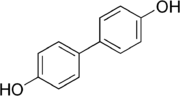
4,4'-Biphenol
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-diol | |
| Other names
4,4'-Dihydroxybiphenyl
4,4'-Diphenol 4,4'-Biphenyldiol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.001 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 186.210 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless or white solid |
| Melting point | 283 °C (541 °F; 556 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | Sublimes |
| Insoluble in water Soluble in ethanol and ether | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | > 93.3 °C (199.9 °F; 366.4 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4,4'-Biphenol is an organic compound which is a phenolic derivative of biphenyl. It is a colorless solid.
4,4'-Biphenol is prepared by dealkylation of the tetra t-butyl derivative, generated by the oxidative coupling of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol. The oxidative coupling of phenol itself typically gives a mixture of isomers.[2] For example, VCl4 reacts with phenols give 4,4'-, 2,4'-, and 2,2'-biphenols:[3]
- 2 C6H5OH + 2 VCl4 → HOC6H4–C6H4OH + 2 VCl3 + 2 HCl
An earlier process using oxygen and copper salts to enable the oxidative coupling was reported [4]
Safety
Vanadium(IV) chloride is estrogenic[5] and cytotoxic.[6]
References
- ^ Chen, Guoliang; Du, Fangyu; Zhou, Qifan; Liu, Dongdong; Fang, Ting; Shi, Yajie; Du, Yang (2018-01-31). "Dimerization of Aromatic Compounds Using Palladium-Carbon-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling by One-Pot Synthesis (Supporting Information)". Synlett. 29 (06): 779–784. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1591892. ISSN 0936-5214.
- ^ Helmut Fiege; Heinz-Werner Voges; Toshikazu Hamamoto; et al. (2002). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313.
- ^ O’Brien, M. K.; Vanasse, B. (2004). "Vanadium(IV) Chloride". In Paquette, L. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. New York, NY: J. Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rv001.
- ^ Hay, Allan (1971). "Coupling of Phenols With Diphenoquinones". US Patent 3,631,208. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ Kuiper, George G. J. M.; Lemmen, Josephine G.; Carlsson, Bo; et al. (1998). "Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor β". Endocrinology. 139: 4252–4263. doi:10.1210/endo.139.10.6216. PMID 9751507.
- ^ Murakami, Y.; Ishii, H.; Hoshina, S.; et al. (2009). "Antioxidant and Cyclooxygenase-2-inhibiting Activity of 4,4'-Biphenol, 2,2'-Biphenol and Phenol" (pdf). Anticancer Research. 29 (6): 2403–2410. PMID 19528508.
