Diphenylethylenediamine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Diphenylethane-1,2-diamine | |
| Other names
1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-diaminoethane
DPEN | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16N2 | |
| Molar mass | 212.29 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 79 to 83 °C (174 to 181 °F; 352 to 356 K) |
| Slightly | |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
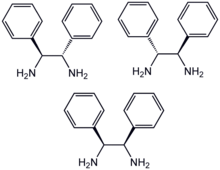
1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine is an organic compound with the formula H2NCHPhCHPhNH2, where Ph is C6H5, phenyl. This diamine is a precursor to a ligand for certain homogeneous hydrogenation catalysts. It can be prepared from benzil by reductive amination.[1]
Optical resolution
DPEN can be obtained as both the chiral and meso diastereomers, depending on the relative stereochemistry of the two CHPhNH2 subunits. The chiral diastereomer, which is of greater value, can be resolved into the R,R- and S,S- enantiomers using tartaric acid as the resolving agent. In methanol, the R,R enantiomer has a specific rotation of [α]23 +106±1°.
TsDPEN
N-tosylated derivative, TsDPENH, is a ligand precursor for catalysts for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. For example, (cymene)Ru(S,S-TsDPEN) catalyzes the hydrogenation of benzil into R,R-hydrobenzoin. In this reaction, formate serves as the source of H2:[2]
- PhC(O)C(O)Ph + 2 H2 → PhCH(OH)CH(OH)Ph
This transformation is an example of desymmetrization, the symmetric molecule benzil is converted to the dissymmetric product
Applications
DPEN and BINAP are the key ingredients of Noyori's 2nd Generation Ruthenium based chiral hydration catalyst, Ryōji Noyori earned the Nobel Prize in 2001.
References
- ^ S. Pikul, E. J. Corey (1998). "(1R,2R)-(+)- and (1S,2S)-(−)- 1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-Ethylenediamine". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 9, p. 387.
- ^ Takao Ikariya, Shohei Hashiguchi, Kunihiko Murata, and Ryōji Noyori (2005). "Preparation of Optically Active (R,R)-Hydrobenzoin from Benzoin or Benzil". Organic Syntheses: 10
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link).
