Minifloat
| Floating-point formats |
|---|
| IEEE 754 |
|
| Other |
| Alternatives |
| Tapered floating point |
| Computer architecture bit widths |
|---|
| Bit |
| Application |
| Binary floating-point precision |
| Decimal floating-point precision |
In computing, minifloats are floating-point values represented with very few bits. Predictably, they are not well suited for general-purpose numerical calculations. They are used for special purposes, most often in computer graphics, where iterations are small and precision has aesthetic effects.[1] Machine learning also uses similar formats like bfloat16. Additionally, they are frequently encountered as a pedagogical tool in computer-science courses to demonstrate the properties and structures of floating-point arithmetic and IEEE 754 numbers.
Minifloats with 16 bits are half-precision numbers (opposed to single and double precision). There are also minifloats with 8 bits or even fewer.[citation needed]
Minifloats can be designed following the principles of the IEEE 754 standard. In this case they must obey the (not explicitly written) rules for the frontier between subnormal and normal numbers and must have special patterns for infinity and NaN. Normalized numbers are stored with a biased exponent. The new revision of the standard, IEEE 754-2008, has 16-bit binary minifloats.
Notation
A minifloat is usually described using a tuple of four numbers, (S, E, M, B):
- S is the length of the sign field. It is usually either 0 or 1.
- E is the length of the exponent field.
- M is the length of the mantissa (significand) field.
- B is the exponent bias.
A minifloat format denoted by (S, E, M, B) is, therefore, S + E + M bits long.
In computer graphics minifloats are sometimes used to represent only integral values. If at the same time subnormal values should exist, the least subnormal number has to be 1. The bias value would be B = E - M - 1 in this case, assuming two special exponent values are used per IEEE.
The (S, E, M, B) notation can be converted to a (B, P, L, U) format as (2, M + 1, B + 1, 2S - B) (with IEEE use of exponents).
Example 8-bit float
| sign | exponent | significand | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A minifloat in 1 byte (8 bit) with 1 sign bit, 4 exponent bits and 3 significand bits (in short, a 1.4.3 minifloat) is demonstrated here. The exponent bias is defined as 7 to center the values around 1 to match other IEEE 754 floats[2][3] so (for most values) the actual multiplier for exponent x is 2x - 7. All IEEE 754 principles should be valid.[4]
Numbers in a different base are marked as ...base, for example, 1012 = 5. The bit patterns have spaces to visualize their parts.
Alternative bias values
At these small sizes other bias values may be interesting, for instance a bias of -2 will make the numbers 0-16 have the same bit representation as the integers 0-16, with the loss that no non-integer values can be represented.
0 0000 000 = 0.0002 × 21 - (-2) = 0.0 × 23 = 0 (subnormal number) 0 0000 001 = 0.0012 × 21 - (-2) = 0.125 × 23 = 1 (subnormal number) 0 0000 111 = 0.1112 × 21 - (-2) = 0.875 × 23 = 7 (subnormal number) 0 0001 000 = 1.0002 × 21 - (-2) = 1.000 × 23 = 8 (normalized number) 0 0001 111 = 1.1112 × 21 - (-2) = 1.875 × 23 = 15 (normalized number) 0 0010 000 = 1.0002 × 22 - (-2) = 1.000 × 24 = 16 (normalized number)
Representation of zero
Zero is represented as zero exponent with a zero mantissa. The zero exponent means zero is a subnormal number with a leading "0." prefix, and with the zero mantissa all bits after the decimal point are zero, meaning this value is interpreted as . Floating point numbers use a signed zero, so is also available and is equal to positive .
0 0000 000 = 0 1 0000 000 = −0
Subnormal numbers
The significand is extended with "0." and the exponent value is treated as 1 higher like the least normalized number:
0 0000 001 = 0.0012 × 21 - 7 = 0.125 × 2-6 = 0.001953125 (least subnormal number) ... 0 0000 111 = 0.1112 × 21 - 7 = 0.875 × 2-6 = 0.013671875 (greatest subnormal number)
Normalized numbers
The significand is extended with "1.":
0 0001 000 = 1.0002 × 21 - 7 = 1 × 2-6 = 0.015625 (least normalized number) 0 0001 001 = 1.0012 × 21 - 7 = 1.125 × 2-6 = 0.017578125 ... 0 0111 000 = 1.0002 × 27 - 7 = 1 × 20 = 1 0 0111 001 = 1.0012 × 27 - 7 = 1.125 × 20 = 1.125 (least value above 1) ... 0 1110 000 = 1.0002 × 214 - 7 = 1.000 × 27 = 128 0 1110 001 = 1.0012 × 214 - 7 = 1.125 × 27 = 144 ... 0 1110 110 = 1.1102 × 214 - 7 = 1.750 × 27 = 224 0 1110 111 = 1.1112 × 214 - 7 = 1.875 × 27 = 240 (greatest normalized number)
Infinity
Infinity values have the highest exponent, with the mantissa set to zero. The sign bit can be either positive or negative.
0 1111 000 = +infinity 1 1111 000 = −infinity
Not a number
NaN values have the highest exponent, with a non-zero value for the mantissa. A float with 1-bit sign and 3-bit mantissa has NaN values.
s 1111 mmm = NaN (if mmm ≠ 000)
Table of values
This is a chart of all possible values for this example 8-bit float.
| … 000 | … 001 | … 010 | … 011 | … 100 | … 101 | … 110 | … 111 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 0000 … | 0 | 0.001953125 | 0.00390625 | 0.005859375 | 0.0078125 | 0.009765625 | 0.01171875 | 0.013671875 |
| 0 0001 … | 0.015625 | 0.017578125 | 0.01953125 | 0.021484375 | 0.0234375 | 0.025390625 | 0.02734375 | 0.029296875 |
| 0 0010 … | 0.03125 | 0.03515625 | 0.0390625 | 0.04296875 | 0.046875 | 0.05078125 | 0.0546875 | 0.05859375 |
| 0 0011 … | 0.0625 | 0.0703125 | 0.078125 | 0.0859375 | 0.09375 | 0.1015625 | 0.109375 | 0.1171875 |
| 0 0100 … | 0.125 | 0.140625 | 0.15625 | 0.171875 | 0.1875 | 0.203125 | 0.21875 | 0.234375 |
| 0 0101 … | 0.25 | 0.28125 | 0.3125 | 0.34375 | 0.375 | 0.40625 | 0.4375 | 0.46875 |
| 0 0110 … | 0.5 | 0.5625 | 0.625 | 0.6875 | 0.75 | 0.8125 | 0.875 | 0.9375 |
| 0 0111 … | 1 | 1.125 | 1.25 | 1.375 | 1.5 | 1.625 | 1.75 | 1.875 |
| 0 1000 … | 2 | 2.25 | 2.5 | 2.75 | 3 | 3.25 | 3.5 | 3.75 |
| 0 1001 … | 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 6.5 | 7 | 7.5 |
| 0 1010 … | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 0 1011 … | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 |
| 0 1100 … | 32 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 |
| 0 1101 … | 64 | 72 | 80 | 88 | 96 | 104 | 112 | 120 |
| 0 1110 … | 128 | 144 | 160 | 176 | 192 | 208 | 224 | 240 |
| 0 1111 … | Inf | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1 0000 … | −0 | −0.001953125 | −0.00390625 | −0.005859375 | −0.0078125 | −0.009765625 | −0.01171875 | −0.013671875 |
| 1 0001 … | −0.015625 | −0.017578125 | −0.01953125 | −0.021484375 | −0.0234375 | −0.025390625 | −0.02734375 | −0.029296875 |
| 1 0010 … | −0.03125 | −0.03515625 | −0.0390625 | −0.04296875 | −0.046875 | −0.05078125 | −0.0546875 | −0.05859375 |
| 1 0011 … | −0.0625 | −0.0703125 | −0.078125 | −0.0859375 | −0.09375 | −0.1015625 | −0.109375 | −0.1171875 |
| 1 0100 … | −0.125 | −0.140625 | −0.15625 | −0.171875 | −0.1875 | −0.203125 | −0.21875 | −0.234375 |
| 1 0101 … | −0.25 | −0.28125 | −0.3125 | −0.34375 | −0.375 | −0.40625 | −0.4375 | −0.46875 |
| 1 0110 … | −0.5 | −0.5625 | −0.625 | −0.6875 | −0.75 | −0.8125 | −0.875 | −0.9375 |
| 1 0111 … | −1 | −1.125 | −1.25 | −1.375 | −1.5 | −1.625 | −1.75 | −1.875 |
| 1 1000 … | −2 | −2.25 | −2.5 | −2.75 | −3 | −3.25 | −3.5 | −3.75 |
| 1 1001 … | −4 | −4.5 | −5 | −5.5 | −6 | −6.5 | −7 | −7.5 |
| 1 1010 … | −8 | −9 | −10 | −11 | −12 | −13 | −14 | −15 |
| 1 1011 … | −16 | −18 | −20 | −22 | −24 | −26 | −28 | −30 |
| 1 1100 … | −32 | −36 | −40 | −44 | −48 | −52 | −56 | −60 |
| 1 1101 … | −64 | −72 | −80 | −88 | −96 | −104 | −112 | −120 |
| 1 1110 … | −128 | −144 | −160 | −176 | −192 | −208 | −224 | −240 |
| 1 1111 … | −Inf | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
There are only 242 different non-NaN values (if +0 and −0 are regarded as different), because 14 of the bit patterns represent NaNs.
Tables like the above can be generated for any combination of SEMB values using a script in Python or in GDScript.
Arithmetic
Addition

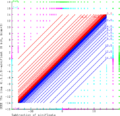
The graphic demonstrates the addition of even smaller (1.3.2.3)-minifloats with 6 bits. This floating-point system follows the rules of IEEE 754 exactly. NaN as operand produces always NaN results. Inf − Inf and (−Inf) + Inf results in NaN too (green area). Inf can be augmented and decremented by finite values without change. Sums with finite operands can give an infinite result (i.e. 14.0 + 3.0 = +Inf as a result is the cyan area, −Inf is the magenta area). The range of the finite operands is filled with the curves x + y = c, where c is always one of the representable float values (blue and red for positive and negative results respectively).
Subtraction, multiplication and division
The other arithmetic operations can be illustrated similarly:
-
Subtraction
-
Multiplication
-
Division
Other sizes
The Radeon R300 and R420 GPUs used an "fp24" floating-point format with 7 bits of exponent and 16 bits (+1 implicit) of mantissa.[5] "Full Precision" in Direct3D 9.0 is a proprietary 24-bit floating-point format. Microsoft's D3D9 (Shader Model 2.0) graphics API initially supported both FP24 (as in ATI's R300 chip) and FP32 (as in Nvidia's NV30 chip) as "Full Precision", as well as FP16 as "Partial Precision" for vertex and pixel shader calculations performed by the graphics hardware.
Khronos defines 10-bit and 11-bit float formats for use with Vulkan. Both formats have no sign bit and a 5-bit exponent. The 10-bit format has a 5-bit mantissa, and the 11-bit format has a 6-bit mantissa.[6][7]
4 bits and fewer
The smallest possible float size that follows all IEEE principles, including normalized numbers, subnormal numbers, signed zero, signed infinity, and multiple NaN values, is a 4-bit float with 1-bit sign, 2-bit exponent, and 1-bit mantissa.[8] In the table below, the columns have different values for the sign and mantissa bits, and the rows are different values for the exponent bits.
| 0 … 0 | 0 … 1 | 1 … 0 | 1 … 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| … 00 … | 0 | 0.5 | −0 | −0.5 |
| … 01 … | 1 | 1.5 | −1 | −1.5 |
| … 10 … | 2 | 3 | −2 | −3 |
| … 11 … | Inf | NaN | −Inf | NaN |
If normalized numbers are not required, the size can be reduced to 3-bit by reducing the exponent down to 1.
| 0 … 0 | 0 … 1 | 1 … 0 | 1 … 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| … 0 … | 0 | 1 | −0 | −1 |
| … 1 … | Inf | NaN | −Inf | NaN |
In situations where the sign bit can be excluded, each of the above examples can be reduced by 1 bit further, keeping only the left half of the above tables. A 2-bit float with 1-bit exponent and 1-bit mantissa would only have 0, 1, Inf, NaN values.
If the mantissa is allowed to be 0-bit, a 1-bit float format would have a 1-bit exponent, and the only two values would be 0 and Inf. The exponent must be at least 1 bit or else it no longer makes sense as a float (it would just be a signed number).
In embedded devices
Minifloats are also commonly used in embedded devices,[citation needed] especially on microcontrollers where floating-point will need to be emulated in software. To speed up the computation, the mantissa typically occupies exactly half of the bits, so the register boundary automatically addresses the parts without shifting.
See also
- Fixed-point arithmetic
- Half-precision floating-point format
- bfloat16 floating-point format
- G.711 A-Law
References
- ^ Mocerino, Luca; Calimera, Andrea (24 November 2021). "AxP: A HW-SW Co-Design Pipeline for Energy-Efficient Approximated ConvNets via Associative Matching". Applied Sciences. 11 (23): 11164. doi:10.3390/app112311164.
- ^ IEEE half-precision has 5 exponent bits with bias 15 (), IEEE single-precision has 8 exponent bits with bias 127 (), IEEE double-precision has 11 exponent bits with bias 1023 (), and IEEE quadruple-precision has 15 exponent bits with bias 16383 (). See the Exponent bias article for more detail.
- ^ O'Hallaron, David R.; Bryant, Randal E. (2010). Computer systems: a programmer's perspective (2 ed.). Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-610804-7.
- ^ Burch, Carl. "Floating-point representation". Hendrix College. Retrieved 29 August 2023.
- ^ Buck, Ian (13 March 2005), "Chapter 32. Taking the Plunge into GPU Computing", in Pharr, Matt (ed.), GPU Gems, ISBN 0-321-33559-7, retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ^ Garrard, Andrew. "10.3. Unsigned 10-bit floating-point numbers". Khronos Data Format Specification v1.2 rev 1. Khronos Group. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ Garrard, Andrew. "10.2. Unsigned 11-bit floating-point numbers". Khronos Data Format Specification v1.2 rev 1. Khronos Group. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ Shaneyfelt, Dr. Ted. "Dr. Shaneyfelt's Floating Point Consruction Gizmo". Dr. Ted Shaneyfelt. Retrieved 29 August 2023.
- Munafo, Robert (15 May 2016). "Survey of Floating-Point Formats". Retrieved 8 August 2016.