Great East
| Governorate of the Great East Gouvernement Groote Oost (Dutch) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governorate of the Dutch East Indies | |||||||||||
| 1938–1946 | |||||||||||
 The Great East region of the Dutch East Indies | |||||||||||
| Capital | Makassar | ||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||
| Monarch | |||||||||||
• 1938–1946 | Wilhelmina | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Merger of the Constituent Entities | 25 May 1938 | ||||||||||
| 1942–1945 | |||||||||||
• Became the State of the Great East | 24 December 1946 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Indonesia | ||||||||||
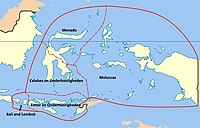
The Great East (Dutch: Groote Oost) was a governorate (gouvernement) of the Dutch East Indies between 1938 and 1946. It comprised all the islands to the east of Borneo (Celebes, the Moluccas, and West New Guinea, with their offshore islands) and of Java (Bali and the Lesser Sunda Islands). Its capital was Macassar on Celebes.[1]
The Great East was created with the merger of its constituent residencies on 25 May 1938 and was ruled by a governor.[2] The first governor was G. A. W. Ch. de Haze Winkelman. Following World War II, the governorate (except for Netherlands New Guinea) became the State of the Great East (later the State of East Indonesia) on 24 December 1946. This state became a constituent of the federal United States of Indonesia in 1949 and was integrated into a unitary Indonesia in 1950 (except West New Guinea, which was only integrated in 1963). As of December 2022, the area is divided into the eastern 17 of Indonesia's 38 provinces.
Administrative divisions
[edit]The Great East gouvernement consisted of the following residencies:[3]
- Bali and Lombok (Singaradja)
- Celebes en Onderhoorigheden (Macassar), including southern Celebes and neighbouring islands
- Menado (Menado), including all of northern Celebes
- Moluccas (Amboina), including the Moluccas, West New Guinea, and other outlying islands such as Wetar and Aru
- Timor en Onderhoorigheden (Kupang), including western Timor and the other Lesser Sunda Islands (except for Bali and Lombok)
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ The emblem of the Headquarters consisted of a light-blue disc, surrounded by the Dutch red-white and blue and charged with the yellow cypher GOBH(Grote Oost en Borneo Hoofdkwartier / Great East and Borneo Headquarters). - Clg. 283/GS/35
References
[edit]- ^ Harvey 1974, p. 106.
- ^ Harvey 1974, p. 62.
- ^ Cribb 2000, p. 129.
- Cribb, Robert (2000). Historical Atlas of Indonesia. Curzon Press. ISBN 0-7007-0985-1.
- Elout, Cornelis Karel (1930), De Groote Oost, The Hague: N.V. Boekhandel v/h W.P. Van Stockum & Zoon.
- Harvey, Barbara Sillars (1974). Tradition, Islam, and Rebellion: South Sulawesi 1950-1965 (PDF) (PhD). Cornell University.
- States and territories established in 1938
- States and territories disestablished in 1946
- Subdivisions of the Dutch East Indies
- Indonesia in World War II
- History of New Guinea
- History of Timor
- West Timor
- Western New Guinea
- 1938 establishments in the Dutch East Indies
- 1940s disestablishments in the Dutch East Indies
- 1946 disestablishments


![Emblem[a] of Great East](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9f/Emblem_of_the_Great_East_and_Borneo_Headquarters.svg/85px-Emblem_of_the_Great_East_and_Borneo_Headquarters.svg.png)