Mihirakula
| Mihirakula | |
|---|---|
| Ruler of the Alchon Huns | |
 | |
| Reign | 515-540 |
| Predecessor | Toramana |
| Successor | Toramana II Pravarasena |


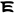 )
)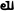

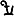



 ,[1] (Ja)yatu Mihirakula ("Let there be victory to Mihirakula").[2] Rev: Dotted border around Fire altar flanked by attendants in the Sasanian Empire style.[3][4][5]
,[1] (Ja)yatu Mihirakula ("Let there be victory to Mihirakula").[2] Rev: Dotted border around Fire altar flanked by attendants in the Sasanian Empire style.[3][4][5]
| Alchon Huns (400–670 CE) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mihirakula (Gupta script: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , Mihirakula), also Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was one of the most important rulers of the Alchon Huns, who led a conquest and gained temporary control of Gandhara, Kashmir, northern and central India. Mihirakula was a son of Toramana, both of Huna heritage, and ruled the Indian part of the Hephthalite Empire. Mihirakula ruled his empire from 502 to 530,[6] from his capital of Sagala (modern-day Sialkot, Pakistan).[7][8]
, Mihirakula), also Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was one of the most important rulers of the Alchon Huns, who led a conquest and gained temporary control of Gandhara, Kashmir, northern and central India. Mihirakula was a son of Toramana, both of Huna heritage, and ruled the Indian part of the Hephthalite Empire. Mihirakula ruled his empire from 502 to 530,[6] from his capital of Sagala (modern-day Sialkot, Pakistan).[7][8]
According to Xuanzang, Mihirakula initially was interested in Buddhism, but after being insulted by Buddhist monks, he turned anti Buddhist.[9] According to Buddhist texts, the Huna king Mihirakula was extremely cruel and barbaric.[10][6][11] He destroyed Buddhist sites, ruined monasteries, killed monks[12]. Yashodharman and Gupta Empire rulers, in and after about 532 CE, reversed Mihirakula's campaign and ended the Mihirakula era.[13][14]
Etymology
The name "Mihirakula" is most likely of Iranian origin and may have the meaning "Mithra's Begotten", as translated by Janos Harmatta.[15] According to Harold Walter Bailey: "A name like Toramana and his son's name Mihirakula interpreted by North Iranian (and not by Western Iranian) are clearly Iranian".[16]
Description
According to Krishna Chandra Sagar, the Huna king Toramana was cruel and barbaric, his son Mihirakula even more so, during their rule.[13] Mihirakula had conquered Sindh by 520 CE, had a large elephant and cavalry-driven army. Mihirakula destroyed Buddhist sites, ruined monasteries, according to Sagar. Yashodharman, about 532 CE, reversed Mihirakula's campaign and started the end of Mihirkula era.[13][10] Mihirakula issued coins, like the Kushana era kings, showing Oesho or Shiva, which suggests that he may also have patronized Shaivism. Other scholars state that there are many legends surrounding this era and historical facts are difficult to ascertain. The Chinese pilgrim Xuanzang (Hsuan Tsang) mentions Mihirakula as conquering Kashmir first, then Gandhara. He is also mentioned as attempting to conquer central and eastern India, but getting vanquished by Yashodharman and the Gupta king Narasimhagupta Baladitya. Mihirakula was captured during the war, but his life spared because Baladitya's mother intervened and argued against capital punishment.[14][17] He returned to Kashmir, states the Chinese pilgrim, with treachery seized power, attacked Gandhara, then died within a few months.[14]
Cosmas Indicopleustes
The 6th-century Alexandrian traveler Cosmas Indicopleustes states that the Hephthalites in India reached the zenith of its power under "Gollas", which is thought to be the same as Mihirakula from the last part of his name.[18][19]
"Higher up in India, that is, farther to the north, are the White Huns. The one called Gollas when going to war takes with him, it is said, no fewer than two thousand elephants, and a great force of cavalry. He is the lord of India, and oppressing the people forces them to pay tribute.
Xuanzang
"The Record of the Western Regions" by the 7th-century Chinese traveler Hsüan-tsang states that Mihirakula destroyed Buddhism and killed monks in Gandhara.[20] Xuanzang wrote in 630 CE that Mihirakula had conquered all India. The Narasimhagupta Baladitya defeated Mihirakula who was finally captured by the Indian king, who later spared his life.[20] Xuanzang states that while Mihirkula lost his conquest, his brother seized power in Kashmir and Gandhara. Mihirakula returned to Kashmir, with treachery seized the throne, attacked Gandhara but died within a year.[14]
There was a king called Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo (Mahirakula), who established his authority in this town (Sagala) and ruled over India. He was of quick talent, and naturally brave. He subdued all the neighbouring provinces without exception.
— Xuanzang "The Record of the Western Regions"[21]
Gwalior inscription
The Gwalior inscription issued in the 15th regnal year created by Matricheta in a Surya temple, mentions Mihirakula. It confirms that Mihirakula reign had included Gwalior around 535 CE.
Sondani columns inscription
Mihirakula suffered a defeat by the Aulikara king Yasodharman of Malwa[22] in 528, and the Gupta emperor Narasimhagupta who previously paid Mihirakula tribute. The defeat at the battle of Sondani, resulted in the loss of Alchon possessions in the Punjab and north India by 542.[23]
Notes
- ^ The "h" (
 ) is an early variant of the Gupta script, seen for example in the Chandragupta type
) is an early variant of the Gupta script, seen for example in the Chandragupta type
- ^ The "h" (
 ) is an early variant of the Gupta script, seen for example in the Chandragupta type
) is an early variant of the Gupta script, seen for example in the Chandragupta type
- ^ Verma, Thakur Prasad (2018). The Imperial Maukharis: History of Imperial Maukharis of Kanauj and Harshavardhana (in Hindi). Notion Press. p. 264. ISBN 9781643248813.
- ^ Sircar, D. C. (2008). Studies in Indian Coins. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 376. ISBN 9788120829732.
- ^ Tandon, Pankaj (2013). Notes on the Evolution of Alchon Coins Journal of the Oriental Numismatic Society, No. 216, Summer. Oriental Numismatic Society. pp. 24–34. also Coinindia Alchon Coins (for an exact description of this coin type)
- ^ a b Grousset, Rene (1970), The Empire of the Steppes, Rutgers University Press, p. 71, ISBN 0-8135-1304-9
- ^ Bakker, Hans (16 July 2014). The World of the Skandapurāṇa. BRILL. ISBN 9789004277144.
- ^ Dani, Ahmad Hasan (1999). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The crossroads of civilizations: A.D. 250 to 750. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 9788120815407.
- ^ Singh, Upinder (2017). Political Violence in Ancient India. Harvard University Press. p. 241. ISBN 978-0-674-97527-9.
- ^ a b Mihirakula, Encyclopaedia Britannica
- ^ Behrendt, Kurt A. (2004). Handbuch der Orientalistik. BRILL. ISBN 9789004135956.
- ^ https://archive.org/details/wonderthatwasind00alba/page/266/mode/2up
- ^ a b c Foreign Influence on Ancient India by Krishna Chandra Sagar p.216
- ^ a b c d Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (1977). Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 242–244. ISBN 978-81-208-0436-4.
- ^ Janos Harmatta, "The Rise of the Old Persian Empire: Cyrus the Great," AAASH Acta Antiqua Acadamie Scientiarum Hungaricae 19, 197, pp. 4-15.
- ^ Bailey, H. W. (1982). Culture of the Sakas in Ancient Iranian Khotan. Caravan Books. p. 81.
- ^ Louis Renou; Jean Filliozat (1957). Political history of India from the earliest times to the 7th century A.D. by J. Filliozat. Susil. pp. 176–183.
- ^ Dani, Ahmad Hasan (1999). History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The crossroads of civilizations, A.D. 250 to 750. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. p. 142. ISBN 8120815408. Retrieved 5 November 2012.
- ^ Indian History. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 396. ISBN 9781259063237.
- ^ a b Early Buddhist Transmission and Trade Networks by Jason Neelis p.168
- ^ Hsüan-tsang, ca 596-664; Beal, Samuel (1884). Si-yu-ki, Buddhist records of the Western world;. London : Trübner. p. 167.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Ojha, N.K. (2001). The Aulikaras of Central India: History and Inscriptions, Chandigarh: Arun Publishing House, ISBN 81-85212-78-3, p.52
- ^ Klaus Vondrovec (2014). Coinage of the Iranian Huns and Their Successors from Bactria to Gandhara (4th to 8th Century CE). ISBN 978-3-7001-7695-4.
