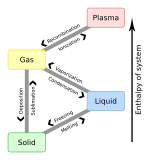
Vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor.[1] There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon.

Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapour (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation occurs on the surface. Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapour of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure. For example, due to constantly decreasing pressures, vapor pumped out of a solution will eventually leave behind a cryogenic liquid.
Boiling is also a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase, but boiling is the formation of vapor as bubbles of vapor below the surface of the liquid. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapor pressure of the substance is greater than or equal to the environmental pressure. The temperature at which boiling occurs is the boiling temperature, or boiling point. The boiling point varies with the pressure of the environment.
Sublimation is a direct phase transition from the solid phase to the gas phase, skipping the intermediate liquid phase. Because it does not involve the liquid phase, it is not a form of vaporization.
The term vaporization has also been used in a colloquial or hyperbolic way to refer to the physical destruction of an object that is exposed to intense heat or explosive force, where the object is actually blasted into small pieces rather than literally converted to gaseous form. Examples of this usage include the "vaporization" of the uninhabited Marshall Island of Elugelab in the 1952 Ivy Mike thermonuclear test.[2]
At the moment of a large enough meteor or comet impact, bolide detonation, a nuclear fission, thermonuclear fusion, or theoretical antimatter weapon detonation, a flux of so many gamma ray, x-ray, ultraviolet, visual light and heat photons strikes matter in a such brief amount of time (a great number of high-energy photons, many overlapping in the same physical space) that all molecules lose their atomic bonds and "fly apart". All atoms lose their electron shells and become positively charged ions, in turn emitting photons of a slightly lower energy than they had absorbed. All such matter becomes a gas of nuclei and electrons which rise into the air due to the extremely high temperature or bond to each other as they cool. The matter vaporized this way is immediately a plasma in a state of maximum entropy and this state steadily reduces via the factor of passing time due to natural processes in the biosphere and the effects of physics at normal temperatures and pressures.
A similar process occurs during ultrashort pulse Laser ablation, where the high flux of incoming electromagnetic radiation strips the target material's surface of electrons, leaving positively charged atoms which undergo a coulomb explosion.[3]
References
- ^ Britannica: Vaporization Archived 2009-11-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ PBS American Experience "Mike" Test Archived 2017-02-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ GmbH, Dirk Müller, Lumera Laser. "Picosecond Lasers for High-Quality Industrial Micromachining". Retrieved 2018-02-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
To From
|
Solid | Liquid | Gas | Plasma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | Melting | Sublimation | ||
| Liquid | Freezing | Vaporization | ||
| Gas | Deposition | Condensation | Ionization | |
| Plasma | Recombination |