John Dolbeer
John Dolbeer | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | March 12, 1827 |
| Died | August 17, 1902 (aged 75) San Francisco, California, US |
| Occupation(s) | Inventor, entrepreneur |
| Spouse | Harriet Schander |
John Dolbeer (March 12, 1827 – August 17, 1902) was a partner in the Dolbeer & Carson Lumber Co., one of the early major Humboldt County, California lumber operations based in Eureka. While in that business, he invented the logging engine, more commonly known as the steam donkey or donkey engine. This invaluable equipment, especially with regard to difficult terrain and very large trees, revolutionized 19th century logging so significantly that variations of the engine were still used well into the 20th Century.
Early years
[edit]John Dolbeer was born in Epsom, New Hampshire, on March 12, 1827, the son of Nicholas Dolbeer and Esther Chase of New Rye. He left the family farm in 1850 at the age of 23 and set out to the California Gold Rush to make his fortune.
Entrepreneurship
[edit]Looking for opportunity beyond the mines, Dolbeer arrived at the Humboldt Bay area where in 1853 he purchased Martin White's Bay Mill in Eureka, California. Finding himself in need of capital after fire destroyed his mill twice, he became partners with William Carson (builder of the Carson Mansion) by the spring of 1863. The two formed what would become one of the first truly huge Redwood lumber operations, the Dolbeer and Carson Lumber Company.[1] The mill operated with his name on it on the Eureka waterfront until the 1970s.
Patents
[edit]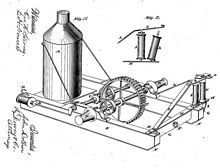
His several patents showed his ingenuity in problem solving, and he had an impact in all facets of the industry, from the actual lumbering operation itself, to transporting and exporting – even owning the barques and brigs to ship the lumber to worldwide markets. Among his most useful and successful patent was that for the Dolbeer Logging Engine in August 1881.[2] This machine was a simple steam engine mounted on a wooden skid which enabled loggers to employ cables to move giant logs across long distances or steep terrain to adjacent railways or waterways. This invention improved log retrieval in difficult terrain and revolutionized the industry. It was so cost effective and useful that the technology continued to be used well into the 20th century. Examples of working Donkey engines can still be found operating during special occasions at Fort Humboldt State Historic Park in Eureka. The patent (Patent number: 256553) was issued April 18, 1882.[3]
Other patents include an apparatus for "steaming piles" (Patent number: 333204) and a device used for measuring footage of timber cut by a sawmill (Patent number: 45482).
Family
[edit]In 1872, late in life, he married Harriet Schander, and in 1873 his son, Chase Dolbeer was born. He established his home on Lombard Street in San Francisco. Four years later, in 1877, the Dolbeers had their daughter, Bertha. Business continued to thrive, despite early lumber mill fires. It was about the time of the second fire that the personal life of Jonathan Dolbeer turned tragic. In 1879, Harriet committed suicide and was called by the San Francisco Call "a suffering invalid", and in 1886 his son Chase was thrown from a wagon and died at the age of 13. His family endured yet a final tragedy after his death when on July 9, 1904, his daughter Bertha committed suicide at the Waldorf Astoria in New York City, putting the battle for the estate in the California Courts through 1908.[4]
Estate
[edit]John Dolbeer died in San Francisco from a heart ailment on August 17, 1902. The bulk of his estate went to his lone surviving daughter Bertha, and was worth nearly one million dollars. Additional sums were given to several charities, and relatives in Epsom, including his niece Ellen Dolbeer Hall (daughter of his brother Calvin) and her husband, Charles Sumner Hall. There is now a prestigious scholarship awarded at the University of California, Berkeley in his name and honor.
References
[edit]- ^ The National Park Service, The Redwood Lumber Industry, 1850-1953 The Lumber Industry in Humboldt County, 1850-1860 Url retrieved September 30, 2008.
- ^ Richard L. Williams, The Loggers, (New York: Time-Life Books, 1976), 112–113; ISBN 0-8094-1527-5
- ^ Wilma, David (March 1, 2003). "John Dolbeer invents the donkey engine and revolutionizes logging in August 1881". HistoryLink.org. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ^ San Francisco County CA Biography Project
