Riemann sum
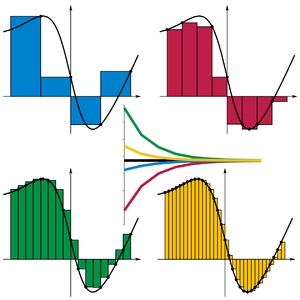
In mathematics, a Riemann sum is a certain kind of approximation of an integral by a finite sum. It is named after nineteenth century German mathematician Bernhard Riemann. One very common application is approximating the area of functions or lines on a graph, but also the length of curves and other approximations.
The sum is calculated by partitioning the region into shapes (rectangles, trapezoids, parabolas, or cubics) that together form a region that is similar to the region being measured, then calculating the area for each of these shapes, and finally adding all of these small areas together. This approach can be used to find a numerical approximation for a definite integral even if the fundamental theorem of calculus does not make it easy to find a closed-form solution.
Because the region filled by the small shapes is usually not exactly the same shape as the region being measured, the Riemann sum will differ from the area being measured. This error can be reduced by dividing up the region more finely, using smaller and smaller shapes. As the shapes get smaller and smaller, the sum approaches the Riemann integral.
Definition
Let be a function defined on a closed interval of the real numbers, , and
- ,
be a partition of I, where
- .
A Riemann sum of f over I with partition P is defined as
where and .[1] It does not matter which point in the interval is taken to be , since as the difference or width of the summands approaches zero, so does the difference between any two points in the interval. This is due to the fact that the choice of in the interval is arbitrary, and so for any given function f defined on an interval I and a fixed partition P, one might produce different Riemann sums depending on which is chosen, as long as holds true.
Some specific types of Riemann sums
Specific choices of give us different types of Riemann sums:
- If for all i, then S is called a left rule[2][3] or left Riemann sum.
- If for all i, then S is called a right rule[2][3] or right Riemann sum.
- If for all i, then S is called the midpoint rule[2][3] or middle Riemann sum.
- If (that is, the supremum of f over ), then S is defined to be an upper Riemann sum or upper Darboux sum.
- If (that is, the infimum of f over ), then S is defined to be an lower Riemann sum or lower Darboux sum.
All these methods are among the most basic ways to accomplish numerical integration. Loosely speaking, a function is Riemann integrable if all Riemann sums converge as the partition "gets finer and finer".
While not technically a Riemann sum, the average of the left and right Riemann sums is the trapezoidal sum and is one of the simplest of a very general way of approximating integrals using weighted averages. This is followed in complexity by Simpson's rule and Newton–Cotes formulas.
Any Riemann sum on a given partition (that is, for any choice of between and ) is contained between the lower and upper Darboux sums. This forms the basis of the Darboux integral, which is ultimately equivalent to the Riemann integral.
Methods
The four methods of Riemann summation are usually best approached with partitions of equal size. The interval [, ] is therefore divided into subintervals, each of length
The points in the partition will then be
Left Riemann sum

For the left Riemann sum, approximating the function by its value at the left-end point gives multiple rectangles with base Δx and height f(a + iΔx). Doing this for i = 0, 1, ..., n − 1, and adding up the resulting areas gives
The left Riemann sum amounts to an overestimation if f is monotonically decreasing on this interval, and an underestimation if it is monotonically increasing.
Right Riemann sum

f is here approximated by the value at the right endpoint. This gives multiple rectangles with base Δx and height f(a + i Δx). Doing this for i = 1, ..., n, and adding up the resulting areas produces
The right Riemann sum amounts to an underestimation if f is monotonically decreasing, and an overestimation if it is monotonically increasing. The error of this formula will be
- ,
where is the maximum value of the absolute value of on the interval.
Midpoint rule

Approximating f at the midpoint of intervals gives f(a + Δx/2) for the first interval, for the next one f(a + 3Δx/2), and so on until f(b − Δx/2). Summing up the areas gives
- .
The error of this formula will be
- ,
where is the maximum value of the absolute value of on the interval.
Trapezoidal rule

In this case, the values of the function f on an interval are approximated by the average of the values at the left and right endpoints. In the same manner as above, a simple calculation using the area formula
for a trapezium with parallel sides b1, b2 and height h produces
The error of this formula will be
where is the maximum value of the absolute value of .
The approximation obtained with the trapezoid rule for a function is the same as the average of the left hand and right hand sums of that function.
Connection with integration
For a one-dimensional Riemann sum over domain , as the maximum size of a partition element shrinks to zero (that is the limit of the norm of the partition goes to zero), some functions will have all Riemann sums converge to the same value. This limiting value, if it exists, is defined as the definite Riemann integral of the function over the domain,
For a finite-sized domain, if the maximum size of a partition element shrinks to zero, this implies the number of partition elements goes to infinity. For finite partitions, Riemann sums are always approximations to the limiting value and this approximation gets better as the partition gets finer. The following animations help demonstrate how increasing the number of partitions (while lowering the maximum partition element size) better approximates the "area" under the curve:
-
Left sum
-
Right sum
-
Middle sum
Since the red function here is assumed to be a smooth function, all three Riemann sums will converge to the same value as the number of partitions goes to infinity.
Example
Taking an example, the area under the curve of y = x2 between 0 and 2 can be procedurally computed using Riemann's method.
The interval [0, 2] is firstly divided into n subintervals, each of which is given a width of ; these are the widths of the Riemann rectangles (hereafter "boxes"). Because the right Riemann sum is to be used, the sequence of x coordinates for the boxes will be . Therefore, the sequence of the heights of the boxes will be . It is an important fact that , and .
The area of each box will be and therefore the nth right Riemann sum will be:
If the limit is viewed as n → ∞, it can be concluded that the approximation approaches the actual value of the area under the curve as the number of boxes increases. Hence:
This method agrees with the definite integral as calculated in more mechanical ways:
Because the function is continuous and monotonically increasing on the interval, a right Riemann sum overestimates the integral by the largest amount (while a left Riemann sum would underestimate the integral by the largest amount). This fact, which is intuitively clear from the diagrams, shows how the nature of the function determines how accurate the integral is estimated. While simple, right and left Riemann sums are often less accurate than more advanced techniques of estimating an integral such as the Trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule.
The example function has an easy-to-find anti-derivative so estimating the integral by Riemann sums is mostly an academic exercise; however it must be remembered that not all functions have anti-derivatives so estimating their integrals by summation is practically important.
Higher dimensions
The basic idea behind a Riemann sum is to "break-up" the domain via a partition into pieces, multiply the "size" of each piece by some value the function takes on that piece, and sum all these products. This can be generalized to allow Riemann sums for functions over domains of more than one dimension.
While intuitively, the process of partitioning the domain is easy to grasp, the technical details of how the domain may be partitioned get much more complicated than the one dimensional case and involves aspects of the geometrical shape of the domain.[4]
Two dimensions
In two dimensions, the domain, may be divided into a number of cells, such that . In two dimensions, each cell then can be interpreted as having an "area" denoted by .[5] The Riemann sum is
where .
Three dimensions
In three dimensions, it is customary to use the letter for the domain, such that under the partition and is the "volume" of the cell indexed by . The three-dimensional Riemann sum may then be written as[6]
with .
Arbitrary number of dimensions
Higher dimensional Riemann sums follow a similar as from one to two to three dimensions. For an arbitrary dimension, n, a Riemann sum can be written as
where , that is, it's a point in the n-dimensional cell with n-dimensional volume .
Generalization
In high generality, Riemann sums can be written
where stands for any arbitrary point contained in the partition element and is a measure on the underlying set. Roughly speaking, a measure is a function that gives a "size" of a set, in this case the size of the set ; in one dimension, this can often be interpreted as the length of the interval, in two dimensions, an area, in three dimensions, a volume, and so on.
See also
- Antiderivative
- Euler method and midpoint method, related methods for solving differential equations
- Lebesgue integral
- Riemann integral, limit of Riemann sums as the partition becomes infinitely fine
- Simpson's rule, a powerful numerical method more powerful than basic Riemann sums or even the Trapezoidal rule
- Trapezoidal rule, numerical method based on the average of the left and right Riemann sum
References
- ^ Hughes-Hallett, Deborah; McCullum, William G. (2005). Calculus (4th ed.). Wiley. p. 252.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) (Among many equivalent variations on the definition, this reference closely resembles the one given here.) - ^ a b c Hughes-Hallett, Deborah; McCullum, William G. (2005). Calculus (4th ed.). Wiley. p. 340.
So far, we have three ways of estimating an integral using a Riemann sum: 1. The left rule uses the left endpoint of each subinterval. 2. The right rule uses the right endpoint of each subinterval. 3. The midpoint rule uses the midpoint of each subinterval.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Ostebee, Arnold; Zorn, Paul (2002). Calculus from Graphical, Numerical, and Symbolic Points of View (Second ed.). p. M-33.
Left-rule, right-rule, and midpoint-rule approximating sums all fit this definition.
- ^ Swokowski, Earl W. (1979). Calculus with Analytic Geometry (Second ed.). Boston, MA: Prindle, Weber & Schmidt. pp. 821–822. ISBN 0-87150-268-2.
- ^ Ostebee, Arnold; Zorn, Paul (2002). Calculus from Graphical, Numerical, and Symbolic Points of View (Second ed.). p. M-34.
We chop the plane region R into m smaller regions R1, R2, R3, ..., Rm, perhaps of different sizes and shapes. The 'size' of a subregion Ri is now taken to be its area, denoted by ΔAi.
- ^ Swokowski, Earl W. (1979). Calculus with Analytic Geometry (Second ed.). Boston, MA: Prindle, Weber & Schmidt. pp. 857–858. ISBN 0-87150-268-2.

![{\displaystyle f:[a,b]\rightarrow \mathbb {R} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fc0d2d0b70573525d149ab82948308455d1853d0)
![{\displaystyle [a,b]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9c4b788fc5c637e26ee98b45f89a5c08c85f7935)

![{\displaystyle P=\left\{[x_{0},x_{1}],[x_{1},x_{2}],\dots ,[x_{n-1},x_{n}]\right\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/096b0a34cf6fae9227f91ca153b55cb9f60e4492)




![{\displaystyle x_{i}^{*}\in [x_{i-1},x_{i}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/dafeab86f1179399f11208ee27a15c76434aed3d)


![{\displaystyle [x_{i-1},x_{i}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/09cb12a889d47020c8ce7046a2eb60785e00c0b6)




![{\displaystyle f(x_{i}^{*})=\sup f([x_{i-1},x_{i}])}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/dff7dfd2109629595f3fdf32681f3e6f7009c047)
![{\displaystyle f(x_{i}^{*})=\inf f([x_{i-1},x_{i}])}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a7b2f108cd78e38003810fff4cdccbdd4d37c77a)







![{\displaystyle A_{\mathrm {left} }=\Delta x\left[f(a)+f(a+\Delta x)+\cdots +f(b-\Delta x)\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b6d14c13eac60f7ba80b6f3d2b87e05793405521)
![{\displaystyle A_{\mathrm {right} }=\Delta x\left[f(a+\Delta x)+f(a+2\,\Delta x)+\cdots +f(b)\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/de29f56f0cace533130d4d5c66bea17903c62b92)



![{\displaystyle A_{\mathrm {mid} }=\Delta x\left[f(a+{\tfrac {\Delta x}{2}})+f(a+{\tfrac {3\,\Delta x}{2}})+\cdots +f(b-{\tfrac {\Delta x}{2}})\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/69c42f45536d54527d206d3f7aec8ccd3f40dcbd)




![{\displaystyle A_{\mathrm {trap} }={\tfrac {1}{2}}\,\Delta x\left[f(a)+2f(a+\Delta x)+2f(a+2\,\Delta x)+\cdots +f(b)\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f07f5b1bcccbd39b36b8a42d8ecca201676f3bf7)



































