Sulfanilic acid

| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid[1] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.075 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 173.19 |
| Density | 1.485 |
| Melting point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| 12.51 g/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.23 (H2O)[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related sulfonic acids
|
Benzenesulfonic acid p-Toluenesulfonic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sulfanilic acid (4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) is an off-white crystalline solid which finds application in quantitative analysis of nitrate and nitrite ions. The solid acid exists as a zwitterion, and has an unusually high melting point.[3]
Synthesis
Sulfanilic acid can be produced by sulfonation of aniline:[4]

Applications
As the compound readily forms diazo compounds, it is used to make dyes and sulfa drugs.[3] This property is also used for the quantitative analysis of nitrate and nitrite ions by diazonium coupling reaction with N-(1-Naphthyl)ethylenediamine, resulting in an azo dye, and the concentration of nitrate or nitrite ions were deduced from the color intensity of the resulting red solution by colorimetry.[5]
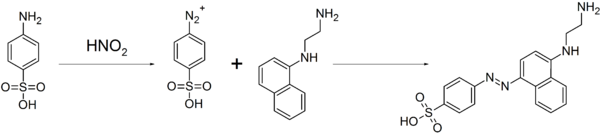
It is also used as a standard in combustion analysis and in the Pauly reaction.
Derivatives
- Methyl orange (azo coupling with dimethylaniline)
- Acid orange 7 (azo coupling with 2-naphthol)
- Chrysoine resorcinol (azo coupling with resorcinol)
End uses
Sulfanilic acid has four primary end uses. It is used as an intermediate in the production of yellow food dye, specific pharmaceutical applications, optical brighteners for white paper and as a concrete additive. The sulfanilic acid intermediate can be purchased in four different grades: technical grade, pure grade, sodium sulfanilate solution and sodium sulfanilate dry powder.
See also
References
- ^ a b Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 789. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
The name 'sulfanilic acid' is not retained.
- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 5–88. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ^ a b "Sulphanilic acid". A Dictionary of Chemistry. Oxford University Press, 2000. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann: Organische Chemie, 2nd Edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 511, ISBN 3-342-00280-8.
- ^ G. H. Jerffery; J. Bassett; J. Mendham; R. C. Denney (1989). "Colorimetry and Spectrophotometry". Vogel's Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 5th Edition. Longman. p. 702. ISBN 0-582-44693-7.
