main function, the headstock is an important decorative detail of a guitar. It is the place where the overwhelming majority of guitar manufacturers draw their logo. Some guitars without machine heads (for example, ones equipped with Floyd Rose SpeedLoader) have a headstock for purely decorative reasons.
Signature headstock outlines
[edit]


Most major guitar brands have signature headstock designs that make their guitars or guitar series easily recognizable. As seen in a section below, even "copied" at the first glance designs retain clear visible changes in dimensions, proportions of elements, etc., so it is almost always possible to tell a major brand of a guitar by looking at the headstock.
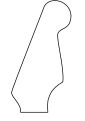
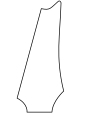
Fender-like curved 6-in-line headstocks
[edit]-
Fender Stratocaster, regular version, used on modern Mexican and American-built guitars (other than the Highway One (Upgrade) series), as well as the brief-lived Korean-made Fender Stratocaster of the early 1990s.
-
Large Fender was first seen on the Jazzmaster, introduced 1959; also seen on the Fender Jaguar, "CBS" version Fender Stratocaster (from 1965 to 1981) and early 1970s Telecaster Deluxe. Currently used on 1970s Stratocaster reissues, Highway One Strats, Squier guitars, and '72 Telecaster Deluxe reissues
-
Gibson Firebird series (also used in reverse)
-
Washburn N-series (reverse)
-
Floyd Rose SpeedLoader Guitars decorative headstock, no machine heads at all
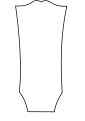
Gibson-like 3+3 headstocks
[edit]-
Gibson, used on most of their acoustic and electric guitars since the 1930s, and many before that.
-
ESP EC-series
-
PRS asymmetric, used on most guitars
-
PRS symmetric, used on Santana 3 model
-
Gibson Flying V, 1958 issue

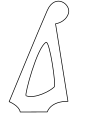
Pointed headstocks, 6-in-line
[edit]-
ESP "pointed" headstock, used on Horizon NT-II and M-II guitars, as well as many signature models (also used in reverse)
-
Ibanez "pointed" Ibanez signature headstock, used on most rock-series solid-body electric guitars (also used in reverse)
-
Jackson "pointed" headstock, used on almost all solid-body electric guitar series (also used in reverse)
-
Washburn "pointed" headstock, used on almost all rocker-series electric guitars (also used in reverse)
Matching headstock
[edit]
On some electric guitars and basses the finish used on the body is also applied to the face of the headstock. Generally, matched-headstock models carry a price premium over their plain counterparts due to the extra processes involved in the finishing process.
Although Fender no longer offers matched headstocks on production models made in the United States or Mexico, certain models from Fender Japan are available with matched headstocks.
The definition of a "matched headstock" varies between manufacturers and players - for example, the headstocks of Gibson guitars are nearly always black, and it is debatable whether a black-bodied Gibson has a matching headstock. Generally, a guitar is only considered to have a matching headstock if the guitar is usually produced without matching body and headstock finishes.
References
[edit]- ^ "What String Trees Are For | zZounds Music Blog". zZounds Music Blog. 2017-10-10. Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- ^ "UG Community @". Ultimate-guitar.com. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Bigsby Guitars & Vibratos - Official Website". Bigsbyguitars.com. Archived from the original on 2008-03-23. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Yamaha SGV Series Takes Guitar To The Extreme". Giles.com. 2000-04-14. Archived from the original on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Peavey.com". Peavey.com. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Warmoth replacement guitar necks: Warmoth "Pro" 13°".
- ^ "Warmoth replacement bass necks: 13° Angled Pegheads".
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2008-10-15. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2008-11-20. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2009-01-25. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Vintage Guitars Info - Gibson solidbody vintage guitar collecting". Provide.net. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Washburn N4VINTAGE Electric Guitar". Archived from the original on 2015-12-22. Retrieved 2015-12-15.
- ^ "Epiphone Musical Instruments - News". Epiphone.com. 2006-05-31. Archived from the original on 2010-02-02. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2008-05-16. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2009-01-23. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2008-08-29. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Epiphone Musical Instruments". Gibson.com. Archived from the original on 2008-05-18. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Gibson Guitar: Electric, Acoustic and Bass Guitars, Baldwin Pianos". Gibson.com. 2008-06-24. Archived from the original on 2006-10-23. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Yamaha SBV500 bass is a true alternative". Musiciansnews.com. Archived from the original on 2003-03-09. Retrieved 2010-08-10.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2018-12-15. Retrieved 2006-07-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)