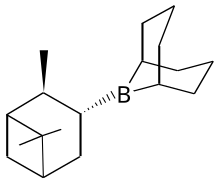
Alpine borane
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
9-(2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-3-yl)-9-bora-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane
| |
| Other names
Alpine-Borane; B-Isopinocampheyl-9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane; B-3-Pinanyl-9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.575 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H31B | |
| Molar mass | 258.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.947 g/mL |
| Boiling point | > 55 °C (131 °F; 328 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H250 | |
| P210, P222, P280, P302+P334, P370+P378, P422 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Alpine borane is the commercial name for an organoboron compound that is used in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid, although it is usually encountered as a solution.
Preparation and reactions
This reagent is generated by treating 9-BBN with α-pinene.
This sterically crowded chiral trialkylborane can stereoselectively reduce ketones, aldehydes, even deutero aldehydes in what is known as the Midland Alpine Borane Reduction, or simply the Midland Reduction:[2]
- C8H12B-pinanyl + RCDO → C8H12BOCHDR + (+)-d-pinene
Hydrolysis of the resulting borinic ester affords the alcohol:
- C8H12BOCHDR + H2O → C8H12BOH + HOCHDR
It is also effective for the stereoselective reduction of certain acetylenic ketones.[3]
Related reagents
A range of alkyl-substituted borane are specialty reagents in organic synthesis. Two such reagents that are closely related to Alpine borane are 9-BBN and diisopinocampheylborane.
References
- ^ R-Alpine-Borane and S-Alpine-Borane at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ M. Mark Midland "B-3-Pinanyl-9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001 John Wiley, New York.doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp173. Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001
- ^ M. Mark Midland and Richard S. Graham. "Asymmetric Reduction of α,β-Acetylenic Ketones with B-3-Pinanyl-9-Borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane: (R)-(+)-1-Octyln-3-ol". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 402.
