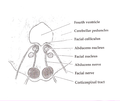
Facial colliculus
| Facial colliculus | |
|---|---|
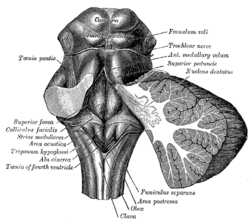 Rhomboid fossa. (Colliculus facialis labeled at center left.) | |
 Human caudal brainstem posterior view (Colliculus facialis is #3) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | colliculus facialis |
| NeuroNames | 624 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.705 |
| FMA | 78480 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The facial colliculus is an elevated area located in the pontine tegmentum (dorsal pons),[citation needed] within the floor of the fourth ventricle (i.e. the rhomboid fossa). It is formed by fibres from the facial motor nucleus looping over the abducens nucleus. The facial colliculus is an essential landmark of the rhomboid fossa.[1]
Anatomy
[edit]The facial colliculus occurs within the rhomboid fossa (i.e. the floor of the fourth ventricle) where it is placed lateral to its (midline) median sulcus.[1]
Structure
[edit]The facial colliculus is formed by brachial motor nerve fibres of the facial nerve (CN VII) looping over the (ipsilateral) abducens nucleus, forming a bump upon the surface.[1]
Clinical significance
[edit]A facial colliculus lesion would result in ipsilateral facial paralysis (i.e. Bell's palsy) and inhibited ipsilateral and unopposed contralateral eye deviation.[1]
Additional images
[edit]-
Axial section of the brainstem (pons) at the level of the facial colliculus
-
Fourth ventricle. Posterior view. Deep dissection.
References
[edit]External links
[edit]- http://www.med.yale.edu/caim/cnerves/cn6/cn6_2.html
- https://web.archive.org/web/20130930042036/http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/virtualbrain/BrainStem/14CNVII.html
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070927162218/http://www.ib.amwaw.edu.pl/anatomy/atlas/image_04be.htm