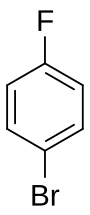
1-Bromo-4-fluorobenzene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Bromo-4-fluorobenzene | |||
| Other names
p-Bromofluorobenzene
p-Fluorophenyl bromide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | PBFB | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.638 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1993 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H4BrF | |||
| Molar mass | 175.000 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Melting point | −16 °C (3 °F; 257 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Structure | |||
| Planar | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H226, H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335, H336 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related halobenzenes
|
1,4-Dichlorobenzene 1,4-Dibromobenzene 1,4-Diiodobenzene | ||
Related compounds
|
Benzene 1,4-Difluorobenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
4-Fluorobromobenzene is a mixed aryl halide (aryl fluoride and aryl bromide) with the formula C6H4BrF. It is a derivative of benzene, with a bromine atom bonded para to a fluorine atom. It has uses as a precursor to some pharmaceuticals, as an agrochemical intermediate, and in organic synthesis.[1] It is a colorless liquid of low acute toxicity.
Production and uses
[edit]4-Fluorobromobenzene is synthesized via bromination of fluorobenzene in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as iron(III) bromide or aluminium tribromide.[2]
4-Bromofluorobenzene is regarded by the Toxic Substances Control Act as a high production volume chemical, that is, a chemical that 1 million pounds (about 500 tonnes) per year is either produced in or imported to the United States. As of 2002, companies producing or importing this compound reported 10 million (4,536,000 kilograms) used. This is up from 500,000 pounds (226,800 kilograms) used in 1986, as reported in the Inventory Update Rule of the Toxic Substances Control Act.[1] [3]
Reactions
[edit]4-Bromofluorobenzene is a standard substrate for cross-coupling reactions[4][5] It forms a Grignard reagent used in the synthesis of 4-fluorophenyl containing compounds,[1][6] such as the pesticide Flusilazole.[7]
Drugs List
[edit]- WIN-35428
- SCH-57871
- Tefludazine & Irindalone
- Seganserin
- Setoperone
- Citalopram
- Paroxetine (from arecoline)
Safety
[edit]This compound is a flammable liquid. It has a flash point of 53 °C.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "4-Bromofluorobenzene [CAS No. 460-00-4] Review of Toxicological Literature" (PDF). National Toxicology Program. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Rosenthal, Joel; Schuster, David I. (2003). "The Anomalous Reactivity of Fluorobenzene in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and Related Phenomena". J. Chem. Educ. 80 (6): 679. Bibcode:2003JChEd..80..679R. doi:10.1021/ed080p679.
- ^ a b "Material Safety Data Sheet". Acros Organics. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Tan, Yichen; Hartwig, John F. (2010). "Palladium-Catalyzed Amination of Aromatic C−H Bonds with Oxime Esters". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (11): 3676–3677. doi:10.1021/ja100676r. PMID 20187645.
- ^ Liégault, Benoît; Lapointe, David; Caron, Laurence; Vlassova, Anna; Fagnou, Keith (2009). "Establishment of Broadly Applicable Reaction Conditions for the Palladium-Catalyzed Direct Arylation of Heteroatom-Containing Aromatic Compounds". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 74 (5): 1826–1834. doi:10.1021/jo8026565. PMID 19206211.
- ^ Patent US4605655 - Neuroleptic agents; no movement disorder side effects - Google Patents
- ^ "4-Bromofluorobenzene". Shandong A&Fine Agrochemicals Co., Ltd. Archived from the original on 13 December 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2015.