Infundibulum (heart)
Appearance
| Conus arteriosus | |
|---|---|
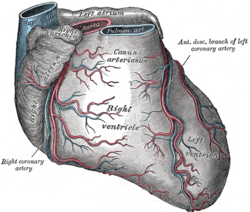 Sternocostal surface of heart. (Conus arteriosus visible at top center.) | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A12.1.02.008 |
| TA2 | 4041 |
| FMA | 7216 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The conus arteriosus is a conical pouch formed from the upper and left angle of the right ventricle in the chordate heart, from which the pulmonary trunk arises.
A tendinous band, which may be named the tendon of the conus arteriosus, extends upward from the right atrioventricular fibrous ring and connects the posterior surface of the conus arteriosus to the aorta. The conus arteriosus is also called the infundibulum, and it is the entrance from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery and pulmonary trunk. The wall of the infundibulum is smooth.
Additional images
-
Front view of human heart and lungs.
External links
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-254803911.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Template:EMedicineDictionary
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 531 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
♥
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 531 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
♥

