Atrioventricular nodal branch
| Atrioventricular nodal branch | |
|---|---|
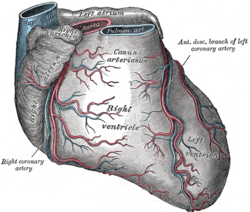 Sternocostal surface of heart. | |
 ARTERIES: RCA = right coronary AB = atrial branches SANB = sinuatrial nodal RMA = right marginal LCA = left coronary CB = circumflex branch LAD/AIB = anterior interventricular LMA = left marginal PIA/PDA = posterior descending AVN = atrioventricular nodal VEINS: SCV = small cardiac ACV = anterior cardiac AIV/GCV = great cardiac MCV = middle cardiac CS = coronary sinus | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ramus nodi atrioventricularis |
| TA98 | A12.2.03.110 A12.2.03.213 |
| TA2 | 4140 |
| FMA | 3851 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The atrioventricular nodal branch is a cardiac artery that is crucial because it feeds the atrioventricular node, necessary for the excitation and contraction of the ventricles. Most frequently (in over 80% of humans) it arises as a distal branch from the right coronary artery near the crux of the heart. In some people, the atrioventricular node instead receives blood from the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery, otherwise known as the left circumflex coronary artery or LCX. Very rarely, in approximately 2% of people, the vascular supply to the atrioventricular node arises from both the right coronary artery and the left circumflex branch. [1]
See also
References
- ^ Sow ML, Ndoye JM, Lo EA. The artery of the atrioventricular node: an anatomic study based on 38 injection-dissections. Surg Radiol Anat 1996;18:183–187
