Lanepitant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
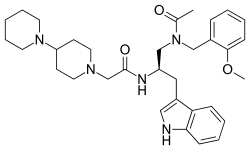
| Other names | LY303870; N-[(R)-2-Indol-3-yl-1-[[N-(o-methoxybenzyl)acetamido]methyl]ethyl][1,4'-bipiperidine]-1'-acetamide |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C33H45N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 559.742 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Lanepitant (INN,[1]: 48 code name LY303870) is a drug developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, and was one of the first compounds developed that act at this target.[2] It was under development as a potential analgesic drug, but despite promising results in initial animal studies, human clinical trials against migraine, arthritis and diabetic neuropathy all failed to show sufficient efficacy to support further development, with the drug being only marginally more effective than placebo and inferior to older comparison drugs such as naproxen.[3][4][5] Failure of analgesic action was thought to be due to poor penetration of the blood–brain barrier in humans, but research has continued into potential applications in the treatment of other disorders with a peripheral site of action, such as corneal neovascularization.[6]
References
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 39" (PDF). World Health Organization. 1998. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ^ Gitter BD, Bruns RF, Howbert JJ, Waters DC, Threlkeld PG, Cox LM, Nixon JA, Lobb KL, Mason NR, Stengel PW, et al. Pharmacological characterization of LY303870: a novel, potent and selective nonpeptide substance P (neurokinin-1) receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Nov;275(2):737-44. PMID 7473161
- ^ Goldstein DJ, Offen WW, Klein EG, Phebus LA, Hipskind P, Johnson KW, Ryan RE Jr. Lanepitant, an NK-1 antagonist, in migraine prevention. Cephalalgia. 2001 Mar;21(2):102-6. PMID 11422091
- ^ Goldstein DJ, Wang O, Todd LE, Gitter BD, DeBrota DJ, Iyengar S. Study of the analgesic effect of lanepitant in patients with osteoarthritis pain. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Apr;67(4):419-26. PMID 10801252
- ^ Goldstein DJ, Wang O, Gitter BD, Iyengar S. Dose-response study of the analgesic effect of lanepitant in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2001 Jan-Feb;24(1):16-22. PMID 11290877
- ^ Bignami F, Giacomini C, Lorusso A, Aramini A, Rama P, Ferrari G. NK1 receptor antagonists as a new treatment for corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 16;55(10):6783-94. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14553. PMID 25228541
