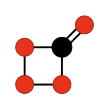
Carbon tetroxide
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3-Trioxetan-4-one
| |||
| Other names
4-Trioxetanone
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.007 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Carbon tetroxide is a highly unstable oxide of carbon with formula CO
4. It was proposed as an intermediate in the O-atom exchange between carbon dioxide (CO
2) and oxygen (O
2) at high temperatures.[1] The C2v isomer, which is -138 kJ mol−1 more stable than the D2d isomer, was first detected in electron-irradiated ices of carbon dioxide via infrared spectroscopy.[2]

The isovalent carbon tetrasulfide is also known from inert gas matrix. It has D2d symmetry with the same atomic arrangement as CO4 (D2d).[3]
References
- ^ Yeung, L. Y.; Okumura, M.; Paci, J. T.; Schatz, G. C.; Zhang, J.; Minton, T. K. (2009). "Hyperthermal O-Atom Exchange Reaction O2 + CO2 through a CO4 Intermediate" (PDF). Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (39): 13940–13942. doi:10.1021/ja903944k. PMID 19743846.
- ^ Jamieson, Mebel, & Kaiser. "Novel Detection of the C2v isomer of carbon tetraoxide (CO4", Chemical Physics Letters, 440 (2007) 105.
- ^ Maity, Surajit; Kim, Y.S.; Kaiser, Ralf I.; Lin, Hong Mao; Sun, Bian Jian; Chang, A.H.H. (July 2013). "On the detection of higher order carbon sulfides (CSx; x=4–6) in low temperature carbon disulfide ices". Chemical Physics Letters. 577: 42–47. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2013.05.039.