Battle of Solachon
| Battle of Solachon | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Byzantine Empire | Sassanid Empire | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Philippicus Heraclius the Elder Eiliphredas Vitalius |
Kardarigan Aphraates Mebodes | ||||||
The Battle of Solachon was fought in 586 CE in northern Mesopotamia between the East Roman (Byzantine) forces, led by Philippicus, and the Sassanid Persians under Kardarigan. The engagement was part of the long and inconclusive Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591. The Battle of Solachon ended in a major Byzantine victory which improved the Byzantine position in Mesopotamia, but it was not in the end decisive. The war dragged on until 591, when it ended with a negotiated settlement between Maurice and the Persian shah Khosrau II (r. 590–628).
In the days before the battle, Philippicus, newly assigned to the Persian front, moved to intercept an anticipated Persian invasion. He chose to deploy his army at Solachon, controlling the various routes of the Mesopotamian plain, and especially access to the main local watering source, the Arzamon river. Kardarigan, confident of victory, advanced against the Byzantines, but they had been warned and were deployed in battle order when Kardarigan reached Solachon. The Persians deployed as well and attacked, gaining the upper hand in the centre, but the Byzantine right wing broke through the Persian left flank. The successful Byzantine wing was thrown into disarray as its men headed off to loot the Persian camp, but Philippicus was able to restore order. Then, while the Byzantine centre was forced to form a shield wall to withstand the Persian pressure, the Byzantine left flank also managed to turn the Persians' right. Under threat of a double envelopment, the Persian army collapsed and fled, with many dying in the desert of thirst or from water poisoning. Kardarigan himself survived and, with a part of his army, held out against Byzantine attacks on a hillock for several days before the Byzantines withdrew.
Background
In 572 the Byzantine ruler Justin II (reigned 565–578) refused to renew the annual payments to Sassanid Persia that had been part of the peace agreement concluded by his uncle, Justinian I (r. 527–565) and the Persian shah Khosrau I (r. 531–579) in 562. This marked the culmination of the progressive deterioration of Byzantine–Persian relations over the previous years, which manifested itself in diplomatic and military manoeuvring in their geopolitical periphery. Thus the Byzantines initiated contacts with the Central Asian Göktürks for a joint effort against Persia, while the Persians intervened in Yemen against the Christian Axumites, allies of Byzantium. Justin furthermore regarded the annual tribute as an indignity unworthy of Romans, and used the outbreak of a major revolt in Persian Armenia in 571–572 as a pretext for refusing to continue the payments.[1]
Justin's refusal was tantamount to a declaration of war, the fourth fought between the two great powers of Late Antiquity in the 6th century. After initial Persian successes such as the capture of Dara, the conflict proved inconclusive and became a drawn-out affair, with Byzantine victories followed by Persian successes, intermittent negotiations, and temporary truces.[2] In 582, Maurice (r. 582–602), who had served as a general in the war, ascended to the Byzantine throne at Constantinople; by that time, the Persians had gained the upper hand in Mesopotamia through their capture of Dara in 574, while the Byzantines prevailed in Arzanene.[3]
Initial moves and dispositions

Following the failure of another round of peace negotiations, about which little is known, Maurice appointed his brother-in-law Philippicus as the commander-in-chief for the Mesopotamian front (magister militum per Orientem) in 584.[3] Philippicus raided the region around the major Persian fortress of Nisibis in 584, while in 585 he raided in Arzanene. The Persian commander, Kardarigan—"black hawk", an honorific title rather than a proper name[4]—responded with an unsuccessful siege of Philippicus' main base, Monokarton.[5]
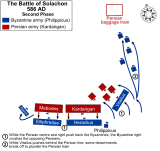
In spring 586 Maurice rejected new Persian proposals involving the conclusion of peace in exchange for renewed payments in gold.[6] The contemporary historian Theophylact Simocatta reports that Philippicus' army was eager to confront the Persians in battle, and the Byzantine commander marched south from his base at Amida, crossed the Arzamon river (modern Zergan in south-east Turkey and north-east Syria) to its eastern bank and advanced some 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) east to the plain of Solachon, where he pitched his camp. This position, south of the fortresses of Mardes and Dara, allowed Philippicus' army to control the passage of the Arzamon river and forced the Persian army under Kardarigan to advance across the waterless plain, away from their supply routes, before meeting the Byzantine force.[7]
On the Persian side, Kardarigan was also eager to fight and confident of victory. He arranged to be escorted by many camels carrying water for his troops in case the Byzantines refused to engage but continued to block access to the Arzamon, and had allegedly prepared iron bars and chains for the prisoners he would take. His movements, however, were detected when the Byzantines' Arab foederati captured a few of his men, allowing Philippicus to prepare his forces. This early warning was of particular importance since Kardarigan intended to attack on Sunday, a day of rest for the Christian Byzantines.[8]
Battle
Both armies appear to have been composed exclusively of cavalry, comprising a mix of lancers and horse-archers, possibly with a few cataphract units included. When Philippicus' scouts reported the Persians' approach, he positioned his men on elevated ground facing the direction from which the Persian army advanced, with his left flank protected by the foothills of Mount Izalas. The Byzantines appear to have been arranged in a single battle line with three divisions. The left division was commanded by Eiliphredas, the dux of Phoenice Libanensis, and included a Hunnic contingent of horse-archers under Apsich. The centre was commanded by the general Heraclius the Elder, later Exarch of Africa and father of Emperor Heraclius (r. 610–641), while the right wing was commanded by the taxiarchos Vitalius.[9] This arrangement was also adopted by the Persians as soon as they came into view of the Byzantine army. On the Persian side, the right division was under Mebodes, the centre under Kardarigan himself, and the left wing under Kardarigan's nephew, Aphraates. Unlike the Persian general, Philippicus remained with a small force at some distance behind the main battle line, directing the battle.[9]
After a short halt to leave their baggage train behind and form a battle line the Persian army quickly advanced on the Byzantines, shooting arrows as they approached. The Byzantines responded in kind and then sallied forth to meet the oncoming enemy. On the Byzantine right Vitalius was quickly victorious, his heavy cavalry breaking through the Persian flank and pushing his opponents to the left behind their own main line. At this point, however, disaster threatened as many of Vitalius' troopers broke formation and headed towards the enemy camp, intending to loot it.[10] Philippicus, however, saw what had happened and reacted quickly. He gave his distinctive helmet to one of his bodyguards, Theodore Ilibinus, and sent him to rally the cavalry on pain of punishment by the army commander himself. The ruse worked: the men recognized the helmet and returned to order just in time to stop the Persians, who had regrouped in the centre and were pushing the numerically inferior Byzantines back.[11]
To counter this, Philippicus ordered the men of the central division to dismount and form a shield-wall with their lances projecting from it (the fulcum formation). It is not clear what happened next, but apparently the Byzantine archers shot at the Persians' horses, breaking their momentum. At the same time, the Byzantine left managed to launch a successful counter-thrust which drove back the opposing Persian right in disarray. Soon the Persian right broke and fled, pursued by the Byzantines.[12] With both wings having disintegrated, the Persian centre was now subjected to an attack from the reformed Byzantine right, which drove them towards the area once occupied by the Persian right. Outnumbered and attacked from several sides, the Persians soon began to break and flee.[12]
The defeated army suffered greatly, not only from the Byzantine pursuit, but also due to lack of water: before the battle, Kardarigan had ordered the water supplies poured to the ground, trying to make his men fight harder to break through the Byzantine army and reach the Arzamon. In addition, the surviving Persians were refused entry into Dara since, according to Simocatta, Persian custom forbade entrance to fugitives. Simocatta also narrates that many Persians died of thirst or from water poisoning when they drank too much water from wells after their ordeal.[13] Kardarigan himself had managed to find refuge on a nearby hilltop with a small detachment and withstood several Byzantine attacks. Finally, after three or four days, the Byzantines, not aware that the enemy commander was there, abandoned the effort. Kardarigan thus escaped, although his men suffered further casualties in the process, up to a thousand according to Simocatta, from Byzantine patrols.[14]
Aftermath
Following the battle Philippicus rewarded the soldiers who had distinguished themselves and divided the spoils of the defeated Persians among them. He then proceeded to invade Arzanene again. However, his attempt to capture the fortress of Chlomaron was thwarted when Kardarigan arrived with reinforcements. The Byzantine army retreated to the fortress of Aphumon, fighting rear-guard actions with the shadowing Persians.[16]
The victory of Solachon allowed the Byzantines to regain the upper hand in the region of the Tur Abdin and, in its aftermath, they began to re-establish their control over the region around Dara.[17] The war continued for a few years without a decision until the revolt of Bahram Chobin caused the rightful Persian shah, Khosrau II (r. 590–628), to find refuge in Byzantine territory. A joint expedition restored him to his throne and a peace treaty was concluded in 591 that left most of Armenia in Byzantine hands.[18]
References
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 131–132, 136–142; Haldon 2001, p. 51.
- ^ Haldon 2001, p. 52; Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 142–166.
- ^ a b Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 167.
- ^ Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 31
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 167–168; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 38–41.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 168; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 41–43.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 168; Haldon 2001, pp. 52–53; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 43–44; Whitby 1988, pp. 280–281.
- ^ Haldon 2001, p. 53; Whitby 1988, p. 281.
- ^ a b Haldon 2001, p. 53.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 169; Haldon 2001, p. 53; Whitby & Whitby 1986, p. 47.
- ^ Haldon 2001, pp. 53, 56; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 47–48.
- ^ a b Haldon 2001, p. 56; Whitby & Whitby 1986, p. 48.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 169; Haldon 2001, p. 56; Whitby & Whitby 1986, p. 49.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 169; Haldon 2001, p. 56; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 48–49.
- ^ Haldon 2001, pp. 54–55.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 169; Whitby & Whitby 1986, pp. 51–55; Whitby 1988, pp. 281–283.
- ^ Whitby 1988, p. 284.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 170–174.
Sources
- Haldon, John (2001). The Byzantine Wars: Battles and Campaigns of the Byzantine Era. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Tempus. ISBN 0-7524-1795-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Greatrex, Geoffrey; Lieu, Samuel N. C. (2002). The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars (Part II, 363–630 AD). London, United Kingdom: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-14687-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Whitby, Michael; Whitby, Mary (1986). The History of Theophylact Simocatta. Oxford, United Kingdom: Claredon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822799-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Whitby, Michael (1988). The Emperor Maurice and his Historian – Theophylact Simocatta on Persian and Balkan Warfare. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-822945-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)