Cyrilla
| Cyrilla | |
|---|---|

| |
| Cyrilla racemiflora in Myrtle Beach, SC | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Cyrillaceae |
| Genus: | Cyrilla Garden |
| Species: | C. racemiflora
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cyrilla racemiflora | |
| |
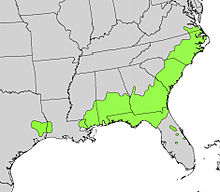
| Natural range within the continental part of the United States | |
Cyrilla racemiflora, the sole species in the genus Cyrilla, is a flowering plant in the family Cyrillaceae, native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the Americas, from the southeastern United States (coastal areas from southeastern Texas east to southeastern Virginia), south through the Caribbean, Mexico (Oaxaca only) and Central America to northern Brazil and Venezuela in South America.[2] Common names include swamp cyrilla, swamp titi,[3] palo colorado,[2] red titi,[4] black titi,[4] white titi,[4] leatherwood,[4] ironwood,[4] he-huckleberry,[4] and myrtle.[4]
Habitat
[edit]Can be found in rainforests, swamps, along streams, bogs, bayheads, backwaters, wet prairies, low pinelands, pocosins, flatwood depressions, preferring acidic, sandy, or peaty soils.
Description
[edit]In tropical rainforests, it is a large tree growing to 15 metres (49 ft) or more tall and greater than 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) in diameter, but only a shrub to 4 metres (13 ft) tall in temperate regions at the northern edge of its range. It is most recognizable from its white flowers which are noticeable on the plant during the summer months. It is primarily evergreen, but during the autumn months some of the leaves turn a brilliant red before falling, and plants at the northern edge of its range tend to be deciduous. The leaves are alternate, simple, oblanceolate to oval, rounded or pointed at the tip, narrowed to the base, thick, without teeth, smooth, sometimes nearly evergreen, reticulate-veined, 4–10 centimetres (2–4 in) long and 1.2–3 centimetres (15⁄32–1+3⁄16 in) broad. The flowers are crowded in 8–15 centimetres (3–6 in) long racemes borne on the previous year's twigs; each flower is 5–10 millimetres (3⁄16–13⁄32 in) diameter, with five white petals, and is subtended by a slender bract. The fruit is a yellow-brown capsule 2–3 millimetres (5⁄64–15⁄128 in) long. The bark of large individuals is a reddish-brown colored thin bark often shaggy in appearance. The bark of smaller individuals is gray to brown, smoothish and lightly fissured.
Taxonomy
[edit]Although generally treated as a single variable species, some botanists in the past have split Cyrilla racemiflora into several species. Synonyms include C. antillana, C. arida, C. brevifolia, C. caroliniana, C. cubensis, C. fuscata, C. nipensis, C. nitidissima, C. parvifolia, C. perrottetii, C. polystachia.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI).; IUCN SSC Global Tree Specialist Group (2019). "Cyrilla racemiflora". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T144305218A149044478. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T144305218A149044478.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ a b Little, Elbert Luther; Wadsworth, Frank H. (1964). Common trees of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands / by Elbert L. Little, Jr., and Frank H. Wadsworth. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.4135.
- ^ "PLANTS Profile for Cyrilla racemiflora L."
- ^ a b c d e f g "Cyrilla racemiflora". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 24 December 2017.

