Dihedral symmetry in three dimensions
 Involutional symmetry Cs, (*) [ ] = |
 Cyclic symmetry Cnv, (*nn) [n] = |
 Dihedral symmetry Dnh, (*n22) [n,2] = | |
| Polyhedral group, [n,3], (*n32) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Tetrahedral symmetry Td, (*332) [3,3] = |
 Octahedral symmetry Oh, (*432) [4,3] = |
 Icosahedral symmetry Ih, (*532) [5,3] = | |
In geometry, dihedral symmetry in three dimensions is one of three infinite sequences of point groups in three dimensions which have a symmetry group that as abstract group is a dihedral group Dihn ( n ≥ 2 ).
Types
- Chiral
- Dn, [n,2]+, (22n) of order 2n – dihedral symmetry or para-n-gonal group (abstract group Dihn)
- Achiral
- Dnh, [n,2], (*22n) of order 4n – prismatic symmetry or full ortho-n-gonal group (abstract group Dihn × Z2)
- Dnd (or Dnv), [2n,2+], (2*n) of order 4n – antiprismatic symmetry or full gyro-n-gonal group (abstract group Dih2n)
For a given n, all three have n-fold rotational symmetry about one axis (rotation by an angle of 360°/n does not change the object), and 2-fold about a perpendicular axis, hence about n of those. For n = ∞ they correspond to three frieze groups. Schönflies notation is used, with Coxeter notation in brackets, and orbifold notation in parentheses. The term horizontal (h) is used with respect to a vertical axis of rotation.
In 2D the symmetry group Dn includes reflections in lines. When the 2D plane is embedded horizontally in a 3D space, such a reflection can either be viewed as the restriction to that plane of a reflection in a vertical plane, or as the restriction to the plane of a rotation about the reflection line, by 180°. In 3D the two operations are distinguished: the group Dn contains rotations only, not reflections. The other group is pyramidal symmetry Cnv of the same order.
With reflection symmetry with respect to a plane perpendicular to the n-fold rotation axis we have Dnh [n], (*22n).
Dnd (or Dnv), [2n,2+], (2*n) has vertical mirror planes between the horizontal rotation axes, not through them. As a result the vertical axis is a 2n-fold rotoreflection axis.
Dnh is the symmetry group for a regular n-sided prisms and also for a regular n-sided bipyramid. Dnd is the symmetry group for a regular n-sided antiprism, and also for a regular n-sided trapezohedron. Dn is the symmetry group of a partially rotated prism.
n = 1 is not included because the three symmetries are equal to other ones:
- D1 and C2: group of order 2 with a single 180° rotation
- D1h and C2v: group of order 4 with a reflection in a plane and a 180° rotation through a line in that plane
- D1d and C2h: group of order 4 with a reflection in a plane and a 180° rotation through a line perpendicular to that plane
For n = 2 there is not one main axes and two additional axes, but there are three equivalent ones.
- D2 (222) of order 4 is one of the three symmetry group types with the Klein four-group as abstract group. It has three perpendicular 2-fold rotation axes. It is the symmetry group of a cuboid with an S written on two opposite faces, in the same orientation.
- D2h (*222) of order 8 is the symmetry group of a cuboid
- D2d (2*2) of order 8 is the symmetry group of e.g.:
- a square cuboid with a diagonal drawn on one square face, and a perpendicular diagonal on the other one
- a regular tetrahedron scaled in the direction of a line connecting the midpoints of two opposite edges (D2d is a subgroup of Td, by scaling we reduce the symmetry).
Subgroups
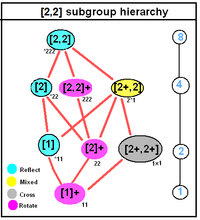 D2h, [2,2], (*222) |
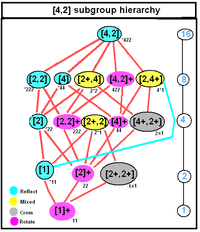 D4h, [4,2], (*224) |
For Dnh, [n,2], (*22n), order 4n
- Cnh, [n+,2], (n*), order 2n
- Cnv, [n,1], (*nn), order 2n
- Dn, [n,2]+, (22n), order 2n
For Dnd, [2n,2+], (2*n), order 4n
- S2n, [2n+,2+], (n×), order 2n
- Cnv, [n+,2], (n*), order 2n
- Dn, [n,2]+, (22n), order 2n
Dnd is also subgroup of D2nh.
Examples
| D2h, [2,2], (*222) Order 8 |
D2d, [4,2+], (2*2) Order 8 |
D3h, [3,2], (*223) Order 12 |
|---|---|---|
 basketball seam paths |
 baseball seam paths |
 Beach ball (ignoring colors) |
Dnh, [n], (*22n):
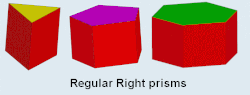 prisms |
D5h, [5], (*225):
 Pentagrammic prism |
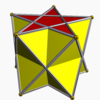 Pentagrammic antiprism |
D4d, [8,2+], (2*4):
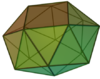 Snub square antiprism |
D5d, [10,2+], (2*5):
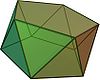 Pentagonal antiprism |
 Pentagrammic crossed-antiprism |
 pentagonal trapezohedron |
D17d, [34,2+], (2*17):
 Heptadecagonal antiprism |
See also
- List of spherical symmetry groups
- Point groups in three dimensions
- Cyclic symmetry in three dimensions
References
- Coxeter, H. S. M. and Moser, W. O. J. (1980). Generators and Relations for Discrete Groups. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-09212-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - N.W. Johnson: Geometries and Transformations, (2015) Chapter 11: Finite symmetry groups
- Conway, John Horton; Huson, Daniel H. (2002), "The Orbifold Notation for Two-Dimensional Groups", Structural Chemistry, 13 (3), Springer Netherlands: 247–257, doi:10.1023/A:1015851621002
External links
- Graphic overview of the 32 crystallographic point groups – form the first parts (apart from skipping n=5) of the 7 infinite series and 5 of the 7 separate 3D point groups
