Einstein Cross
| QSO 2237+0305 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Observation data (Epoch J2000) | |
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Right ascension | 22h 40m 30.3s |
| Declination | +3° 21′ 31″ |
| Redshift | 1.695 |
| Distance | 8,000,000,000 ly (2,500,000,000 pc) |
| Type | LeQ |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | less than 2" |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 16.78 |
| Other designations | |
| LEDA 69457, Z 378-15 | |
| See also: Quasar, List of quasars | |
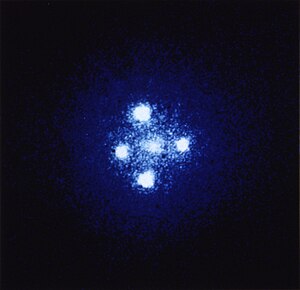
The Einstein Cross or Q2237+030 or QSO 2237+0305 is a gravitationally lensed quasar that sits directly behind ZW 2237+030, Huchra's Lens. Four images of the same distant quasar appear around a foreground galaxy due to strong gravitational lensing.[1][2]
The quasar's redshift indicated that it is located about 8 billion light years from Earth, while the lensing galaxy is at a distance of 400 million light years. The apparent dimensions of the entire foreground galaxy are 0.87x0.34 arcminutes[citation needed], while the apparent dimension of the cross in its centre accounts for only 1.6x1.6 arcseconds.
The Einstein Cross can be found in Pegasus at 22h 40m 30.3s, +3° 21′ 31″.
Amateur astronomers are able to see some of the cross using telescopes but it requires extremely dark skies and telescope mirrors with diameters of 18 inches (46 cm) or greater.[3]
The individual images are labelled A through D (i.e. QSO 2237+0305 A), the lensing galaxy is sometimes referred to as QSO 2237+0305 G.

See also
References
- ^ NASA and ESA (September 13, 1990). "The Gravitational Lens G2237 + 0305". HubbleSite. Retrieved July 25, 2006.
- ^ Drakeford, Jason; Corum, Jonathan; Overbye, Dennis (March 5, 2015). "Einstein's Telescope - video (02:32)". New York Times. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- ^ Crinklaw, Greg. "Focus on Einstein's Cross". Retrieved 2013-06-29.
External links
- Simbad
- Information about Einstein's Cross on Skyhound.com
- Einstein's Cross core
- Einstein's Cross by Jay Reynolds Freeman
- Photo of the Einstein Cross at Astronomy Picture of the Day (March 11, 2007)
- Google Sky
