Military government
Appearance
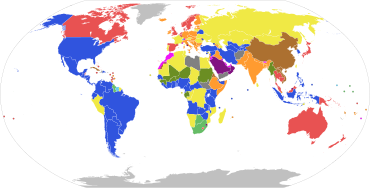
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Constitutional monarchy with a ceremonial monarch
Parliamentary republic with a ceremonial president
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Presidential republic
Hybrid systems:
Semi-presidential republic: Executive president is independent of the legislature; head of government is appointed by the president and is accountable to the legislature
Assembly-independent republic: Head of government (president or directory) is elected by the legislature, but is not accountable to it
Other systems:
Semi-constitutional monarchy: Monarch holds significant executive or legislative power
Absolute monarchy: Monarch has unlimited power
One-party state: Power is constitutionally linked to a single political party
Military junta: Committee of military leaders controls the government; constitutional provisions are suspended
Provisional government: No constitutionally defined basis to current regime
Dependent territories or places without governments
Note: this chart represents de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
A military government is generally any form of government that is administered by military forces, whether or not this government is legal under the laws of the jurisdiction at issue, and whether this government is formed by natives or by an occupying power. It is usually carried out by military workers.
Types of military government include:
- Military occupation of acquired foreign territory and the administration thereof
- Martial law, temporary military rule of domestic territory
- Military dictatorship, an authoritarian government controlled by a military and its political designees, called a military junta when done extralegally
- Military junta, a government led by a committee of military leaders.
- Stratocracy, a government traditionally or constitutionally run by a military.
- Military democracy, a war based society that practices democracy. With an elected and removeable general as supreme chief, a council of elders and a popular assembly.
