Cadazolid
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H29F2N3O8 |
| Molar mass | 585.55 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cadazolid is an experimental antibiotic of the oxazolidinone class made by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. which is effective against Clostridium difficile, a major cause of drug resistant diarrhea in the elderly.[1] Current drug treatments for this infection involve orally delivered antibiotics, principally fidaxomicin, metronidazole and vancomycin; the last two drugs are the principal therapeutic agents in use, but fail in approximately 20 to 45% of the cases. The drug is in Phase III trials.[1] The drug works by inhibiting synthesis of proteins in the bacteria, thus inhibiting the production of toxins and the formation of spores.[2]
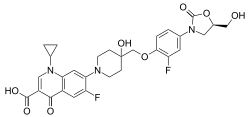
Structure
The chemical structure of cadazolid combines the pharmacophores of oxazolidinone and fluoroquinolone.[2]
Clinical trials
In a study published in the journal Anaerobe, cadazolid has been shown to be effective in vitro against 133 strains of Clostridium difficile all collected from Sweden.[3]
In phase I tests, sixty four male patients reacted favourably to cadazolid which primarily acted and remained in the colon while displaying little toxicity even in regimes involving large doses.[1]
References
- ^ a b c Boschert, Sherry (19 Sep 2012). "Promising C. difficile Antibiotic in Pipeline". Internal Medicine News. International Medical News Group. Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- ^ a b "Cadazolid". .actelion.com. Retrieved 2013-05-22.
- ^ "Anaerobe - In vitro activity of cadazolid against Clostridium difficile strains isolated from primary and recurrent infections in Stockholm, Sweden". Anaerobe. 20: 32–35. 2013-02-26. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.02.003. Retrieved 2013-05-22.
