Tartronic acid
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxypropanedioic acid
| |
| Other names
tartronic acid,
2-tartronic acid, hydroxymalonic acid, 2-hydroxymalonic acid, hydroxypropanedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.184 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O5 | |
| Molar mass | 120.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | beige powder |
| Melting point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related carboxylic acids
|
Tartaric acid Malic acid Mesoxalic acid Lactic acid 3-Hydroxypropionic acid Malonic acid Propionic acid Oxalic acid |
Related compounds
|
Glyceric acid Glyceraldehyde Tartonaldehyde Glycerol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
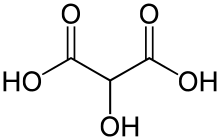
Tartronic acid or 2-hydroxymalonic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the structural formula of HOOCCH(OH)COOH.
Its derivative, 2-methyltartronic acid, is isomalic acid.
Uses
Tartronic acids are best known as a reactant in the catalytic oxidation with air to form mesoxalic acid, another type of hydroxydicarboxylic acid.[1]
References
- ^ Fordham P.; Besson M.; Gallezot P. (1997). "Catalytic oxidation with air of tartronic acid to mesoxalic acid on bismuth-promoted platinum". Catal. Lett. 46 (3–4): 195–199(5). doi:10.1023/A:1019082905366. Retrieved 2007-07-06.
- Hall A. N.; Kulka D.; Walker T. K. (1955). "Formation of arabinose, ribulose and tartronic acid from 2-keto-d-gluconic acid". Biochem. J. 60 (2): 271–274(4). PMC 1215693. PMID 14389236.
External links
- US-Patent 4319045: "Process for production of a tartronic acid solution", max 20% Tartronic acid besides other dicarbonic acids
- US-Patent 5750037: Use of tartronic acid as an oxygen scavenger
- Literature overview about synthesis

