Elizabeth Murray (painter)
Elizabeth Murray | |
|---|---|
 Dotty Dimple, a watercolour by Elizabeth Murray in 1869 | |
| Born | Elizabeth Heaphy 1815 |
| Died | 8 December 1882 (aged 66–67) |
| Nationality | English |
| Other names | Elizabeth Heaphy Murray |
| Occupation(s) | Painter, author |
| Notable work | Sixteen Years of an Artist's Life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands |
| Spouse | Henry John Murray |
| Parents |
|
| Family |
|
Elizabeth Murray (1815 – 8 December 1882), born Elizabeth Heaphy, was a British watercolourist. She primarily painted portraits and landscapes of the Canary Islands, where she lived for ten years. She was a member of the Royal Institute of Painters in Water Colours, and she founded the Society of Female Artists in London.
Murray's father was Thomas Heaphy, also a watercolour painter. She first learned to paint from him, and they travelled and painted together. She continued to travel and live across the world, and paint scenes and portraits from these places: in particular, Rome, Morocco, the Canary Islands (particularly Tenerife), and New England. She married Henry John Murray, a British consul whom she met when living in Morocco, and moved with him as he was assigned to the Canary Islands.
In 1859, Murray published a two-volume monograph, Sixteen Years of an Artist's Life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands. This was received negatively in the Canary Islands because of its criticism of Canarian society, Spanish officials, and its comments about the decline of Tenerife. Possibly because of the resultant animosity towards the Murrays, her husband requested to be transferred to a new location, and in 1860 they moved to Portland, Maine in the United States where he took up a new consulate position.
Biography
Elizabeth Heaphy was born in 1815 in London to Mary Stevenson and Thomas Heaphy. Thomas Heaphy was a prolific watercolour painter[1] and a founding member of the Royal Society of British Artists. He primarily painted battle scenes and portraits of officers, such as the one he painted of Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington.[2]
Heaphy grew up in an environment that allowed her to cultivate her artistic abilities. She played with her father's anatomical figures, and began to study and practice drawing with them.[2] Around 1820, when she was five years old, her mother died.[1][3]
Heaphy had four siblings: Thomas and Mary Ann, who were also both painters, Charles, an explorer and soldier, and another sister whose name is unknown.[3]
Stay in Rome (1831)
In 1831, Heaphy moved to Rome along with her father and her brother Thomas. She developed her painting skills here, influenced by the atmosphere of the city. Her work drew the attention of French painter Horace Vernet, who was surprised with her ability and became interested in her studies. However, Vernet returned to France on 1 January 1835 at the request of King Louis Philippe I, who wanted him to paint the Palace of Versailles.[4]
During her stay in Rome, where she became known as the petite anglaise (little Englishwoman), she painted ancient sculptures and scenes of everyday life.[4]
Return to England
On her return trip to England, Heaphy and her father stopped in Cambrai, France. Finding the city beautiful, she sat down to paint and attracted the attention of a crowd. However when she finished her painting, she was accused of being a spy and taken to prison. She left prison after a few hours and was placed under surveillance at a hotel while her father's coach was searched. When the French authorities didn't find any papers related to political affairs, Heaphy and her father were released. They were invited to paint the fortresses within the city, but her father refused and they left the city.[4]
Stay in Morocco (1842–1850)
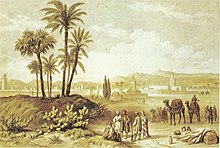
During her time in Morocco, Elizabeth became fascinated by the Moroccan landscape, the souq, and the local women. This became the first volume of her work Sixteen Years of an Artist's Life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands, in which she described Morocco and her adventures. She had decorated her home "in a Moorish–English mix", and called it her "dollhouse". It had a large patio, and a fresco depicting flowers and birds. During the French bombing of Morocco, there was a period of time where she converted it into a merchandise warehouse.[4]
In 1846, Heaphy married Henry John Murray, a British consul in Tangier. From that time on, she would move along with her husband as a part of his work with the consulate. After her marriage she began to sign her paintings as "Elizabeth Murray" instead of "E. Heaphy".[1]
In 1849, Richard Bartlett, the British consul general in the Canary Islands, died.[5] As a result, Henry John Murray was appointed by the Queen as British consul general to the Canary Islands on 23 August 1850.[6]
Stay in Tenerife (1850–1859)
On their way to the Canary Islands, the Murrays passed through Andalusia, where they visited Cádiz and Seville. While in Andalusia she began to take interest in the paintings of Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, for whom she began to feel "a great predilection". She also marvelled at the Seville Cathedral. On her journey to the Canary Islands, she studied the other passengers and painted some of them. When she was 120 miles from Tenerife, she was able to see Mount Teide, and her first impression was full of imagination because of its splendour and characteristics:
The atmosphere is clear, soft, and grateful to the eye, persuaded by that mellow light in which every object of sight is seen with a distinctness of outline and a depth of colour that impress their image with such vividness on the mind that the imagination can at any time recall their principal features. He that her eyes to see, and has once beheld the Peak of Teneriffe in all its glory, can never forget a spectacle which has nothing to match in any other part of the world.
— Elizabeth Heaphy de Murray, Sixteen years of an artist's life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands[7]
She arrived in Tenerife on 23 August 1850 on the warship Hibernia. She travelled around the entire island, noting her observations for her monograph and painting both landscapes and everyday life.[1]
In her monograph she rarely mentions her husband, saying he is sometimes very busy and that this is why she spent large amounts of time in the countryside. He was very good at his job, both for Britain and the Canary Islands, for whom he offered all his help when they were enduring periods of economic difficulty.[4] However, surviving newspapers that mention the Murrays' presence focus on Elizabeth and her works, not her husband.[8]
The first place that Murray visited was La Matanza de Acentejo, where she stayed in a house where she could see Teide, describing the town as providing perhaps the best view of the volcano than anywhere else on the island. She also stayed in places including La Orotava and Puerto de la Cruz. She travelled to Gran Canaria with a group of Englishmen, describing Las Palmas as sad and uninteresting but its inhabitants as kind and pleasant.
During one of her trips to London, Murray founded The Society of Female Artists. Some years before this, she was named a member of the Royal Institute of Painters in Water Colours.[1]
Involvement with the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Miguel Arcángel
On 31 October 1849, Queen Isabella II decreed the creation of the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Miguel Arcángel (RACBA; the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Miguel Arcángel), headquartered in the capital city Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Seven months later, in May 1850, Murray was named Honorary Academic of RACBA and became fully involved in the Academy's activities. She participated in all exhibitions between 1850 and 1856, and became well-recognised for her work.[9][10] In her first exhibitions she showed paintings of the places she had visited such as Greece, Morocco, and Seville; later she exhibited her paintings of the Canarian landscape and the people in Tenerife.[1]
Murray introduced the watercolour technique in the Canary Islands. Her works depicting the Canary Island landscapes stood out, although she mostly devoted herself to portraiture. Her passion for architecture led her to study and paint the architecture of the Canary Islands, such as the Augustinian convents in Los Realejos and Icod de los Vinos, and the towers of the Church of La Concepción and of Santo Domingo.[11]
Friendship with the Diston family

The Murrays were close friends with the Diston family. Alfred Diston was born on 8 January 1793 in Lowestoft, England and arrived in the commercial centre of Puerto de la Cruz in Tenerife in 1810. Here he married María Soledad de Orea, with whom he had a daughter, Soledad "Solita" Diston y Orea.[12][13] He was named an Honorary Academic of RACBA on 24 October 1851, possibly sponsored by French naturalist and ethnologist Sabin Berthelot.
His relationship with the Murray family is reflected in Diston's diaries. Elizabeth Murray also painted a portrait of Diston and was in charge of his daughter Solita's artistic education. Solita's first exhibition was with RACBA in 1854, and she later went to England with Murray to continue her studies.
Description and criticism of Canarian society (1859)

In 1859, Murray published her monograph Sixteen Years of an Artist's Life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands. In it she described Canarian society at that time and explained some questions regarding her artwork and the representation of said society. Alfred Diston's contribution to support Murray, Notes furnished Mrs. Murray for her intended work on these islands, was very important.[14] Its description was historically and culturally significant with regards to the festivities, customs, and folklore of the islands, as well as demographic data and descriptions of the cities.[1]
However, society disapproved of Murray's work because of her criticism of Canarian society; for her references to Spanish officials, whom she described as negligent and dishonest;[8] and for her comments about the decline of Tenerife.[11]
Her monograph, which was written in English, was publicised in the Canarian press and immediately received negative reviews. Criticism was published in El Omnibus, a literary review and news publication from Las Palmas, but became more intense when El Eco del Comercio translated to Spanish and published some of her chapters referring to the Canary Islands. From this point on, her fame began to decline and she stopped being accepted in artistic circles.[1]
The Murrays' decline in popularity as a result of the monograph's publication is possibly why Consul Murray requested to be transferred to a new location.[8] On 3 March 1860, he was assigned to the American states of Maine and New Hampshire, and the Murrays moved to Portland, Maine.
Stay in Portland (1860–1876)
Murray was very active during the sixteen years she lived in the United States. She is mentioned in Portland newspapers such as the Portland Daily Press, and in works like Portland and Vicinity by Edward H. Elwell.
Murray also resumed writing, although she stopped writing about her travels and instead wrote about more technical questions about painting with watercolours. Her work culminated in writing The Modern System of Painting in Watercolour from the Living Model. Historian José Luis García Pérez has considered two possible reasons for her change in writing style: the fear of making new enemies as a result of her writing, and the absence of the type of exoticism she found in Morocco and Spain; he favours the latter hypothesis.[1]
Later years
On 8 May 1876, Henry Murray was assigned to Buenos Aires. However, historian José Luis García Pérez has pointed out that the only evidence of this assignment is the official registration of his destination by the Foreign and Commonwealth Office. On 1 October 1879, Henry Murray retired from his diplomatic duties. Elizabeth Murray died on 8 December 1882 in San Remo, although there is also a source saying she died in February 1882.[1]
Artwork
Murray primarily worked in watercolour to paint portraits, miniatures, and landscapes featuring Mediterranean and Orientalist themes. Her early work was clearly influenced by her father, Thomas Heaphy; after his death she expanded her artistic style to include landscapes from her trips to Morocco, Andalusia, and the Canary Islands. Her paintings are Romantic, with Victorian brushstrokes.[1]
Artistic context: Romantic and Victorian
Romanticism was a cultural movement that not only sought to break away from classicism and rococo, but was also a movement in opposition to the ideas of the Enlightenment (such as rationalism) and principles such as order, calm, and harmony. It emphasised individualism and the subjective.[15]
English painters painted the geography of other regions and ancient cities, usually medieval. Many English painters who were on their way to other parts of Europe, such as Switzerland or Italy, settled in France. Although Murray didn't settle in France, she did travel through the country when travelling to and from Italy. However, Murray practiced painting landscapes primarily when she stayed in Morocco and the Canary Islands. During her time in Spain she felt especially attracted to Seville, as did Richard Ford, a traveller and Hispanist who wrote about his travels in Spain and possibly gave Murray the idea to write about her trips.[16][1] Murray was part of a group of travellers who, like herself, described Spain as a country with a lot of fervour and vitality, even as it was impacted by apathy and backwardness. These travellers and their romantic spirit helped to develop a romantic image of Spain.[1]
Influences

Murray's primary influence was that of her father, Thomas Heaphy, a great portrait painter who used precise strokes to paint realistic faces of the people he was portraying. During her stay in Rome under the tutelage of Horace Vernet, Murray improved her skills and learned a good sense of composition.[1]
She was also influenced by Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, who she admits to admiring in her monograph. She went on to copy one of his paintings, La visión de San Antonio de Padua, which was exhibited at the Academia de Bellas Artes de Santa Cruz de Tenerife in 1850.[1][4]
Technique and materials
Murray primarily worked with watercolours. Watercolour began to be used in England at the beginning of the 18th century, using the "traditional English method" which consisted of superimposing fine layers of carefully mixed colours to create the intended effects of colour and depth.[17] However, Murray didn't use the traditional methods, but instead usually used the gouache technique in her works. Her works stand out for their colourful palette, in which she abundantly used chestnut, blue, violet, pink, black, scarlet, and gold, as well as olive and tar colours applied in bright and intense shades. Her portraits were highly accurate and delicate.[1]
Composition
Murray created portraits with the same style, especially across gender. She looked for parallelism around a vertical axis, but did not look for perspective. In some portraits she used foreshortening, such as in Beggars at a church door at Rome.[18] In some of her works, Murray uses up to eight different people in the parallels she establishes; in this sense she differs from her father, as he used a greater number of subjects in his paintings. The colours and tonalities in her paintings are similar to those of her father's.
Works
José Luis García Pérez has pointed out that it is difficult to know the exact dates Murray's paintings were created, and that because of her travels it is likely she sketched the initial drawings and then took more time to finish them.[1] Many of the dates of her paintings refer to the year they were exhibited—when she arrived in a new place she tended to exhibit work from where she had previously been, so when she arrived in the Canary Islands she exhibited work with Greek and Moroccan themes, and when she arrived in Portland she exhibited her work related to Spain.
Murray created around 85 pieces that can be divided into three groups: portraits, which were the highlights of her artwork; general scenes; and landscapes.[1]
Disciples
Murray's constant moves prevented her from having a large number of disciples. There is no record of her having any disciples during her time in Morocco. During her ten years in the Canary Islands, she had two pupils: Soledad Diston and Juan B. Fierro Van de Walle Fierro y Valcarcel. Murray also had a group of American disciples during her time in Portland.
Soledad Diston y Orea
Soledad Diston, also known as Solita, was born on 2 November 1837 in Puerto de la Cruz. She was the daughter of Alfred Diston and María de la Soledad de Orea.[11][19] She was 13 years old when Murray arrived in the Canary Islands. The quick friendship between the Murrays and Distons meant that Soledad's first artistic endeavours were under the tutelage of Elizabeth Murray. She even travelled with Murray to Tenerife to continue her studies.[4]
In 1854, Soledad Diston joined Murray in an exhibition at the Academia de Bellas Artes de Santa Cruz de Tenerife. She also created a floral tapestry to adorn the church in the port of La Orotava during the Feast of Corpus Christi on 29 May 1856.
Most of Diston's works were portraits that accurately captured peoples' faces. Among them are Retrato de San Juan Nepomuceno;[10] one of her brother, Francisco Diston y Orea;[11] one of her maternal grandmother, Doña Francisca de Luna y Médicis de Orea; Daniel Tierney; Doña Fanny Hamilton y Edwards; Don Juan N. Verdugo y Dapelo; and Don Pedro Grijalba. However, her artistic career was not very long; it was interrupted by her marriage, during which she didn't continue her art.[4]
Juan B. Fierro y Van de Walle Fierro y Valcárcel
Juan B. Fierro y Van de Walle Fierro y Valcárcel was born in Santa Cruz de La Palma on 8 May 1841. He was captain of the island militias and deputy of the island of La Palma on several occasions. He was also the director of La Cosmológica, a scientific society founded in the last quarter of the 19th century during a time when many such societies were being founded in the Canary Islands, such as the Museo Etnográfico y de Historia Natural (Ethnographic and Natural History Museum) which was founded in 1881.[20][4]
Researcher José Luis García Pérez attests that he was a disciple of Murray through the artist's grandson, who owns Murray's painting La Odalisca. Fierro created a large number of costumbrista paintings, and watercolours of the typical clothing in La Palma. The latter are reminiscent of Diston's work, but with stronger colours and poorly-drawn faces. Fierro also practiced caricature and painting on photographs. Four of his most notable paintings are Puerto de Santa Cruz de La Palma, painted 2 May 1876; Rada de Santa Cruz de La Palma, from 1883; La Plaza de Santo Domingo en Santa Cruz de la Palma, from 1891; and the portrait D. Félix Poggio y Lugo.[4]
Fierro died on 2 November 1930 in his hometown, at the age of 89.
American disciples
Murray arrived in the United States at the time when watercolour and gouache were gaining interest from young artists. The geographical separation of the American continent and Europe affected the development of artists and their work; the arrival of foreign artists encouraged their development, and they began to see nature through the eyes of their teachers. Murray's exhibits in academies and artistic societies were among the things that encouraged these artists; additionally, they were surrounded by a group of painters who opened studios to teach. Murray also published The Modern System of Painting in Watercolour from the Living Model in 1865, into which she poured all of her experience.[4]
Two of Murray's American students stand out in particular: Julia C. Furbish in 1864, and Mary Rolfe in 1869. Furbish was successful in the Boston area, and specialised in portraiture. She created a copy of Murray's The Gipsy Cigar Girl, which was quite successful. Rolfe learned to use Murray's painting technique and to use colours like olive; additionally, she was primarily focused on the faces of those she portrayed. Her work Egiptian Girl exhibited with great success at Hale's Art Gallery in 1869. The later trajectory of these two artists, however, is not known.[4]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r García Pérez, José Luis (1982). Elizabeth Murray: un nombre en el siglo XIX [Elizabeth Murray: a name in the 19th century] (in Spanish). Santa Cruz de Tenerife: Aula de Cultura, Cabildo Insular de Tenerife. ISBN 9788450053692. OCLC 16930884.
- ^ a b Clayton, Ellen C. (1876). English Female Authors. Vol. 2. London: Tinsley Brothers. LCCN 11007894. OL 242142W.
- ^ a b O'Donoghue, Freeman Marius. "Heaphy, Thomas (1775-1835)". Dictionary of National Biography, 1885-1900. 25. Smith, Elder & Co.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l García Pérez, José Luis (1980). "Elizabeth Murray". Coloquio de historia canario-americano (in Spanish). IV. Las Palmas, Gran Canaria: Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria: 604–647.
- ^ Notes and Queries: A Medium of Intercommunication for Literary Men, General Readers Etc. ... Oxford University Press. 1904.
- ^ The London Gazette. T. Neuman. 1850. pp. 2301–.
- ^ Murray, Elizabeth (1859). Sixteen years of an artist's life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands. London: Hurst and Blackett.
- ^ "Murray, Elisabeth". Real Academia Canaria de Bellas Artes (in Spanish). Retrieved March 17, 2018.
- ^ a b Hernández Socorro, María de los Reyes; Fuentes Pérez, Gerardo; Gaviño de Franchy, Carlos (2008). El despertar de la cultura en la época contemporánea artistas y manifestaciones culturales del siglo XIX en Canarias [The cultural awakening in the contemporary era: artists and cultural events of the 19th century in the Canary Islands]. Historia cultural de arte en Canarias (in Spanish). Santa Cruz de Tenerife: Viceconsejería de Cultura y Deporte. ISBN 9788479475338. OCLC 868769484.
- ^ a b c d Reina Jiménez, Mª del Carmen (2010). Mujer y cultura en Canarias [Women and culture in the Canary Islands] (PDF) (in Spanish). Las Palmas, Gran Canaria: Colectivo de Mujeres Canarias. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-05-08. Retrieved 2018-03-18.
- ^ González Lemus, Nicolás (2012). "De los viajeros británicos a Canarias a lo largo de la Historia" [Visits by British travellers to the Canary Islands throughout history]. Anuario de Estudios Atlánticos (in Spanish) (58). Las Palmas, Gran Canaria: Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria.
- ^ "Diston, Alfred". Real Academia Canaria de Bellas Artes (in Spanish). Retrieved March 17, 2018.
- ^ Castillo, Francisco Javier; Díaz Alayón, Carmen (2007). "Álvarez Rixo y Elizabeth Murray: Rectificaciones y notas sobre un manuscrito" [Álvarez Rixo and Elizabeth Murray: Corrections and notes on a manuscript]. Revista de Filología de la Universidad de la Laguna (in Spanish) (25): 97–106. ISSN 0212-4130.
- ^ "Romanticism". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- ^ Calvo Serraller, Francisco (1995). La imagen romántica de España: arte y arquitectura del siglo XIX [Romantic imagery of Spain: art and architecture of the 19th century] (in Spanish). Madrid: Alianza Editorial. ISBN 9788420671307. OCLC 34245754.
- ^ Mayer, Ralph; Manuel Ibeas, Juan; Sheehan, Steven (1988). Materiales y técnicas del arte [Art materials and techniques] (in Spanish) (Nueva edición revisada y ampliada ed.). Madrid: Tursen. ISBN 9788487756177. OCLC 36016643.
- ^ Lajo, Rosina; Surroca, José (2001). Léxico de arte [Lexicon of art] (in Spanish) (4a ed.). Tres Cantos, Madrid: Akal, D.L. ISBN 9788446009245. OCLC 630319810.
- ^ Lorenzo-Cáceres, Andrés de (1931). "Costumes of the Canary Islands". Revista de historia (in Spanish). 4 (31). La Laguna de Tenerife: Facultad de Filosofía y Letras de la Universidad de La Laguna: 82–84.
- ^ Aguilar Janeiro, María del Carmen (1991–1992). "La sociedad 'La cosmológica' de Santa Cruz de La Palma: pasado, presente y futuro" [The society 'La Cosmológica' of Santa Cruz de La Palma: past, present and future]. Parabiblos: Cuadernos de Biblioteconomía y Documentación (in Spanish) (5–6). Las Palmas, Gran Canaria: Asociación Canaria de Archiveros, Bibliotecarios y Documentalistas: 69–71.
External links
 Media related to Elizabeth Murray at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Elizabeth Murray at Wikimedia Commons English Wikisource has original text related to this article: Elizabeth Murray
English Wikisource has original text related to this article: Elizabeth Murray Spanish Wikiquote has quotations related to: Elizabeth Murray
Spanish Wikiquote has quotations related to: Elizabeth Murray- Sixteen Years of an Artist's Life in Morocco, Spain, and the Canary Islands on Wikisource and Internet Archive
