Collatz conjecture
- For even numbers, divide by 2;
- For odd numbers, multiply by 3 and add 1.

The Collatz conjecture[a] is one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics. The conjecture asks whether repeating two simple arithmetic operations will eventually transform every positive integer into 1. It concerns sequences of integers in which each term is obtained from the previous term as follows: if a term is even, the next term is one half of it. If a term is odd, the next term is 3 times the previous term plus 1. The conjecture is that these sequences always reach 1, no matter which positive integer is chosen to start the sequence. The conjecture has been shown to hold for all positive integers up to 2.95×1020, but no general proof has been found.
It is named after the mathematician Lothar Collatz, who introduced the idea in 1937, two years after receiving his doctorate.[4] The sequence of numbers involved is sometimes referred to as the hailstone sequence, hailstone numbers or hailstone numerals (because the values are usually subject to multiple descents and ascents like hailstones in a cloud),[5] or as wondrous numbers.[6]
Paul Erdős said about the Collatz conjecture: "Mathematics may not be ready for such problems."[7] Jeffrey Lagarias stated in 2010 that the Collatz conjecture "is an extraordinarily difficult problem, completely out of reach of present day mathematics".[8] However, though the Collatz conjecture itself remains open, efforts to solve the problem have led to new techniques and many partial results.[8][9]
Statement of the problem





Consider the following operation on an arbitrary positive integer:
- If the number is even, divide it by two.
- If the number is odd, triple it and add one.
In modular arithmetic notation, define the function f as follows:
Now form a sequence by performing this operation repeatedly, beginning with any positive integer, and taking the result at each step as the input at the next.
In notation: (that is: ai is the value of f applied to n recursively i times; ai = f i(n)).
The Collatz conjecture is: This process will eventually reach the number 1, regardless of which positive integer is chosen initially. That is, for each , there is some with .
If the conjecture is false, it can only be because there is some starting number which gives rise to a sequence that does not contain 1. Such a sequence would either enter a repeating cycle that excludes 1, or increase without bound. No such sequence has been found.
The smallest i such that ai < a0 is called the stopping time of n. Similarly, the smallest k such that ak = 1 is called the total stopping time of n.[2] If one of the indexes i or k doesn't exist, we say that the stopping time or the total stopping time, respectively, is infinite.
The Collatz conjecture asserts that the total stopping time of every n is finite. It is also equivalent to saying that every n ≥ 2 has a finite stopping time.
Since 3n + 1 is even whenever n is odd, one may instead use the "shortcut" form of the Collatz function: This definition yields smaller values for the stopping time and total stopping time without changing the overall dynamics of the process.
Empirical data
For instance, starting with n = 12 and applying the function f without "shortcut", one gets the sequence 12, 6, 3, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1.
The number n = 19 takes longer to reach 1: 19, 58, 29, 88, 44, 22, 11, 34, 17, 52, 26, 13, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1 .
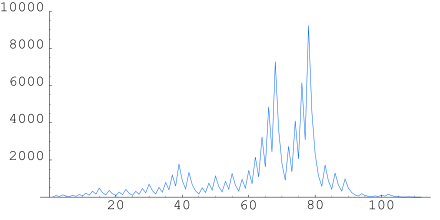
The sequence for n = 27, listed and graphed below, takes 111 steps (41 steps through odd numbers, in bold), climbing as high as 9232 before descending to 1.
- 27, 82, 41, 124, 62, 31, 94, 47, 142, 71, 214, 107, 322, 161, 484, 242, 121, 364, 182, 91, 274, 137, 412, 206, 103, 310, 155, 466, 233, 700, 350, 175, 526, 263, 790, 395, 1186, 593, 1780, 890, 445, 1336, 668, 334, 167, 502, 251, 754, 377, 1132, 566, 283, 850, 425, 1276, 638, 319, 958, 479, 1438, 719, 2158, 1079, 3238, 1619, 4858, 2429, 7288, 3644, 1822, 911, 2734, 1367, 4102, 2051, 6154, 3077, 9232, 4616, 2308, 1154, 577, 1732, 866, 433, 1300, 650, 325, 976, 488, 244, 122, 61, 184, 92, 46, 23, 70, 35, 106, 53, 160, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1
(sequence A008884 in the OEIS)
Numbers with a total stopping time longer than that of any smaller starting value form a sequence beginning with:
- 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 18, 25, 27, 54, 73, 97, 129, 171, 231, 313, 327, 649, 703, 871, 1161, 2223, 2463, 2919, 3711, 6171, ... (sequence A006877 in the OEIS).
The starting values whose maximum trajectory point is greater than that of any smaller starting value are as follows:
- 1, 2, 3, 7, 15, 27, 255, 447, 639, 703, 1819, 4255, 4591, 9663, 20895, 26623, 31911, 60975, 77671, 113383, 138367, 159487, 270271, 665215, 704511, ... (sequence A006884 in the OEIS)
Number of steps for n to reach 1 are
- 0, 1, 7, 2, 5, 8, 16, 3, 19, 6, 14, 9, 9, 17, 17, 4, 12, 20, 20, 7, 7, 15, 15, 10, 23, 10, 111, 18, 18, 18, 106, 5, 26, 13, 13, 21, 21, 21, 34, 8, 109, 8, 29, 16, 16, 16, 104, 11, 24, 24, ... (sequence A006577 in the OEIS)
The starting value having the largest total stopping time while being
- less than 10 is 9, which has 19 steps,
- less than 100 is 97, which has 118 steps,
- less than 1000 is 871, which has 178 steps,
- less than 104 is 6171, which has 261 steps,
- less than 105 is 77031, which has 350 steps,
- less than 106 is 837799, which has 524 steps,
- less than 107 is 8400511, which has 685 steps,
- less than 108 is 63728127, which has 949 steps,
- less than 109 is 670617279, which has 986 steps,
- less than 1010 is 9780657630, which has 1132 steps,[10]
- less than 1011 is 75128138247, which has 1228 steps,
- less than 1012 is 989345275647, which has 1348 steps.[11] (sequence A284668 in the OEIS)
These numbers are the lowest ones with the indicated step count, but not necessarily the only ones below the given limit. As an example, 9780657631 has 1132 steps, as does 9780657630.
The starting values having the smallest total stopping time with respect to their number of digits (in base 2) are the powers of two since 2n is halved n times to reach 1, and is never increased.
Visualizations
-
Directed graph showing the orbits of the first 1000 numbers.
-
The x axis represents starting number, the y axis represents the highest number reached during the chain to 1. This plot shows a restricted y axis: some x values produce intermediates as high as 2.7×107 (for x = 9663)
-
The same plot as the previous one but on log scale, so all y values are shown. The first thick line towards the middle of the plot corresponds to the tip at 27, which reaches a maximum at 9232.
-
The tree of all the numbers having fewer than 20 steps.
-
The number of iterations it takes to get to one for the first 100 million numbers.
Supporting arguments
Although the conjecture has not been proven, most mathematicians who have looked into the problem think the conjecture is true because experimental evidence and heuristic arguments support it.
Experimental evidence
The conjecture has been checked by computer for all starting values up to 268 ≈ 2.95×1020. All values tested so far converge to 1.[12]
This computer evidence is still not rigorous proof that the conjecture is true for all starting values, as counterexamples may be found when considering very large (or possibly immense) positive integers, as in the case of the disproven Pólya conjecture and Mertens conjecture.
However, such verifications may have other implications. Certain constraints on any non-trivial cycle, such as lower bounds on the length of the cycle, can be proven based on the value of the lowest term in the cycle. Therefore, computer searches to rule out cycles that have a small lowest term can strengthen these constraints.[13][14][15]
A probabilistic heuristic
If one considers only the odd numbers in the sequence generated by the Collatz process, then each odd number is on average 3/4 of the previous one.[16] (More precisely, the geometric mean of the ratios of outcomes is 3/4.) This yields a heuristic argument that every Hailstone sequence should decrease in the long run, although this is not evidence against other cycles, only against divergence. The argument is not a proof because it assumes that Hailstone sequences are assembled from uncorrelated probabilistic events. (It does rigorously establish that the 2-adic extension of the Collatz process has two division steps for every multiplication step for almost all 2-adic starting values.)
Stopping times
As proven by Riho Terras, almost every positive integer has a finite stopping time.[17] In other words, almost every Collatz sequence reaches a point that is strictly below its initial value. The proof is based on the distribution of parity vectors and uses the central limit theorem.
In 2019, Terence Tao improved this result by showing, using logarithmic density, that almost all (in the sense of logarithmic density) Collatz orbits are descending below any given function of the starting point, provided that this function diverges to infinity, no matter how slowly. Responding to this work, Quanta Magazine wrote that Tao "came away with one of the most significant results on the Collatz conjecture in decades".[9][18]
Lower bounds
In a computer-aided proof, Krasikov and Lagarias showed that the number of integers in the interval [1,x] that eventually reach 1 is at least equal to x0.84 for all sufficiently large x.[19]
Cycles
In this part, consider the shortcut form of the Collatz function A cycle is a sequence (a0, a1, ..., aq) of distinct positive integers where f(a0) = a1, f(a1) = a2, ..., and f(aq) = a0.
The only known cycle is (1,2) of period 2, called the trivial cycle.
Cycle length
The length of a non-trivial cycle is known to be at least 114208327604 (or 186265759595 without shortcut). If it can be shown that for all positive integers less than the Collatz sequences reach 1, then this bound would raise to 217976794617 (355504839929 without shortcut).[20][14] In fact, Eliahou (1993) proved that the period p of any non-trivial cycle is of the form where a, b and c are non-negative integers, b ≥ 1 and ac = 0. This result is based on the continued fraction expansion of ln 3/ln 2.[14]
k-cycles
A k-cycle is a cycle that can be partitioned into k contiguous subsequences, each consisting of an increasing sequence of odd numbers, followed by a decreasing sequence of even numbers.[15] For instance, if the cycle consists of a single increasing sequence of odd numbers followed by a decreasing sequence of even numbers, it is called a 1-cycle.
Steiner (1977) proved that there is no 1-cycle other than the trivial (1; 2).[21] Simons (2005) used Steiner's method to prove that there is no 2-cycle.[22] Simons and de Weger (2005) extended this proof up to 68-cycles; there is no k-cycle up to k = 68.[15] Hercher extended the method further and proved that there exists no k-cycle with k ≤ 91.[20] As exhaustive computer searches continue, larger k values may be ruled out. To state the argument more intuitively; we do not have to search for cycles that have less than 92 subsequences, where each subsequence consists of consecutive ups followed by consecutive downs.[clarification needed]
Other formulations of the conjecture
In reverse

There is another approach to prove the conjecture, which considers the bottom-up method of growing the so-called Collatz graph. The Collatz graph is a graph defined by the inverse relation
So, instead of proving that all positive integers eventually lead to 1, we can try to prove that 1 leads backwards to all positive integers. For any integer n, n ≡ 1 (mod 2) if and only if 3n + 1 ≡ 4 (mod 6). Equivalently, n − 1/3 ≡ 1 (mod 2) if and only if n ≡ 4 (mod 6). Conjecturally, this inverse relation forms a tree except for the 1–2–4 loop (the inverse of the 4–2–1 loop of the unaltered function f defined in the Statement of the problem section of this article).
When the relation 3n + 1 of the function f is replaced by the common substitute "shortcut" relation 3n + 1/2, the Collatz graph is defined by the inverse relation,
For any integer n, n ≡ 1 (mod 2) if and only if 3n + 1/2 ≡ 2 (mod 3). Equivalently, 2n − 1/3 ≡ 1 (mod 2) if and only if n ≡ 2 (mod 3). Conjecturally, this inverse relation forms a tree except for a 1–2 loop (the inverse of the 1–2 loop of the function f(n) revised as indicated above).
Alternatively, replace the 3n + 1 with n′/H(n′) where n′ = 3n + 1 and H(n′) is the highest power of 2 that divides n′ (with no remainder). The resulting function f maps from odd numbers to odd numbers. Now suppose that for some odd number n, applying this operation k times yields the number 1 (that is, fk(n) = 1). Then in binary, the number n can be written as the concatenation of strings wk wk−1 ... w1 where each wh is a finite and contiguous extract from the representation of 1/3h.[23] The representation of n therefore holds the repetends of 1/3h, where each repetend is optionally rotated and then replicated up to a finite number of bits. It is only in binary that this occurs.[24] Conjecturally, every binary string s that ends with a '1' can be reached by a representation of this form (where we may add or delete leading '0's to s).
As an abstract machine that computes in base two
Repeated applications of the Collatz function can be represented as an abstract machine that handles strings of bits. The machine will perform the following three steps on any odd number until only one 1 remains:
- Append 1 to the (right) end of the number in binary (giving 2n + 1);
- Add this to the original number by binary addition (giving 2n + 1 + n = 3n + 1);
- Remove all trailing 0s (that is, repeatedly divide by 2 until the result is odd).
Example
The starting number 7 is written in base two as 111. The resulting Collatz sequence is:
111
1111
10110
10111
100010
100011
110100
11011
101000
1011
10000
As a parity sequence
For this section, consider the shortcut form of the Collatz function
If P(...) is the parity of a number, that is P(2n) = 0 and P(2n + 1) = 1, then we can define the Collatz parity sequence (or parity vector) for a number n as pi = P(ai), where a0 = n, and ai+1 = f(ai).
Which operation is performed, 3n + 1/2 or n/2, depends on the parity. The parity sequence is the same as the sequence of operations.
Using this form for f(n), it can be shown that the parity sequences for two numbers m and n will agree in the first k terms if and only if m and n are equivalent modulo 2k. This implies that every number is uniquely identified by its parity sequence, and moreover that if there are multiple Hailstone cycles, then their corresponding parity cycles must be different.[2][17]
Applying the f function k times to the number n = 2ka + b will give the result 3ca + d, where d is the result of applying the f function k times to b, and c is how many increases were encountered during that sequence. For example, for 25a + 1 there are 3 increases as 1 iterates to 2, 1, 2, 1, and finally to 2 so the result is 33a + 2; for 22a + 1 there is only 1 increase as 1 rises to 2 and falls to 1 so the result is 3a + 1. When b is 2k − 1 then there will be k rises and the result will be 3ka + 3k − 1. The power of 3 multiplying a is independent of the value of a; it depends only on the behavior of b. This allows one to predict that certain forms of numbers will always lead to a smaller number after a certain number of iterations: for example, 4a + 1 becomes 3a + 1 after two applications of f and 16a + 3 becomes 9a + 2 after four applications of f. Whether those smaller numbers continue to 1, however, depends on the value of a.
As a tag system
For the Collatz function in the shortcut form
Hailstone sequences can be computed by the 2-tag system with production rules
- a → bc, b → a, c → aaa.
In this system, the positive integer n is represented by a string of n copies of a, and iteration of the tag operation halts on any word of length less than 2. (Adapted from De Mol.)
The Collatz conjecture equivalently states that this tag system, with an arbitrary finite string of a as the initial word, eventually halts (see Tag system for a worked example).
Extensions to larger domains
Iterating on all integers
An extension to the Collatz conjecture is to include all integers, not just positive integers. Leaving aside the cycle 0 → 0 which cannot be entered from outside, there are a total of four known cycles, which all nonzero integers seem to eventually fall into under iteration of f. These cycles are listed here, starting with the well-known cycle for positive n:
Odd values are listed in large bold. Each cycle is listed with its member of least absolute value (which is always odd) first.
| Cycle | Odd-value cycle length | Full cycle length |
|---|---|---|
| 1 → 4 → 2 → 1 ... | 1 | 3 |
| −1 → −2 → −1 ... | 1 | 2 |
| −5 → −14 → −7 → −20 → −10 → −5 ... | 2 | 5 |
| −17 → −50 → −25 → −74 → −37 → −110 → −55 → −164 → −82 → −41 → −122 → −61 → −182 → −91 → −272 → −136 → −68 → −34 → −17 ... | 7 | 18 |
The generalized Collatz conjecture is the assertion that every integer, under iteration by f, eventually falls into one of the four cycles above or the cycle 0 → 0.
Iterating on rationals with odd denominators
The Collatz map can be extended to (positive or negative) rational numbers which have odd denominators when written in lowest terms. The number is taken to be 'odd' or 'even' according to whether its numerator is odd or even. Then the formula for the map is exactly the same as when the domain is the integers: an 'even' such rational is divided by 2; an 'odd' such rational is multiplied by 3 and then 1 is added. A closely related fact is that the Collatz map extends to the ring of 2-adic integers, which contains the ring of rationals with odd denominators as a subring.
When using the "shortcut" definition of the Collatz map, it is known that any periodic parity sequence is generated by exactly one rational.[25] Conversely, it is conjectured that every rational with an odd denominator has an eventually cyclic parity sequence (Periodicity Conjecture[2]).
If a parity cycle has length n and includes odd numbers exactly m times at indices k0 < ⋯ < km−1, then the unique rational which generates immediately and periodically this parity cycle is
| (1) |
For example, the parity cycle (1 0 1 1 0 0 1) has length 7 and four odd terms at indices 0, 2, 3, and 6. It is repeatedly generated by the fraction as the latter leads to the rational cycle
Any cyclic permutation of (1 0 1 1 0 0 1) is associated to one of the above fractions. For instance, the cycle (0 1 1 0 0 1 1) is produced by the fraction
For a one-to-one correspondence, a parity cycle should be irreducible, that is, not partitionable into identical sub-cycles. As an illustration of this, the parity cycle (1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0) and its sub-cycle (1 1 0 0) are associated to the same fraction 5/7 when reduced to lowest terms.
In this context, assuming the validity of the Collatz conjecture implies that (1 0) and (0 1) are the only parity cycles generated by positive whole numbers (1 and 2, respectively).
If the odd denominator d of a rational is not a multiple of 3, then all the iterates have the same denominator and the sequence of numerators can be obtained by applying the "3n + d " generalization[26] of the Collatz function
2-adic extension
The function is well-defined on the ring of 2-adic integers, where it is continuous and measure-preserving with respect to the 2-adic measure. Moreover, its dynamics is known to be ergodic.[2]
Define the parity vector function Q acting on as
The function Q is a 2-adic isometry.[27] Consequently, every infinite parity sequence occurs for exactly one 2-adic integer, so that almost all trajectories are acyclic in .
An equivalent formulation of the Collatz conjecture is that
Iterating on real or complex numbers

The Collatz map can be extended to the real line by choosing any function which evaluates to when is an even integer, and to either or (for the "shortcut" version) when is an odd integer. This is called an interpolating function. A simple way to do this is to pick two functions and , where:
and use them as switches for our desired values:
- .
One such choice is and . The iterations of this map lead to a dynamical system, further investigated by Marc Chamberland.[28] He showed that the conjecture does not hold for positive real numbers since there are infinitely many fixed points, as well as orbits escaping monotonically to infinity. The function has two attracting cycles of period : and . Moreover, the set of unbounded orbits is conjectured to be of measure .
Letherman, Schleicher, and Wood extended the study to the complex plane.[29] They used Chamberland's function for complex sine and cosine and added the extra term , where is any entire function. Since this expression evaluates to zero for real integers, the extended function
is an interpolation of the Collatz map to the complex plane. The reason for adding the extra term is to make all integers critical points of . With this, they show that no integer is in a Baker domain, which implies that any integer is either eventually periodic or belongs to a wandering domain. They conjectured that the latter is not the case, which would make all integer orbits finite.

Most of the points have orbits that diverge to infinity. Coloring these points based on how fast they diverge produces the image on the left, for . The inner black regions and the outer region are the Fatou components, and the boundary between them is the Julia set of , which forms a fractal pattern, sometimes called a "Collatz fractal".

There are many other ways to define a complex interpolating function, such as using the complex exponential instead of sine and cosine:
- ,
which exhibit different dynamics. In this case, for instance, if , then . The corresponding Julia set, shown on the right, consists of uncountably many curves, called hairs, or rays.
Optimizations
Time–space tradeoff
The section As a parity sequence above gives a way to speed up simulation of the sequence. To jump ahead k steps on each iteration (using the f function from that section), break up the current number into two parts, b (the k least significant bits, interpreted as an integer), and a (the rest of the bits as an integer). The result of jumping ahead k is given by
- fk(2ka + b) = 3c(b, k)a + d(b, k).
The values of c (or better 3c) and d can be precalculated for all possible k-bit numbers b, where d(b, k) is the result of applying the f function k times to b, and c(b, k) is the number of odd numbers encountered on the way.[30] For example, if k = 5, one can jump ahead 5 steps on each iteration by separating out the 5 least significant bits of a number and using
- c(0...31, 5) = { 0, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 1, 4, 1, 3, 2, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 },
- d(0...31, 5) = { 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 20, 1, 26, 1, 10, 4, 4, 13, 40, 2, 5, 17, 17, 2, 2, 20, 20, 8, 22, 8, 71, 26, 26, 80, 242 }.
This requires 2k precomputation and storage to speed up the resulting calculation by a factor of k, a space–time tradeoff.
Modular restrictions
For the special purpose of searching for a counterexample to the Collatz conjecture, this precomputation leads to an even more important acceleration, used by Tomás Oliveira e Silva in his computational confirmations of the Collatz conjecture up to large values of n. If, for some given b and k, the inequality
- fk(2ka + b) = 3c(b)a + d(b) < 2ka + b
holds for all a, then the first counterexample, if it exists, cannot be b modulo 2k.[13] For instance, the first counterexample must be odd because f(2n) = n, smaller than 2n; and it must be 3 mod 4 because f2(4n + 1) = 3n + 1, smaller than 4n + 1. For each starting value a which is not a counterexample to the Collatz conjecture, there is a k for which such an inequality holds, so checking the Collatz conjecture for one starting value is as good as checking an entire congruence class. As k increases, the search only needs to check those residues b that are not eliminated by lower values of k. Only an exponentially small fraction of the residues survive.[31] For example, the only surviving residues mod 32 are 7, 15, 27, and 31.
Integers divisible by 3 cannot form a cycle, so these integers do not need to be checked as counter examples. [32]
Syracuse function
If k is an odd integer, then 3k + 1 is even, so 3k + 1 = 2ak′ with k′ odd and a ≥ 1. The Syracuse function is the function f from the set I of positive odd integers into itself, for which f(k) = k′ (sequence A075677 in the OEIS).
Some properties of the Syracuse function are:
- For all k ∈ I, f(4k + 1) = f(k). (Because 3(4k + 1) + 1 = 12k + 4 = 4(3k + 1).)
- In more generality: For all p ≥ 1 and odd h, fp − 1(2ph − 1) = 2 × 3p − 1h − 1. (Here fp − 1 is function iteration notation.)
- For all odd h, f(2h − 1) ≤ 3h − 1/2
The Collatz conjecture is equivalent to the statement that, for all k in I, there exists an integer n ≥ 1 such that fn(k) = 1.
Undecidable generalizations
In 1972, John Horton Conway proved that a natural generalization of the Collatz problem is algorithmically undecidable.[33]
Specifically, he considered functions of the form where a0, b0, ..., aP − 1, bP − 1 are rational numbers which are so chosen that g(n) is always an integer. The standard Collatz function is given by P = 2, a0 = 1/2, b0 = 0, a1 = 3, b1 = 1. Conway proved that the problem
- Given g and n, does the sequence of iterates gk(n) reach 1?
is undecidable, by representing the halting problem in this way.
Closer to the Collatz problem is the following universally quantified problem:
- Given g, does the sequence of iterates gk(n) reach 1, for all n > 0?
Modifying the condition in this way can make a problem either harder or easier to solve (intuitively, it is harder to justify a positive answer but might be easier to justify a negative one). Kurtz and Simon[34] proved that the universally quantified problem is, in fact, undecidable and even higher in the arithmetical hierarchy; specifically, it is Π0
2-complete. This hardness result holds even if one restricts the class of functions g by fixing the modulus P to 6480.[35]
Iterations of g in a simplified version of this form, with all equal to zero, are formalized in an esoteric programming language called FRACTRAN.
In computational complexity
Collatz and related conjectures are often used when studying computation complexity.[36][37] The connection is made through the Busy Beaver function, where BB(n) is the maximum number of steps taken by any n state Turing machine that halts. There is a 15 state Turing machine that halts if and only if a conjecture by Paul Erdős (closely related to the Collatz conjecture) is false. Hence if BB(15) was known, and this machine did not stop in that number of steps, it would be known to run forever and hence no counterexamples exist (which proves the conjecture true). This is a completely impractical way to settle the conjecture; instead it is used to suggest that BB(15) will be very hard to compute, at least as difficult as settling this Collatz-like conjecture.
See also
Notes
- ^ It is also known as the 3n + 1 problem (or conjecture), the 3x + 1 problem (or conjecture), the Ulam conjecture (after Stanisław Ulam), Kakutani's problem (after Shizuo Kakutani), the Thwaites conjecture (after Bryan Thwaites), Hasse's algorithm (after Helmut Hasse), or the Syracuse problem (after Syracuse University).[1][3]
References
- ^ Maddux, Cleborne D.; Johnson, D. Lamont (1997). Logo: A Retrospective. New York: Haworth Press. p. 160. ISBN 0-7890-0374-0.
The problem is also known by several other names, including: Ulam's conjecture, the Hailstone problem, the Syracuse problem, Kakutani's problem, Hasse's algorithm, and the Collatz problem.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lagarias, Jeffrey C. (1985). "The 3x + 1 problem and its generalizations". The American Mathematical Monthly. 92 (1): 3–23. doi:10.1080/00029890.1985.11971528. JSTOR 2322189.
- ^ According to Lagarias (1985),[2] p. 4, the name "Syracuse problem" was proposed by Hasse in the 1950s, during a visit to Syracuse University.
- ^ O'Connor, J.J.; Robertson, E.F. (2006). "Lothar Collatz". St Andrews University School of Mathematics and Statistics, Scotland.
- ^ Pickover, Clifford A. (2001). Wonders of Numbers. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 116–118. ISBN 0-19-513342-0.
- ^ Hofstadter, Douglas R. (1979). Gödel, Escher, Bach. New York: Basic Books. pp. 400–2. ISBN 0-465-02685-0.
- ^ Guy, Richard K. (2004). ""E16: The 3x+1 problem"". Unsolved Problems in Number Theory (3rd ed.). Springer-Verlag. pp. 330–6. ISBN 0-387-20860-7. Zbl 1058.11001.
- ^ a b Lagarias, Jeffrey C., ed. (2010). The Ultimate Challenge: The 3x + 1 Problem. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 978-0-8218-4940-8. Zbl 1253.11003.
- ^ a b Tao, Terence (2022). "Almost all orbits of the Collatz map attain almost bounded values". Forum of Mathematics, Pi. 10: e12. arXiv:1909.03562. doi:10.1017/fmp.2022.8. ISSN 2050-5086.
- ^ Leavens, Gary T.; Vermeulen, Mike (December 1992). "3x + 1 search programs". Computers & Mathematics with Applications. 24 (11): 79–99. doi:10.1016/0898-1221(92)90034-F.
- ^ Roosendaal, Eric. "3x+1 delay records". Retrieved 14 March 2020. (Note: "Delay records" are total stopping time records.)
- ^ Barina, David (2020). "Convergence verification of the Collatz problem". The Journal of Supercomputing. 77 (3): 2681–2688. doi:10.1007/s11227-020-03368-x. S2CID 220294340.
- ^ a b Garner, Lynn E. (1981). "On the Collatz 3n + 1 algorithm". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 82 (1): 19–22. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-1981-0603593-2. JSTOR 2044308.
- ^ a b c Eliahou, Shalom (1993). "The 3x + 1 problem: new lower bounds on nontrivial cycle lengths". Discrete Mathematics. 118 (1): 45–56. doi:10.1016/0012-365X(93)90052-U.
- ^ a b c Simons, J.; de Weger, B. (2005). "Theoretical and computational bounds for m-cycles of the 3n + 1 problem" (PDF). Acta Arithmetica. 117 (1): 51–70. Bibcode:2005AcAri.117...51S. doi:10.4064/aa117-1-3. Archived from the original on 2022-03-18. Retrieved 2023-03-28.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Lagarias (1985),[2] section "A heuristic argument".
- ^ a b Terras, Riho (1976). "A stopping time problem on the positive integers" (PDF). Acta Arithmetica. 30 (3): 241–252. doi:10.4064/aa-30-3-241-252. MR 0568274.
- ^ Hartnett, Kevin (December 11, 2019). "Mathematician Proves Huge Result on 'Dangerous' Problem". Quanta Magazine.
- ^ Krasikov, Ilia; Lagarias, Jeffrey C. (2003). "Bounds for the 3x + 1 problem using difference inequalities". Acta Arithmetica. 109 (3): 237–258. arXiv:math/0205002. Bibcode:2003AcAri.109..237K. doi:10.4064/aa109-3-4. MR 1980260. S2CID 18467460.
- ^ a b Hercher, C. (2023). "There are no Collatz m-cycles with m <= 91" (PDF). Journal of Integer Sequences. 26 (3): Article 23.3.5.
- ^ Steiner, R. P. (1977). "A theorem on the syracuse problem". Proceedings of the 7th Manitoba Conference on Numerical Mathematics. pp. 553–9. MR 0535032.
- ^ Simons, John L. (2005). "On the nonexistence of 2-cycles for the 3x + 1 problem". Math. Comp. 74: 1565–72. Bibcode:2005MaCom..74.1565S. doi:10.1090/s0025-5718-04-01728-4. MR 2137019.
- ^ Colussi, Livio (9 September 2011). "The convergence classes of Collatz function". Theoretical Computer Science. 412 (39): 5409–5419. doi:10.1016/j.tcs.2011.05.056.
- ^ Hew, Patrick Chisan (7 March 2016). "Working in binary protects the repetends of 1/3h: Comment on Colussi's 'The convergence classes of Collatz function'". Theoretical Computer Science. 618: 135–141. doi:10.1016/j.tcs.2015.12.033.
- ^ Lagarias, Jeffrey (1990). "The set of rational cycles for the 3x+1 problem". Acta Arithmetica. 56 (1): 33–53. doi:10.4064/aa-56-1-33-53. ISSN 0065-1036.
- ^ Belaga, Edward G.; Mignotte, Maurice (1998). "Embedding the 3x+1 Conjecture in a 3x+d Context". Experimental Mathematics. 7 (2): 145–151. doi:10.1080/10586458.1998.10504364. S2CID 17925995.
- ^ Bernstein, Daniel J.; Lagarias, Jeffrey C. (1996). "The 3x + 1 conjugacy map". Canadian Journal of Mathematics. 48 (6): 1154–1169. doi:10.4153/CJM-1996-060-x. ISSN 0008-414X.
- ^ Chamberland, Marc (1996). "A continuous extension of the 3x + 1 problem to the real line". Dynam. Contin. Discrete Impuls Systems. 2 (4): 495–509.
- ^ Letherman, Simon; Schleicher, Dierk; Wood, Reg (1999). "The (3n + 1)-problem and holomorphic dynamics". Experimental Mathematics. 8 (3): 241–252. doi:10.1080/10586458.1999.10504402.
- ^ Scollo, Giuseppe (2007). "Looking for class records in the 3x + 1 problem by means of the COMETA grid infrastructure" (PDF). Grid Open Days at the University of Palermo.
- ^ Lagarias (1985),[2] Theorem D.
- ^ Clay, Oliver Keatinge. "The Long Search for Collatz Counterexamples". p. 208. Retrieved 26 July 2024.
- ^ Conway, John H. (1972). "Unpredictable iterations". Proc. 1972 Number Theory Conf., Univ. Colorado, Boulder. pp. 49–52.
- ^ Kurtz, Stuart A.; Simon, Janos (2007). "The undecidability of the generalized Collatz problem". In Cai, J.-Y.; Cooper, S. B.; Zhu, H. (eds.). Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Theory and Applications of Models of Computation, TAMC 2007, held in Shanghai, China in May 2007. pp. 542–553. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-72504-6_49. ISBN 978-3-540-72503-9. As PDF
- ^ Ben-Amram, Amir M. (2015). "Mortality of iterated piecewise affine functions over the integers: Decidability and complexity". Computability. 1 (1): 19–56. doi:10.3233/COM-150032.
- ^ Michel, Pascal (1993). "Busy beaver competition and Collatz-like problems". Archive for Mathematical Logic. 32 (5): 351–367. doi:10.1007/BF01409968.
- ^ "Hardness of busy beaver value BB(15)".
External links
- Matthews, Keith. "3 x + 1 page".
- An ongoing volunteer computing project Archived 2021-08-30 at the Wayback Machine by David Bařina verifies Convergence of the Collatz conjecture for large values. (furthest progress so far)
- (BOINC) volunteer computing project Archived 2017-12-04 at the Wayback Machine that verifies the Collatz conjecture for larger values.
- An ongoing volunteer computing project by Eric Roosendaal verifies the Collatz conjecture for larger and larger values.
- Another ongoing volunteer computing project by Tomás Oliveira e Silva continues to verify the Collatz conjecture (with fewer statistics than Eric Roosendaal's page but with further progress made).
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Collatz Problem". MathWorld.
- Collatz Problem at PlanetMath..
- Nochella, Jesse. "Collatz Paths". Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Eisenbud, D. (8 August 2016). Uncrackable? The Collatz conjecture (short video). Numberphile. Archived from the original on 2021-12-11 – via YouTube.
- Eisenbud, D. (August 9, 2016). Uncrackable? Collatz conjecture (extra footage). Numberphile. Archived from the original on 2021-12-11 – via YouTube.
- Alex Kontorovich (featuring) (30 July 2021). The simplest math problem no one can solve (short video). Veritasium – via YouTube.
- Are computers ready to solve this notoriously unwieldy math problem?

![{\displaystyle f(n)={\begin{cases}n/2&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0{\pmod {2}},\\[4px]3n+1&{\text{if }}n\equiv 1{\pmod {2}}.\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9b2a03faf9d31a8de0abb3c4a3d318490105da12)




![{\displaystyle f(n)={\begin{cases}{\frac {n}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0{\pmod {2}},\\[4px]{\frac {3n+1}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 1{\pmod {2}}.\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ae238aa62598cce67c57371012b818b65d1ad6e3)






![{\displaystyle R(n)={\begin{cases}\{2n\}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0,1,2,3,5\\[4px]\left\{2n,{\frac {n-1}{3}}\right\}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 4\end{cases}}{\pmod {6}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/41a322eb17a1ca4fa107beb57cac4867b0c89c07)
![{\displaystyle R(n)={\begin{cases}\{2n\}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0,1\\[4px]\left\{2n,{\frac {2n-1}{3}}\right\}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 2\end{cases}}{\pmod {3}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/443d6acdf06087446392a7e48e733c009d60c4fc)
![{\displaystyle f(n)={\begin{cases}{\frac {n}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0\\[4px]{\frac {3n+1}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 1\end{cases}}{\pmod {2}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a240a4b8a847f8d81e77a3e609b865b8a998c487)
![{\displaystyle f(n)={\begin{cases}{\frac {n}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 0\\[4px]{\frac {3n+1}{2}}&{\text{if }}n\equiv 1.\end{cases}}{\pmod {2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8fbad5e3e25f45b2f51c7ef1d36bfc3da5c3e5e2)




![{\displaystyle T_{d}(x)={\begin{cases}{\frac {x}{2}}&{\text{if }}x\equiv 0{\pmod {2}},\\[4px]{\frac {3x+d}{2}}&{\text{if }}x\equiv 1{\pmod {2}}.\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/160f092b9c61909d7176b6ab67678ec85bc73a20)
![{\displaystyle T(x)={\begin{cases}{\frac {x}{2}}&{\text{if }}x\equiv 0{\pmod {2}}\\[4px]{\frac {3x+1}{2}}&{\text{if }}x\equiv 1{\pmod {2}}\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/87de26c7247f378d6f1a08f32578751a4a1ee3a2)




























