Kinetic inductance detector
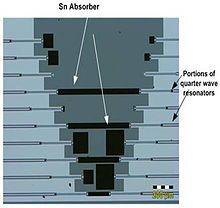
The kinetic inductance detector (KID) — also known as a microwave kinetic inductance detector (MKID) — is a type of superconducting photon detector first developed by scientists at the California Institute of Technology and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in 2003.[1] These devices operate at cryogenic temperatures, typically below 1 kelvin. They are being developed for high-sensitivity astronomical detection for frequencies ranging from the far-infrared to X-rays.
Principle of operation
Photons incident on a strip of superconducting material break Cooper pairs and create excess quasiparticles. The kinetic inductance of the superconducting strip is inversely proportional to the density of Cooper pairs, and thus the kinetic inductance increases upon photon absorption. This inductance is combined with a capacitor to form a microwave resonator whose resonant frequency changes with the absorption of photons. This resonator-based readout is useful for developing large-format detector arrays, as each KID can be addressed by a single microwave tone and many detectors can be measured using a single broadband microwave channel, a technique known as frequency-division multiplexing.
Applications
KIDs are being developed for a range of astronomy applications, including millimeter and submillimeter wavelength detection at the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory,[2] the Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) on the Llano de Chajnantor Observatory,[3] and the IRAM 30-m telescope.[4] They are also being developed for optical and near-infrared detection at the Palomar Observatory.[5]
See also
References
- ^ Day, P. K.; LeDuc, H. G.; Mazin, B. A.; Vayonakis, A.; Zmuidzinas, J. (2003). "A broadband superconducting detector suitable for use in large arrays". Nature. 425 (6960): 817–821. Bibcode:2003Natur.425..817D. doi:10.1038/nature02037. PMID 14574407.
- ^ Maloney, Philip R.; Czakon, Nicole G.; Day, Peter K.; Downes, Thomas P.; Duan, Ran; Gao, Jiansong; Glenn, Jason; Golwala, Sunil R.; Hollister, Matt I.; Leduc, Henry G.; Mazin, Benjamin A.; McHugh, Sean G.; Noroozian, Omid; Nguyen, Hien T.; Sayers, Jack; Schlaerth, James A.; Siegel, Seth; Vaillancourt, John E.; Vayonakis, Anastasios; Wilson, Philip; Zmuidzinas, Jonas (2010). "MUSIC for sub/Millimeter astrophysics" (PDF). Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy V. Vol. 7741. pp. 77410F. doi:10.1117/12.857751.
- ^ Heyminck, S.; Klein, B.; Güsten, R.; Kasemann, C.; Baryshev, A.; Baselmans, J.; Yates, S.; Klapwijk, T. M. (2010). "Development of a MKID Camera for APEX". Twenty-First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology: 262. Bibcode:2010stt..conf..262H.
- ^ Monfardini, A.; et al. (2011). "A dual-band millimeter-wave kinetic inductance camera for the IRAM 30 m telescope". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 194 (2): 24. arXiv:1102.0870. Bibcode:2011ApJS..194...24M. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/194/2/24.
- ^ Mazin, B. A.; O'Brien, K.; McHugh, S.; Bumble, B.; Moore, D.; Golwala, S.; Zmuidzinas, J. (2010). "ARCONS: a highly multiplexed superconducting optical to near-IR camera". Proc. SPIE. Ground-based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy III. 7735: 773518. arXiv:1007.0752. Bibcode:2010SPIE.7735E..18M. doi:10.1117/12.856440.
External links
- SRON website on kinetic inductance detectors
- Research group of Prof. B. Mazin at UC Santa Barbara
- YouTube video on kinetic inductance from MIT
- Champlin, K.S.; Armstrong, D.B.; Gunderson, P.D. (1964). "Charge carrier inertia in semiconductors". Proceedings of the IEEE. 52 (6). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): 677–685. doi:10.1109/proc.1964.3049. ISSN 0018-9219.
