Nitrosyl azide
Appearance

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N4O | |
| Molar mass | 72.027 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nitrosylazide is a highly unstable nitrogen oxide, chemical formula N4O, which can be synthesized via the following reaction of sodium azide and nitrosyl chloride at low temperatures:
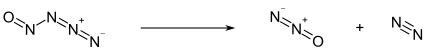
Below −50 °C, nitrosylazide exists as a pale yellow solid. Above this temperature, it decomposes into nitrous oxide (N2O) and molecular nitrogen (N2):
References
- Cotton, F. Albert & Geoffrey Wilkinson (1999). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 331. ISBN 0-471-19957-5.